click here
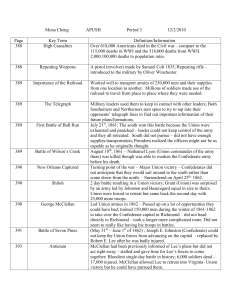
... Bull Run (1st Manassas): Union troops gathered south of Washington D.C. for hope of seizing Manassas, VA ...
... Bull Run (1st Manassas): Union troops gathered south of Washington D.C. for hope of seizing Manassas, VA ...
Key Terms Ch 14 Pages 388-399
... there) was killed though was able to weaken the Confederate army before his death. Turning point of the war – Major Union victory – Confederates did not anticipate that they would sail around to the south rather than come down from the north. – Surrendered on April 25th, 1862. 2 day battle resulting ...
... there) was killed though was able to weaken the Confederate army before his death. Turning point of the war – Major Union victory – Confederates did not anticipate that they would sail around to the south rather than come down from the north. – Surrendered on April 25th, 1862. 2 day battle resulting ...
Civil War Layered Book Foldable
... of Richmond, Virginia failed as the Confederacy won. The Union would continue to try to capture Richmond for over three years. At this early battle, both sides realized that their armies needed to be well trained and equipped. The Union’s other strategy was to capture the Mississippi River. This wou ...
... of Richmond, Virginia failed as the Confederacy won. The Union would continue to try to capture Richmond for over three years. At this early battle, both sides realized that their armies needed to be well trained and equipped. The Union’s other strategy was to capture the Mississippi River. This wou ...
The civil War 1863-1865
... Lee was then sieged at Petersburg, VA from June 9, 1864-March 25, 1865; more trench warfare than an actual siege. ...
... Lee was then sieged at Petersburg, VA from June 9, 1864-March 25, 1865; more trench warfare than an actual siege. ...
The Civil War Begins - Lake County Schools
... House, Virginia, on April 9, 1865. Lee’s army had diminished, which contributed to Union General Grant’s many victories near the end of the war. In a sign of respect, Grant allowed Lee to keep his saber and horse. - General Joseph Johnston was the last Confederate general who continued to fight. He ...
... House, Virginia, on April 9, 1865. Lee’s army had diminished, which contributed to Union General Grant’s many victories near the end of the war. In a sign of respect, Grant allowed Lee to keep his saber and horse. - General Joseph Johnston was the last Confederate general who continued to fight. He ...
Civil War Fill in the Blank
... unable to take two major cities, ______________ along the Mississippi River, and the southern capital of __________________, Virginia. After Union forces failed to capture the capital, the South went on the offensive behind General Robert E. __________. After crossing the Potomac River, General ____ ...
... unable to take two major cities, ______________ along the Mississippi River, and the southern capital of __________________, Virginia. After Union forces failed to capture the capital, the South went on the offensive behind General Robert E. __________. After crossing the Potomac River, General ____ ...
CW Study Guide Ans.
... 13. Fort Sumter – First shots of the Civil War. Confederate in South Carolina fired on a Union fort beginning the Civil War. 14. Battle of Manassas – First major battle of the Civil War. Confederate Army defeats the Union at Bull Run. 15. Battle of Vicksburg – Union victory. Union seized control of ...
... 13. Fort Sumter – First shots of the Civil War. Confederate in South Carolina fired on a Union fort beginning the Civil War. 14. Battle of Manassas – First major battle of the Civil War. Confederate Army defeats the Union at Bull Run. 15. Battle of Vicksburg – Union victory. Union seized control of ...
The American Civil War
... Grant was named commander of all Union forces in the Spring 1864 after several Union commanders had failed Sherman’s March to the Sea began at Atlanta in September 1864. - Ended in Savannah in December. - Carried out destructive tactics to bring the South to its knees ...
... Grant was named commander of all Union forces in the Spring 1864 after several Union commanders had failed Sherman’s March to the Sea began at Atlanta in September 1864. - Ended in Savannah in December. - Carried out destructive tactics to bring the South to its knees ...
chapter 10 vocabulary
... Well know unit east of the Mississippi River, which fought in more battles than any other cavalry unit (352) ...
... Well know unit east of the Mississippi River, which fought in more battles than any other cavalry unit (352) ...
wealth invested in industry 25% of nation`s resources
... responsible for guarding Washington, D.C. and attacking Richmond, Virginia ...
... responsible for guarding Washington, D.C. and attacking Richmond, Virginia ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide
... ROBERT E. LEE DID NOT ACCEPT COMMAND OF THE UNION TROOPS BECAUSE HIS HOME STATE WAS VIRGINIA. THE EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION DECREED FREEDOM FOR ALL ENSLAVED PEOPLE IN THE STATES AT WAR WITH THE UNION. THE INFAMOUS PRISON IN THE SOUTH WAS CALLED ANDERSONVILLE. BENJAMIN GRIERSONʼS FORCES TRAVELED 600 ...
... ROBERT E. LEE DID NOT ACCEPT COMMAND OF THE UNION TROOPS BECAUSE HIS HOME STATE WAS VIRGINIA. THE EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION DECREED FREEDOM FOR ALL ENSLAVED PEOPLE IN THE STATES AT WAR WITH THE UNION. THE INFAMOUS PRISON IN THE SOUTH WAS CALLED ANDERSONVILLE. BENJAMIN GRIERSONʼS FORCES TRAVELED 600 ...
