Study Guide
... 1. __________ - created on ______________. It defines the _______ major branches of government and how it should rule. The Constitution is also a ______ of the _______ and ________ that we have in the U.S. 2. The __________________ is a part of the constitution and plays an important part in how our ...
... 1. __________ - created on ______________. It defines the _______ major branches of government and how it should rule. The Constitution is also a ______ of the _______ and ________ that we have in the U.S. 2. The __________________ is a part of the constitution and plays an important part in how our ...
Fort Sumter: The Confederates attack Fort Sumter (Union property
... arguments over states’ rights. Secession: To withdraw from a group, in this case, from the Union. First Bull Run: The first major battle of the Civil War, a Confederate victory. Stonewall Jackson: A famous Confederate general that worked cooperatively with Lee; he earned his nickname for his defense ...
... arguments over states’ rights. Secession: To withdraw from a group, in this case, from the Union. First Bull Run: The first major battle of the Civil War, a Confederate victory. Stonewall Jackson: A famous Confederate general that worked cooperatively with Lee; he earned his nickname for his defense ...
pg_11 Antietam Worksheet 2016-2017
... pierce the Confederate center after a terrible struggle for this key defensive position. Unfortunately for the Union army this temporal advantage in the center was not followed up with further advances. Late in the day, Maj. General Ambrose Burnside’s corps pushed across a bullet-strewn stone bridge ...
... pierce the Confederate center after a terrible struggle for this key defensive position. Unfortunately for the Union army this temporal advantage in the center was not followed up with further advances. Late in the day, Maj. General Ambrose Burnside’s corps pushed across a bullet-strewn stone bridge ...
The Civil War, 1861-1865 Union Confederate Resource Advantages
... Battles of the American Civil War ...
... Battles of the American Civil War ...
Chapter 3.
... What advantage did Grant’s army have over Lee’s at Richmond? The Union army received food, supplies, and soldiers. The confederate army was running out of all of these things. ...
... What advantage did Grant’s army have over Lee’s at Richmond? The Union army received food, supplies, and soldiers. The confederate army was running out of all of these things. ...
Civil War: Beginning To End
... • Confederate forces under Jubal Early probe and fire upon the northern defenses of Washington, D.C., throwing the Capital into a state of high alert. • After forcing the Confederate army of John Bell Hood out of Atlanta, Georgia, General William T. Sherman captures the city, a major munitions cente ...
... • Confederate forces under Jubal Early probe and fire upon the northern defenses of Washington, D.C., throwing the Capital into a state of high alert. • After forcing the Confederate army of John Bell Hood out of Atlanta, Georgia, General William T. Sherman captures the city, a major munitions cente ...
Robert E. Lee - English Worksheets Land
... Robert E. Lee was from an aristocratic Virginia family that included many famous politicians and military figures. He saw himself as the next generation of his family’s greatness, and at the age of 18 he went to West Point Military Academy, where he finished without any demerits. He earned perfec ...
... Robert E. Lee was from an aristocratic Virginia family that included many famous politicians and military figures. He saw himself as the next generation of his family’s greatness, and at the age of 18 he went to West Point Military Academy, where he finished without any demerits. He earned perfec ...
THE CIVIL WAR – The War on the Battlefield
... the North captured Fort Fisher in North Carolina and closed the last Confederate ...
... the North captured Fort Fisher in North Carolina and closed the last Confederate ...
The Civil War Part 2
... to attack communication and transportation networks. • Grant’s Army of Tennessee captured Confederate forts on Tennessee and Cumberland rivers in February 1862. ...
... to attack communication and transportation networks. • Grant’s Army of Tennessee captured Confederate forts on Tennessee and Cumberland rivers in February 1862. ...
Social Studies Chapter 6 Review
... -In 1864, Union General William Tecumseh Sherman led his army through Georgia. He burned down most of Atlanta and from there headed to Savannah on the Atlantic coast in what is known as “the March to the Sea.” The goal of this march was to burn anything and everything that could help the South win t ...
... -In 1864, Union General William Tecumseh Sherman led his army through Georgia. He burned down most of Atlanta and from there headed to Savannah on the Atlantic coast in what is known as “the March to the Sea.” The goal of this march was to burn anything and everything that could help the South win t ...
Civil War Jeopardy Review
... As part of the terms of surrender, Confederate soldiers were allowed to keep their livestock and the officers could keep their weapons, including their: ...
... As part of the terms of surrender, Confederate soldiers were allowed to keep their livestock and the officers could keep their weapons, including their: ...
The 4th Rhode Island Stands Alone at Antietam
... McClellan's Army of the Potomac. Part of the 9th Corps, they were tasked with cutting off the rebel army from its only line of retreat, the Harper's Ferry road. Unfortunately for the Ocean State men, the 3,000 men of Confederate Gen. A.P. Hill's command were coming up that same road, wearing their ...
... McClellan's Army of the Potomac. Part of the 9th Corps, they were tasked with cutting off the rebel army from its only line of retreat, the Harper's Ferry road. Unfortunately for the Ocean State men, the 3,000 men of Confederate Gen. A.P. Hill's command were coming up that same road, wearing their ...
