People of the Civil War - Mrs. Pollnow`s US History and Western
... • “Total War” • “Scorched-earth policy” • “Sherman’s March” • Take Atlanta, march to the sea ...
... • “Total War” • “Scorched-earth policy” • “Sherman’s March” • Take Atlanta, march to the sea ...
Introduction
... • The American Civil War began in early 1861 when Confederate troops in South Carolina fired on the Union Fort Sumter. • Lincoln called for 75,000 men to stop the rebellion and both sides mobilized for war. • The first major battle took place at the Battle of Bull Run. • After the initial onslaught ...
... • The American Civil War began in early 1861 when Confederate troops in South Carolina fired on the Union Fort Sumter. • Lincoln called for 75,000 men to stop the rebellion and both sides mobilized for war. • The first major battle took place at the Battle of Bull Run. • After the initial onslaught ...
Jeopardy - Alvin ISD
... A. The Kansas-Nebraska Act is passed in Congress B. Jefferson Davis named President of the Confederacy C. General Robert E. Lee surrenders his forces at Appomattox Court ...
... A. The Kansas-Nebraska Act is passed in Congress B. Jefferson Davis named President of the Confederacy C. General Robert E. Lee surrenders his forces at Appomattox Court ...
Chapter 19, Section 1.
... took Yorktown after hesitating for fear of being outnumbered. Organized and trained the Union Army. ...
... took Yorktown after hesitating for fear of being outnumbered. Organized and trained the Union Army. ...
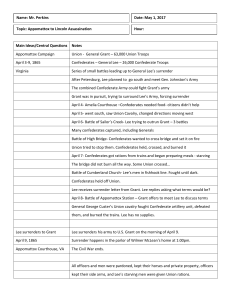
The Road To Appomattox (Filled Out)
... The Road to the Confederate Surrender at Appomattox Court House, VA Sunday, April 9, 1865 ...
... The Road to the Confederate Surrender at Appomattox Court House, VA Sunday, April 9, 1865 ...
Unit 8 - Maps - Interactive Maps - Major Battles of the Civil War
... 3. Who led the Savannah Campaign, marching across the Southern states and inflicting more than one hundred million dollars in damages? ...
... 3. Who led the Savannah Campaign, marching across the Southern states and inflicting more than one hundred million dollars in damages? ...
File
... Many confederates captured, including Generals Battle of High Bridge- Confederates wanted to cross bridge and set it on fire Union tried to stop them. Confederates held, crossed, and burned it April 7- Confederates got rations from trains and began preparing meals - starving The bridge did not burn ...
... Many confederates captured, including Generals Battle of High Bridge- Confederates wanted to cross bridge and set it on fire Union tried to stop them. Confederates held, crossed, and burned it April 7- Confederates got rations from trains and began preparing meals - starving The bridge did not burn ...
Chapter 11 Vocab Words
... • Stonewall Jackson: Confederate General that was accidentally shot by his own men and died a few days later. • Ulysses S. Grant: Commanding General of the Union Army during the Civil War, later becomes president of the U.S. • Robert E. Lee: Commander of the Confederate Army, surrendered at Appomat ...
... • Stonewall Jackson: Confederate General that was accidentally shot by his own men and died a few days later. • Ulysses S. Grant: Commanding General of the Union Army during the Civil War, later becomes president of the U.S. • Robert E. Lee: Commander of the Confederate Army, surrendered at Appomat ...
CH 11 Section 4.
... Sherman’s troops invaded Georgia. His forces marched across the state to the sea. They destroyed cities and farms as they went. They did the same in South Carolina. The South was quickly becoming a wasteland. ...
... Sherman’s troops invaded Georgia. His forces marched across the state to the sea. They destroyed cities and farms as they went. They did the same in South Carolina. The South was quickly becoming a wasteland. ...
Key Figures of the Civil War
... • Leader of the Army of Northern Virginia in the Confederate Army • Used tried and true strategies • Lost many soldiers at Gettysburg when he ordered a frontal assault • His army was almost destroyed • Surrendered to General Grant at Appomattox Courthouse ...
... • Leader of the Army of Northern Virginia in the Confederate Army • Used tried and true strategies • Lost many soldiers at Gettysburg when he ordered a frontal assault • His army was almost destroyed • Surrendered to General Grant at Appomattox Courthouse ...
The Important People of the Civil War
... Content Objective: Students will learn about the key leaders on and off the Battle Field Language Objective: Students will create a foldable of important Civil War Leaders. ...
... Content Objective: Students will learn about the key leaders on and off the Battle Field Language Objective: Students will create a foldable of important Civil War Leaders. ...
