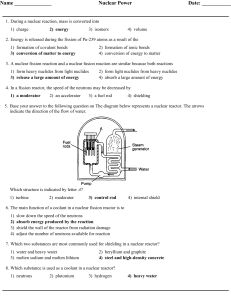
Nuclear Power Date
... Which phrase best describes this type of reaction and the overall energy change that occurs? 1) nuclear, and energy is released 3) chemical, and energy is released ...
... Which phrase best describes this type of reaction and the overall energy change that occurs? 1) nuclear, and energy is released 3) chemical, and energy is released ...
Physics 102, Class 25 The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... • Protons and Neutrons ATTRACT other Protons and Neutrons by the “strong nuclear force” – only works at short distances ...
... • Protons and Neutrons ATTRACT other Protons and Neutrons by the “strong nuclear force” – only works at short distances ...
Syllabus overview
... 3.1.1 State that temperature determines the direction of thermal energy transfer between two objects. Students should be familiar with the concept of thermal equilibrium. 3.1.2 State the relation between the Kelvin and Celsius scales of temperature. T/K = t/°C + 273 is sufficient. 3.1.3 State that t ...
... 3.1.1 State that temperature determines the direction of thermal energy transfer between two objects. Students should be familiar with the concept of thermal equilibrium. 3.1.2 State the relation between the Kelvin and Celsius scales of temperature. T/K = t/°C + 273 is sufficient. 3.1.3 State that t ...
120 min This paper - University of Southampton
... paired, so spin and parity are defined by unpaired neutron. Neutrons fill shells as follows ( with j = l + 1/2 fills before j = l − 1/2 due to specific features of the spinorbit interactions): (1s1/2)2 (1p3/2)4 (1p1/2)1 Therefore there is one unpaired neutron in 1p1/2 state forming state with parity ...
... paired, so spin and parity are defined by unpaired neutron. Neutrons fill shells as follows ( with j = l + 1/2 fills before j = l − 1/2 due to specific features of the spinorbit interactions): (1s1/2)2 (1p3/2)4 (1p1/2)1 Therefore there is one unpaired neutron in 1p1/2 state forming state with parity ...
SMART Notebook
... - Since most carbon is carbon-12, the number is pretty close to 12u. - But, the little bit of carbon-13 does pull up the number a bit, so we get 12.01u. - The number of neutrons strongly affects the stability of the nucleus. This is why some isotopes are more common than others. - Because different ...
... - Since most carbon is carbon-12, the number is pretty close to 12u. - But, the little bit of carbon-13 does pull up the number a bit, so we get 12.01u. - The number of neutrons strongly affects the stability of the nucleus. This is why some isotopes are more common than others. - Because different ...
Nuclear Fission sim
... • In nuclear reactions, energy comes from converting tiny amounts of mass lost when the bonds between protons and neutrons are broken and made. These bonds are due to the strong force. • The strong force is a thousand times stronger than the electrical force which holds atoms and ions together in ch ...
... • In nuclear reactions, energy comes from converting tiny amounts of mass lost when the bonds between protons and neutrons are broken and made. These bonds are due to the strong force. • The strong force is a thousand times stronger than the electrical force which holds atoms and ions together in ch ...
Document
... An industrially important element contains 26 electrons and rusts in the presence of air and moisture. Identify the element. ...
... An industrially important element contains 26 electrons and rusts in the presence of air and moisture. Identify the element. ...
General CHemistry Unit 2 Homework Notes
... The particles in a liquid stay relatively close together, but they can move around each other. Gas particles are far apart; they move rapidly and collide with each other and with the walls of the container. TOPIC FOUR: THE MOLE & STOICHIMETRY (PAGE 4) The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom i ...
... The particles in a liquid stay relatively close together, but they can move around each other. Gas particles are far apart; they move rapidly and collide with each other and with the walls of the container. TOPIC FOUR: THE MOLE & STOICHIMETRY (PAGE 4) The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom i ...
File
... NUCLEAR FUSION Nuclear Fusion: The combining of atomic nuclei to form a larger atom is called fusion Nuclear fusion occurs in the sun where hydrogen atoms 1 helium fuse to form ...
... NUCLEAR FUSION Nuclear Fusion: The combining of atomic nuclei to form a larger atom is called fusion Nuclear fusion occurs in the sun where hydrogen atoms 1 helium fuse to form ...
Scientists` Consensus Ideas Atomic Structure and Nuclear Interactions
... 14. Some elements change into other elements as a result of nuclear reactions. Physical and chemical interactions do not convert one element into another element. 15. Nuclear radiation refers to the particles and energy released during nuclear reactions. Three sources of nuclear radiation are radioa ...
... 14. Some elements change into other elements as a result of nuclear reactions. Physical and chemical interactions do not convert one element into another element. 15. Nuclear radiation refers to the particles and energy released during nuclear reactions. Three sources of nuclear radiation are radioa ...
View - Rutgers Physics
... model for the nucleus, in which we treat the nucleus much as we would a drop of water, with a cohesive force and a surface tension. There is, however, one further term we need to consider in our understanding of the binding energy, which can be understood only quantum mechanically, using the indepen ...
... model for the nucleus, in which we treat the nucleus much as we would a drop of water, with a cohesive force and a surface tension. There is, however, one further term we need to consider in our understanding of the binding energy, which can be understood only quantum mechanically, using the indepen ...
Period 10 Activity Solutions: Nuclear Reactions
... c) The leftmost point of the graph is deuterium ( 21 H ). What is the binding energy per nucleon of deuterium? _1 MeV_ d) The next point to the right is helium ( 42 He ). What is the binding energy per nucleon of helium? _7 MeV_ e) How much energy is given off per nucleon if two deuterium nuclei fus ...
... c) The leftmost point of the graph is deuterium ( 21 H ). What is the binding energy per nucleon of deuterium? _1 MeV_ d) The next point to the right is helium ( 42 He ). What is the binding energy per nucleon of helium? _7 MeV_ e) How much energy is given off per nucleon if two deuterium nuclei fus ...