Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations
... energy. Such emissions are called radioactivity (or radioactive decay) and such unstable atoms are referred to as radioactive isotopes. Different isotopes are commonly identified by their element name or chemical symbol and their mass. For example, uranium-235 (U-235) and uranium-238 (U-238) are two ...
... energy. Such emissions are called radioactivity (or radioactive decay) and such unstable atoms are referred to as radioactive isotopes. Different isotopes are commonly identified by their element name or chemical symbol and their mass. For example, uranium-235 (U-235) and uranium-238 (U-238) are two ...
Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations
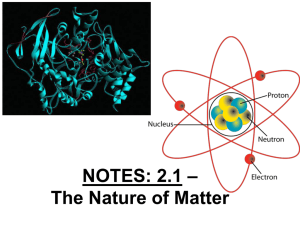
... Atoms are composed of three main subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose ...
... Atoms are composed of three main subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose ...
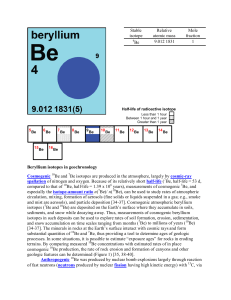
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... Cosmogenic 10Be and 7Be isotopes are produced in the atmosphere, largely by cosmic-ray spallation of nitrogen and oxygen. Because of its relatively short half-life (7 Be, half-life = 53 d, compared to that of 10Be, half-life = 1.39 x 106 years), measurements of cosmogenic 7Be, and especially the iso ...
... Cosmogenic 10Be and 7Be isotopes are produced in the atmosphere, largely by cosmic-ray spallation of nitrogen and oxygen. Because of its relatively short half-life (7 Be, half-life = 53 d, compared to that of 10Be, half-life = 1.39 x 106 years), measurements of cosmogenic 7Be, and especially the iso ...
Review 1st Qtr KEY
... PART I: You should know the basics (terms & basic facts) about… Hypothesis theory law scientific method mass weight volume physical change chemical change mixture element compound molecule heterogeneous homogeneous states of matter ...
... PART I: You should know the basics (terms & basic facts) about… Hypothesis theory law scientific method mass weight volume physical change chemical change mixture element compound molecule heterogeneous homogeneous states of matter ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
Lecture4
... atom which has 6 protons in its nucleus is a carbon atom. Different numbers of neutrons may exist in a carbon nucleus; there can be 5, 6, 7 or 8. Each of these atoms is a different isotope of carbon. All elements have isotope(s). Some isotopes are stable and some are unstable. An unstable atom has t ...
... atom which has 6 protons in its nucleus is a carbon atom. Different numbers of neutrons may exist in a carbon nucleus; there can be 5, 6, 7 or 8. Each of these atoms is a different isotope of carbon. All elements have isotope(s). Some isotopes are stable and some are unstable. An unstable atom has t ...
Atomic Crossword Name: Period: ____
... 11. A _____________ electron is in the outermost shell of an atom 12. Formed when atoms share electrons 14. Has a different number of neutrons than normal 15. The splitting of an atomic nucleus (usually with heavy elements) 17. British scientist who formulated our modern atomic theory 22. The mergin ...
... 11. A _____________ electron is in the outermost shell of an atom 12. Formed when atoms share electrons 14. Has a different number of neutrons than normal 15. The splitting of an atomic nucleus (usually with heavy elements) 17. British scientist who formulated our modern atomic theory 22. The mergin ...
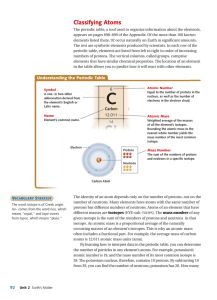
Classifying Atoms
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
Honors Review Unit 2 answers
... Used an “oil drop” experiment to discover the charge and mass of an electron. ___Millikan__ Proposed the “Plum Pudding” model of the atom. _____Thomson________ Used the word “atomos” to describe matter. _____Democritos________ Called the “Father of Modern Chemistry”. ___Lavoisier_________ Discovered ...
... Used an “oil drop” experiment to discover the charge and mass of an electron. ___Millikan__ Proposed the “Plum Pudding” model of the atom. _____Thomson________ Used the word “atomos” to describe matter. _____Democritos________ Called the “Father of Modern Chemistry”. ___Lavoisier_________ Discovered ...