Major Battles of the Civil War (50)
... On September 17, 1862, McClellan and Lee clashed at ______________, marking one of the bloodiest days in the war. At the Battle of _________________, General Meade forced Confederate troops to retreat from Pennsylvania. After a six-week siege, the city of __________________ surrendered to Grant’s ar ...
... On September 17, 1862, McClellan and Lee clashed at ______________, marking one of the bloodiest days in the war. At the Battle of _________________, General Meade forced Confederate troops to retreat from Pennsylvania. After a six-week siege, the city of __________________ surrendered to Grant’s ar ...
Chapter 22 Summary The Civil War took up where Napoleon and
... The Civil War took up where Napoleon and the Duke of Wellington had left off in 1815. Commanders were willing to sustain high casualties if the objective of a battle was important enough. As in the eighteenth century, however, the general who realized that he had been outfoxed was duty bound to dise ...
... The Civil War took up where Napoleon and the Duke of Wellington had left off in 1815. Commanders were willing to sustain high casualties if the objective of a battle was important enough. As in the eighteenth century, however, the general who realized that he had been outfoxed was duty bound to dise ...
Lincoln`s Reelection Appomattox Court House
... • Lee asks for Confederacy to arm slaves and on Mar. 13th they agree - desperate • Lee dug in at Petersburg. – There Grant held him to a nine month siege. ...
... • Lee asks for Confederacy to arm slaves and on Mar. 13th they agree - desperate • Lee dug in at Petersburg. – There Grant held him to a nine month siege. ...
8th his ch16 study guide
... 5) AFRICAN AMERICANS IN THE NORTH GREETED THE EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION JOYFULLY. 6) WILLIAM TECUMSEH SHERMANʼS “MARCH TO THE SEA” HEADED TOWARD SAVANNAH, GEORGIA. 7) IN THE CIVIL WAR, FOR THE FIRST TIME, THOUSANDS OF WOMEN SERVED AS NURSES. 8) “ PEACE DEMOCRATS” BECAME KNOWN AS COPPERHEADS. 9) HABE ...
... 5) AFRICAN AMERICANS IN THE NORTH GREETED THE EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION JOYFULLY. 6) WILLIAM TECUMSEH SHERMANʼS “MARCH TO THE SEA” HEADED TOWARD SAVANNAH, GEORGIA. 7) IN THE CIVIL WAR, FOR THE FIRST TIME, THOUSANDS OF WOMEN SERVED AS NURSES. 8) “ PEACE DEMOCRATS” BECAME KNOWN AS COPPERHEADS. 9) HABE ...
The US Civil War
... • Given command after a series of victories, including Vicksburg • Hi plan was to concentrate on Sherman’s march through Georgia and his own assault in Virginia ...
... • Given command after a series of victories, including Vicksburg • Hi plan was to concentrate on Sherman’s march through Georgia and his own assault in Virginia ...
Document
... 1863 document issued by Abraham Lincoln. Declared slaves free in the areas under rebellion. It made the Civil War a moral issue. Emancipation Proclamation ...
... 1863 document issued by Abraham Lincoln. Declared slaves free in the areas under rebellion. It made the Civil War a moral issue. Emancipation Proclamation ...
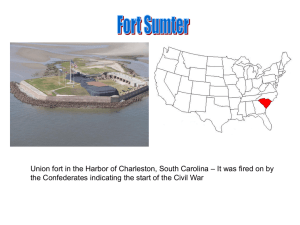
us history 4-2
... Union fort in the Harbor of Charleston, South Carolina – It was fired on by the Confederates indicating the start of the Civil War ...
... Union fort in the Harbor of Charleston, South Carolina – It was fired on by the Confederates indicating the start of the Civil War ...
The End is Near…
... over the capital, the Confederates were on their way back. The Confederate government began to quickly pack up their things and escape their capital. Southerners living in Richmond began to set fires that ripped through the city and nearby gunpowder caused a giant explosion near the waterfront. The ...
... over the capital, the Confederates were on their way back. The Confederate government began to quickly pack up their things and escape their capital. Southerners living in Richmond began to set fires that ripped through the city and nearby gunpowder caused a giant explosion near the waterfront. The ...
document
... • On July 1st an army of Confederate solders entered Gettysburg. • Union sent 15,000 troop to attack the middle of general Meade's defensive line. • In the end the union won. ...
... • On July 1st an army of Confederate solders entered Gettysburg. • Union sent 15,000 troop to attack the middle of general Meade's defensive line. • In the end the union won. ...