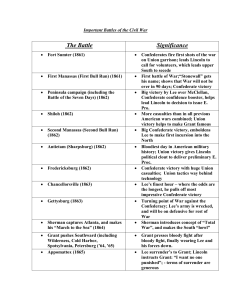
Battle
... victory helps to make Grant famous Big Confederate victory, emboldens Lee to make first incursion into the North Bloodiest day in American military history; Union victory gives Lincoln political clout to deliver preliminary E. Proc. Confederate victory with huge Union casualties; Union tactics way b ...
... victory helps to make Grant famous Big Confederate victory, emboldens Lee to make first incursion into the North Bloodiest day in American military history; Union victory gives Lincoln political clout to deliver preliminary E. Proc. Confederate victory with huge Union casualties; Union tactics way b ...
4.2 The Civil War Begins
... • The South hoped Britain would support them in the war, but Britain needed supplies of wheat and corn from the North, so they remained neutral • More and more people in the North felt slavery should be abolished; Lincoln did not feel he had the Constitutional right to end slavery where it already e ...
... • The South hoped Britain would support them in the war, but Britain needed supplies of wheat and corn from the North, so they remained neutral • More and more people in the North felt slavery should be abolished; Lincoln did not feel he had the Constitutional right to end slavery where it already e ...
Civil War Review Guide
... 3. John Brown was involved in two events leading up to the Civil War. What were those two events and what happened? Pottawatomie Massacre (Bleeding Kansas) and Harpers Ferry 4. What precedent did the Supreme Court establish regarding rights of African Americans in the Dred Scott v. Sanford case? The ...
... 3. John Brown was involved in two events leading up to the Civil War. What were those two events and what happened? Pottawatomie Massacre (Bleeding Kansas) and Harpers Ferry 4. What precedent did the Supreme Court establish regarding rights of African Americans in the Dred Scott v. Sanford case? The ...
Name - Humble ISD
... had 8. ______________________________ Confederate general that led an all out infantry charge on Union lines on the 3rd day of Gettysburg, its failure led to the end of the battle 9. _____________________________ Union general sent to attack Atlanta and march to the sea, his use of total war cut a p ...
... had 8. ______________________________ Confederate general that led an all out infantry charge on Union lines on the 3rd day of Gettysburg, its failure led to the end of the battle 9. _____________________________ Union general sent to attack Atlanta and march to the sea, his use of total war cut a p ...
The Civil War - Guided Viewing
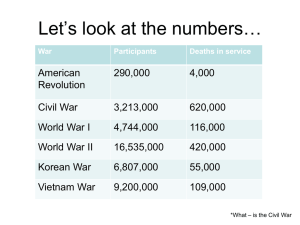
... 11. What millionaire in Memphis posted a sign calling for anyone who wanted to “go kill some Yankees?” 12. Population in the North: 13. Free population in the South: 14. The value of all the goods produced in the South at the beginning of the Civil War added up to less than ________ of the goods pro ...
... 11. What millionaire in Memphis posted a sign calling for anyone who wanted to “go kill some Yankees?” 12. Population in the North: 13. Free population in the South: 14. The value of all the goods produced in the South at the beginning of the Civil War added up to less than ________ of the goods pro ...
21 The Furnace of the Civil War
... 1. Which two states of the Southeast saw little of the major fighting of the Civil War? 2. In which four states were the slaves all freed by state action—without and federal involvement? 3. Which two states kept slavery until it was finally abolished by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution? ...
... 1. Which two states of the Southeast saw little of the major fighting of the Civil War? 2. In which four states were the slaves all freed by state action—without and federal involvement? 3. Which two states kept slavery until it was finally abolished by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution? ...
File
... strategy to attack Richmond, the Confederate capital, through a route entitled the Peninsular Campaign. In this attempt, McClellan met Lee’s army at the Second Battle of Bull Run and were re routed. McClellan then received a copy of Lee’s orders and found out that an army led by Stonewall Jackson ...
... strategy to attack Richmond, the Confederate capital, through a route entitled the Peninsular Campaign. In this attempt, McClellan met Lee’s army at the Second Battle of Bull Run and were re routed. McClellan then received a copy of Lee’s orders and found out that an army led by Stonewall Jackson ...
Major Battles of the Civil War
... arms against the Union, but it may be necessary for me to carry a musket in the defense of my native state, Virginia.” – Robert E Lee ...
... arms against the Union, but it may be necessary for me to carry a musket in the defense of my native state, Virginia.” – Robert E Lee ...
Civil War Battles and the End of the War
... has armies eat off the line, using anything it could and killing or destroying anything left. This was called Total War. After arriving in Georgia, Sherman headed to South Carolina. He called it “Total War” ...
... has armies eat off the line, using anything it could and killing or destroying anything left. This was called Total War. After arriving in Georgia, Sherman headed to South Carolina. He called it “Total War” ...
The Battles of Bull Run
... First Battle of Bull Run On July 21, 1861 General McDowell ordered the divisions of Hunter and Heintzelman (from Centreville) to march southwest on the Warrenton Turnpike and then to turn northwest to Sudley Springs while Tyler's division marched directly towards Stone Bridge. Tyler’s army blocked ...
... First Battle of Bull Run On July 21, 1861 General McDowell ordered the divisions of Hunter and Heintzelman (from Centreville) to march southwest on the Warrenton Turnpike and then to turn northwest to Sudley Springs while Tyler's division marched directly towards Stone Bridge. Tyler’s army blocked ...
The Civil War
... – Lee escaped, but cornered at Appomattox Court House – Surrendered April 9, 1865 ...
... – Lee escaped, but cornered at Appomattox Court House – Surrendered April 9, 1865 ...