Atomic Structure AKS Correlation Use the modern atomic theory to
... Discovered e-, experiment, predictable shells, indivisible All matter made of plum pudding discovered p+, Bohr model 1st to think atoms model Atoms mostly about matter Matter cannot be empty space, dense and its’ makecreated or center up of atoms destroyed Atoms of same element look the same Chem re ...
... Discovered e-, experiment, predictable shells, indivisible All matter made of plum pudding discovered p+, Bohr model 1st to think atoms model Atoms mostly about matter Matter cannot be empty space, dense and its’ makecreated or center up of atoms destroyed Atoms of same element look the same Chem re ...
Atomic Mass
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
Exam III Review
... b. Causes the disruption of cells in living tissue. c. Can be useful in the treatment of cancer. d. All of the above. 13. An atom is a. A tiny, indivisible particle. b. The smallest piece of matter. c. The smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical identity of that element. d. An arti ...
... b. Causes the disruption of cells in living tissue. c. Can be useful in the treatment of cancer. d. All of the above. 13. An atom is a. A tiny, indivisible particle. b. The smallest piece of matter. c. The smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical identity of that element. d. An arti ...
1 - cloudfront.net
... How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. What does the number 84 represent in the name ...
... How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. What does the number 84 represent in the name ...
Review for Periodic - Mr-Durands
... 1. Find Scandium (Sc) on the table what is the atomic number? 2. What is the atomic mass of Chromium (Cr)? 3. What is the number of neutrons for Cesium (Cs)? 4. What is the difference between atomic mass and number? 5. How do isotopes affect the atomic mass of an element? 6. What is a group on the p ...
... 1. Find Scandium (Sc) on the table what is the atomic number? 2. What is the atomic mass of Chromium (Cr)? 3. What is the number of neutrons for Cesium (Cs)? 4. What is the difference between atomic mass and number? 5. How do isotopes affect the atomic mass of an element? 6. What is a group on the p ...
Notes
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
Quiz: The Atom (Open Notes)
... 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. The atomic number of an atom is determined by th ...
... 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. The atomic number of an atom is determined by th ...
atomic number - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
Atomic Structure
... •Isotope is the same element with different number of ________________________ therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. •Ion is same element with a different number of __________________. A ...
... •Isotope is the same element with different number of ________________________ therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. •Ion is same element with a different number of __________________. A ...
Extension 18.2: Isotopes
... number times the proton’s mass): M nucleus ≈ A x mproton. So different forms of an element may have different mass. ...
... number times the proton’s mass): M nucleus ≈ A x mproton. So different forms of an element may have different mass. ...
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure - Mercer Island School District
... • English schoolteacher John Dalton, 1803 – Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of ato ...
... • English schoolteacher John Dalton, 1803 – Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of ato ...
Unit 2 Notes - School City of Hobart
... • For a nuclide to be considered radioactive, it must have an unstable nucleus due to an imbalance between # of protons and neutrons ~1:1 ratio = stable *The further an isotope is from a 1:1 ratio, the more likely it is to be radioactive (Figure 21.2, p.881) • Types of Nuclear Decay (aka Radioactivi ...
... • For a nuclide to be considered radioactive, it must have an unstable nucleus due to an imbalance between # of protons and neutrons ~1:1 ratio = stable *The further an isotope is from a 1:1 ratio, the more likely it is to be radioactive (Figure 21.2, p.881) • Types of Nuclear Decay (aka Radioactivi ...
Name Period Nuclear Study Packet Set 1 1. What subatomic
... 3. Potassium-42 has a half life of 12 hours. At present, a given ore sample contains 34.2 mg of K-42. How much did it contain yesterday at the same time. 4. What percent of a sample of a radioactive element whose half life is 5 years will decay after 25 years? 5. What are some ways that nuclea ...
... 3. Potassium-42 has a half life of 12 hours. At present, a given ore sample contains 34.2 mg of K-42. How much did it contain yesterday at the same time. 4. What percent of a sample of a radioactive element whose half life is 5 years will decay after 25 years? 5. What are some ways that nuclea ...
Lesson 13 - Highline Public Schools
... weighted average of the masses of the isotopes in a sample of the element. The most common isotope of an element, frequently has a mass that is close to the average atomic mass given in the periodic table. ...
... weighted average of the masses of the isotopes in a sample of the element. The most common isotope of an element, frequently has a mass that is close to the average atomic mass given in the periodic table. ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.