Fort Sum ter • T he C ivil W ar began on A pril 12, 1861, when C
... • Georgia was free from major battles during the first few years of the Civil War. • In 1863, close to 58,000 Union troops moved into northwest Georgia where they battled the Confederate Army along Chickamauga Creek. • The battle resulted in both sides losing over 16,000 men, and forced the Union Ar ...
... • Georgia was free from major battles during the first few years of the Civil War. • In 1863, close to 58,000 Union troops moved into northwest Georgia where they battled the Confederate Army along Chickamauga Creek. • The battle resulted in both sides losing over 16,000 men, and forced the Union Ar ...
The Battle Of Chickamauga - ushistory
... The Union troops followed it and brushed with it at Davis's Cross Roads. Bragg was determined to reoccupy Chattanooga and decided to meet a part of Rosecrans's army, defeat it, and then move back into the city. On September 17 he headed north, intending to attack the isolated XXI Corps. As Bragg mar ...
... The Union troops followed it and brushed with it at Davis's Cross Roads. Bragg was determined to reoccupy Chattanooga and decided to meet a part of Rosecrans's army, defeat it, and then move back into the city. On September 17 he headed north, intending to attack the isolated XXI Corps. As Bragg mar ...
Battle Of Shiloh Handout
... wait to attack until the next day. This decision gave Buell’s army and the remainder of Grant’s troops time to get there and to provide reinforcements. General Buell’s men and a division of Grant’s army under Major General Lewis Wallace finally arrived on the field. These two new arrivals added 23,0 ...
... wait to attack until the next day. This decision gave Buell’s army and the remainder of Grant’s troops time to get there and to provide reinforcements. General Buell’s men and a division of Grant’s army under Major General Lewis Wallace finally arrived on the field. These two new arrivals added 23,0 ...
Civil Unrest in the South:
... Union cavalry were sent to find his army. 2. Gen. John Buford located the rear elements of Lee’s army. He chose to defend the high ground. 3. Lee concentrated his forces to attack the location. 4. Maj. Gen. John Reynolds arrived with infantry to support Buford. He was quickly killed. 5. Fighting all ...
... Union cavalry were sent to find his army. 2. Gen. John Buford located the rear elements of Lee’s army. He chose to defend the high ground. 3. Lee concentrated his forces to attack the location. 4. Maj. Gen. John Reynolds arrived with infantry to support Buford. He was quickly killed. 5. Fighting all ...
Chapter 22 The Civil War Vocabulary Review Directions: Match the
... 5.) the right of an accused person to appear in court so a judge can determine whether he or she is being imprisoned lawfully 6.) a speech by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863 at the site of the Battle of Gettysburg in memory of the Union soldiers who had died trying to protect the ideals of freedom ...
... 5.) the right of an accused person to appear in court so a judge can determine whether he or she is being imprisoned lawfully 6.) a speech by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863 at the site of the Battle of Gettysburg in memory of the Union soldiers who had died trying to protect the ideals of freedom ...
1. Define: Secession: leaving the Union Secede: to leave
... invade the North. They lost the battle and were forced back into Virginia. 14. The Battle of Gettysburg was fought in July, 1863. It was the turning point of the war. Why was this battle important? Gettysburg was fought in Pennsylvania. It was the second time the Confederates invaded the North. The ...
... invade the North. They lost the battle and were forced back into Virginia. 14. The Battle of Gettysburg was fought in July, 1863. It was the turning point of the war. Why was this battle important? Gettysburg was fought in Pennsylvania. It was the second time the Confederates invaded the North. The ...
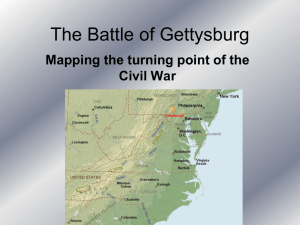
The Battle of Gettysburg
... July 2, Gen. Longstreet was ordered by Lee to attack. But Longstreet was quite slow in getting his troops into position and didn't attack until 4 p.m. that afternoon thus giving the Union Army even more time to strengthen its position. ...
... July 2, Gen. Longstreet was ordered by Lee to attack. But Longstreet was quite slow in getting his troops into position and didn't attack until 4 p.m. that afternoon thus giving the Union Army even more time to strengthen its position. ...
Civil War Battles - WAQT You Gotta Know
... ● On April 6, 1862, 40,000 Confederate soldiers attacked Union soldiers stationed by the Tennessee River ● Repeated attacks failed to drive the the Union soldiers from their hastily made position, “Hornet’s Nest” ● Artillery helped the Confederates, until Union reinforcements arrived and pushed them ...
... ● On April 6, 1862, 40,000 Confederate soldiers attacked Union soldiers stationed by the Tennessee River ● Repeated attacks failed to drive the the Union soldiers from their hastily made position, “Hornet’s Nest” ● Artillery helped the Confederates, until Union reinforcements arrived and pushed them ...
Unit 3 Day 6 1862
... Specified Content: Ironclads, Shiloh, New Orleans, Gen. Lee, Antietam, Fredericksburg ...
... Specified Content: Ironclads, Shiloh, New Orleans, Gen. Lee, Antietam, Fredericksburg ...