Matter and the Periodic Table
... Groups: Also known as families, the 18 vertical rows The elements in each group have similar characteristics. ...
... Groups: Also known as families, the 18 vertical rows The elements in each group have similar characteristics. ...
PP 04 Atoms_ molecules_ ions
... Binary Compound: A compound made up of two elements in any ratio. (NaCl) (Mg3P2) Diatomic Molecules: Molecules made up of wo atoms of the same element that are chemically combined. (Cl2, F2, O2) Atomic Structure Problem: List & describe the three subatomic particles. Atomic Structure Problem: Fill i ...
... Binary Compound: A compound made up of two elements in any ratio. (NaCl) (Mg3P2) Diatomic Molecules: Molecules made up of wo atoms of the same element that are chemically combined. (Cl2, F2, O2) Atomic Structure Problem: List & describe the three subatomic particles. Atomic Structure Problem: Fill i ...
I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
... same number of protons ○ The number of neutrons can vary ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
... same number of protons ○ The number of neutrons can vary ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
Atomic Structure
... b. Credited with the discovery of the neutron c. Credited with the discovery of the electron and the “plum pudding” model of the atom. d. Used the now famous “gold foil” experiment to prove the existence of the nucleus. He also showed most of an atom is empty space! e. Credited with the “planetary” ...
... b. Credited with the discovery of the neutron c. Credited with the discovery of the electron and the “plum pudding” model of the atom. d. Used the now famous “gold foil” experiment to prove the existence of the nucleus. He also showed most of an atom is empty space! e. Credited with the “planetary” ...
Dating the Earth Power Point
... many protons in a nucleus. In this case the element will emit radiation in the form of positively charged particles called alpha particles. • Beta decay - Beta decay is caused when there are too many neutrons in a nucleus. In this case the element will emit radiation in the form of negatively charge ...
... many protons in a nucleus. In this case the element will emit radiation in the form of positively charged particles called alpha particles. • Beta decay - Beta decay is caused when there are too many neutrons in a nucleus. In this case the element will emit radiation in the form of negatively charge ...
Document
... An industrially important element contains 26 electrons and rusts in the presence of air and moisture. Identify the element. ...
... An industrially important element contains 26 electrons and rusts in the presence of air and moisture. Identify the element. ...
Problem Set 4 - Morrisville.org
... 54) How long will it take 100 grams of radioactive sample to decay so that only 6.25 grams remain and the samples half life is 3 days? 55) How long is the half life of an isotope if 2.0 grams of sample remain from a 64 gram sample after 30 years? After having read through chapter 25, respond to thes ...
... 54) How long will it take 100 grams of radioactive sample to decay so that only 6.25 grams remain and the samples half life is 3 days? 55) How long is the half life of an isotope if 2.0 grams of sample remain from a 64 gram sample after 30 years? After having read through chapter 25, respond to thes ...
The Chemical Basis of Life Chapter 4
... • Elements that make up less than 0.01 percent of you body mass, but are critical to your health. ...
... • Elements that make up less than 0.01 percent of you body mass, but are critical to your health. ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 11) Group: a vertical column in the periodic table of the elements that have similar properties; also called a family. 12) Period: a horizontal row in the periodic table of elements that have varying properties. 13) Reactive: indicates how likely an element is to undergo a chemical change. 14) Metal ...
... 11) Group: a vertical column in the periodic table of the elements that have similar properties; also called a family. 12) Period: a horizontal row in the periodic table of elements that have varying properties. 13) Reactive: indicates how likely an element is to undergo a chemical change. 14) Metal ...
Isotopes
... • Atoms of the same element with different atomic masses are called isotopes. • Atoms of the same element have the same properties. • But what causes the chemical properties of an atom? • So atoms of different isotopes of an element must have the same number of protons and electrons. • Whatever cau ...
... • Atoms of the same element with different atomic masses are called isotopes. • Atoms of the same element have the same properties. • But what causes the chemical properties of an atom? • So atoms of different isotopes of an element must have the same number of protons and electrons. • Whatever cau ...
Atomic Structure Power Point
... So how can you have part of a neutron, such as 119.97 ? Because of ISOTOPES ! An isotope is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each i ...
... So how can you have part of a neutron, such as 119.97 ? Because of ISOTOPES ! An isotope is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each i ...
Unit 2 Overview
... periodic table possesses. In part two, we will relate the number of neutrons to the formation of isotopes which are linked to radioactive behavior allowing us to study many applications of radioactivity in everyday life. In part three, we will seek to understand how the electron is inextricably link ...
... periodic table possesses. In part two, we will relate the number of neutrons to the formation of isotopes which are linked to radioactive behavior allowing us to study many applications of radioactivity in everyday life. In part three, we will seek to understand how the electron is inextricably link ...
Lecture 2
... protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. • While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
... protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. • While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
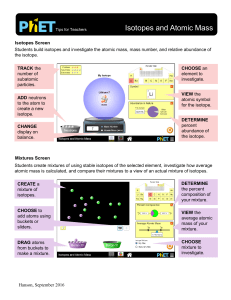
Isotopes and Atomic Mass
... • On the Mixtures screen, students attempted to match Nature’s Mix using My Mix view. This is not possible for all elements shown in the simulation. • Students who need additional practice in interpreting atomic symbols, calculating mass number, or identifying the number of protons, neutrons, and el ...
... • On the Mixtures screen, students attempted to match Nature’s Mix using My Mix view. This is not possible for all elements shown in the simulation. • Students who need additional practice in interpreting atomic symbols, calculating mass number, or identifying the number of protons, neutrons, and el ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... 4. Atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. 5. The total number of nucleons (particles in the nucleus) in the atom make up the mass number. 6. A neutral nuclear particle having a mass of about 1 AMU is called the neutron. 7. The proton is ...
... 4. Atoms of the same element that differ in their number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. 5. The total number of nucleons (particles in the nucleus) in the atom make up the mass number. 6. A neutral nuclear particle having a mass of about 1 AMU is called the neutron. 7. The proton is ...
Isotope Worksheet
... atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, ! ...
... atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, ! ...
Isotope Worksheet
... In other words, isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Since any atom having 9 protons (Z = 9) must be an atom of fluorine, we can omit the Z-value and just use the symbol F for many purposes, i.e., we can write 19F instead of 19F. ...
... In other words, isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Since any atom having 9 protons (Z = 9) must be an atom of fluorine, we can omit the Z-value and just use the symbol F for many purposes, i.e., we can write 19F instead of 19F. ...
Homework 1B1 - 3 - Uddingston Grammar School
... (a) Complete the diagram to show how the electrons are arranged. You may wish to use the data booklet to help you. ...
... (a) Complete the diagram to show how the electrons are arranged. You may wish to use the data booklet to help you. ...
isotopes
... Can we write isotopes in a different way? • You can also use the mass number and the name of the element to designate the atom or isotope – This is called hyphen notation • For example, two isotopes of carbon are carbon-12 and carbon-13 – The nuclear symbols for these two isotopes would be: ...
... Can we write isotopes in a different way? • You can also use the mass number and the name of the element to designate the atom or isotope – This is called hyphen notation • For example, two isotopes of carbon are carbon-12 and carbon-13 – The nuclear symbols for these two isotopes would be: ...
Chapter 2
... understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 7. Expl ...
... understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 7. Expl ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioacti ...
... Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioacti ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.