Nuclear Physics Rutherford`s model of the atom
... Gamma: Atomic decay (gamma) is where the nucleus emits a gamma ray which can lead to nuclear fission or fusion. This happens most often after alpha or beta decay, this is due to the fact that the atom has just had so much happen, it is in an unstable state. The particle requires some form of energy ...
... Gamma: Atomic decay (gamma) is where the nucleus emits a gamma ray which can lead to nuclear fission or fusion. This happens most often after alpha or beta decay, this is due to the fact that the atom has just had so much happen, it is in an unstable state. The particle requires some form of energy ...
Chapter 4 Review Worksheet. Name
... _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________ ...
... _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________ ...
200
... • If you think you know the answer raise your hand • The score will be kept on the board • There is 1 Daily Double question in the first round, 2 in Double Jeopardy, which are worth any amount that the team wishes to bet. ...
... • If you think you know the answer raise your hand • The score will be kept on the board • There is 1 Daily Double question in the first round, 2 in Double Jeopardy, which are worth any amount that the team wishes to bet. ...
Jeopardy
... • If you think you know the answer raise your hand • The score will be kept on the board • There is 1 Daily Double question in the first round, 2 in Double Jeopardy, which are worth any amount that the team wishes to bet. ...
... • If you think you know the answer raise your hand • The score will be kept on the board • There is 1 Daily Double question in the first round, 2 in Double Jeopardy, which are worth any amount that the team wishes to bet. ...
Document
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
Name: Chapter 4 and 5 Study Guide Who was the Greek
... 27. What element, with the exception of those in water, is the most abundant in your body? ...
... 27. What element, with the exception of those in water, is the most abundant in your body? ...
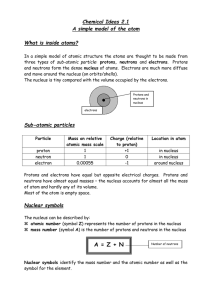
atomic number = ZE = Element symbol
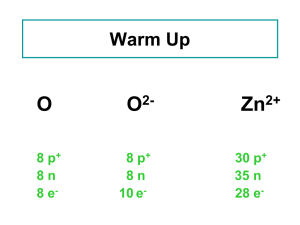
... Atoms are composed of three main subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose ...
... Atoms are composed of three main subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose ...
Measuring the Atom
... There are many subatomic particles, but we will limit our discussion to protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
... There are many subatomic particles, but we will limit our discussion to protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
Isotopes-Chemistry
... Same Element Different AtomIsotopes All atoms of a particular element are not exactly alike. Some elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
... Same Element Different AtomIsotopes All atoms of a particular element are not exactly alike. Some elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
Unit Test: Atomic Structure
... A. Methane is a compound of carbon and hydrogen. A sample contains 1.2 g of carbon and 0.40 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in methane? B. Benzene is another compound of carbon and hydrogen. A 78 g sample of bnzene contains 72 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in benzene? 6 ...
... A. Methane is a compound of carbon and hydrogen. A sample contains 1.2 g of carbon and 0.40 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in methane? B. Benzene is another compound of carbon and hydrogen. A 78 g sample of bnzene contains 72 g of hydrogen. What is the mass % of hydrogen in benzene? 6 ...
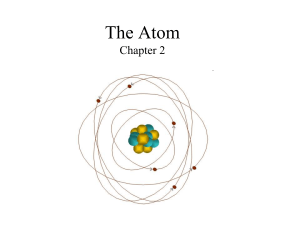
The Atom Chapter 2
... • The existence of multiple pure forms of an element, in the same phase (solid, liquid, or gas), that differ in structure • Different forms are called allotropes • Can exhibit varied physical properties and chemical behaviors ...
... • The existence of multiple pure forms of an element, in the same phase (solid, liquid, or gas), that differ in structure • Different forms are called allotropes • Can exhibit varied physical properties and chemical behaviors ...
File
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. You will also learn about ions, which are atoms that have the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons. What are isotopes? In addition to its a ...
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. You will also learn about ions, which are atoms that have the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons. What are isotopes? In addition to its a ...
Elements Unit Test
... 2. It wasn’t until an English scientist by the name of Robert Boyle came along, that the world finally accepted the fact that there are more than the original four elements of; a. b. c. d. ...
... 2. It wasn’t until an English scientist by the name of Robert Boyle came along, that the world finally accepted the fact that there are more than the original four elements of; a. b. c. d. ...
Atoms and Molecules
... • Atoms are made of protons, neutrons and electrons • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
... • Atoms are made of protons, neutrons and electrons • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
Chapter 3
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 66.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 66.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
Chapter 3
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 60.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
... by mass for example: NaCl is always 60.66% chlorine and 39.34% sodium • Law of Multiple Proportions: when two elements can form two compounds, the masses that combine are in simple whole number ratios, CO and CO2 ...
1 The Nucleus Total number of nucleons: mass number Number of
... Fusion (release more E) H-bomb ...
... Fusion (release more E) H-bomb ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review (15-16)_2
... (14) ____________ Which column from above contains the alkaline earth metals? (15) ____________ Which column from above contains the Noble Gases? (16) ____________ Which column from above contains the most reactive non-metals? (17) ____________ Which column from above contains VERY non-reactive elem ...
... (14) ____________ Which column from above contains the alkaline earth metals? (15) ____________ Which column from above contains the Noble Gases? (16) ____________ Which column from above contains the most reactive non-metals? (17) ____________ Which column from above contains VERY non-reactive elem ...
TEST II Study Guide-Atomic Theory Honors Chemistry
... 6. ______ What type of bombarding particle was used in Rutherford's "gold foil" experiment? A) alpha; B) beta; C) gamma; D) neutron; E) neutrino; F) X rays. 7. ______ This color-blind English schoolteacher studied the findings of many of his contemporaries, and put forth the first comprehensive atom ...
... 6. ______ What type of bombarding particle was used in Rutherford's "gold foil" experiment? A) alpha; B) beta; C) gamma; D) neutron; E) neutrino; F) X rays. 7. ______ This color-blind English schoolteacher studied the findings of many of his contemporaries, and put forth the first comprehensive atom ...
Mass of individual atoms
... If we had been using the Potassium-40 to Argon-40 dating system, the half-life of potassium-40 is 1.3 billion years. In this case, the rock is 2 half-lives x 1.3 b.y./half-life = 2.6 b.y. ...
... If we had been using the Potassium-40 to Argon-40 dating system, the half-life of potassium-40 is 1.3 billion years. In this case, the rock is 2 half-lives x 1.3 b.y./half-life = 2.6 b.y. ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Quick Notes
... Atom: the smallest unit of an element that contains the properties of that element Ex: if you have 1 gold atom, you can’t break that apart anymore and still have gold Nucleus: the center of an atom. Contains both Protons and Neutrons Protons are POSITIVE Neutrons are NEUTRAL Electrons are NEGATI ...
... Atom: the smallest unit of an element that contains the properties of that element Ex: if you have 1 gold atom, you can’t break that apart anymore and still have gold Nucleus: the center of an atom. Contains both Protons and Neutrons Protons are POSITIVE Neutrons are NEUTRAL Electrons are NEGATI ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.