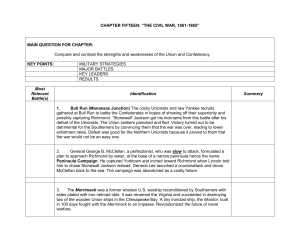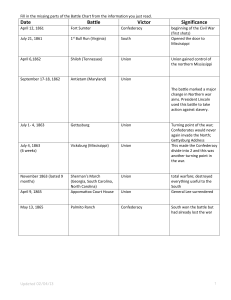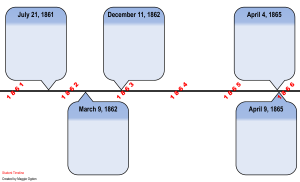
first Battle of Bull Run - Virginia and the Civil War
... December 11, 1862 General Robert E. Lee, Commander of the Army of Northern Virginia, defeated Union troops at Fredericksburg, Virginia. Lee kept Union troops from ...
... December 11, 1862 General Robert E. Lee, Commander of the Army of Northern Virginia, defeated Union troops at Fredericksburg, Virginia. Lee kept Union troops from ...
1st Bull Run- (1 Manassas) JULY 21, 1861 Battle Notes: •Both sides
... •There was no clear winner on the battlefield •Since Lee retreated back to Virginia, Antietam is considered a Union strategic victory Battle Significance ...
... •There was no clear winner on the battlefield •Since Lee retreated back to Virginia, Antietam is considered a Union strategic victory Battle Significance ...
Causes of Confederate Defeat in the Civil War
... the Civil War Contributed by Aaron Sheehan-Dean The surrender of Confederate general Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia at Appomattox Court House on April 9, 1865, effectively ended the American Civil War (1861–1865). But why did Lee surrender? And why in the spring of 1865? Historians have a ...
... the Civil War Contributed by Aaron Sheehan-Dean The surrender of Confederate general Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia at Appomattox Court House on April 9, 1865, effectively ended the American Civil War (1861–1865). But why did Lee surrender? And why in the spring of 1865? Historians have a ...
blue belly
... States from England. It was like the speeches of Martin Luther King, Jr.; it did not make any change by itself, but it was a founding point for change to come. ...
... States from England. It was like the speeches of Martin Luther King, Jr.; it did not make any change by itself, but it was a founding point for change to come. ...
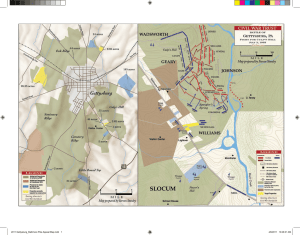
Gettysburg - Culp`s HIll - July 3, 1863 (Apr 2011)
... the Round Tops with Longstreet’s and Hill’s divisions, and then attacking the Union right at Culp’s and East Cemetery Hills with Ewell’s divisions. By evening, the Federals retained Little Round Top and had repulsed most of Ewell’s men. During the morning of July 3, the Confederate infantry were dri ...
... the Round Tops with Longstreet’s and Hill’s divisions, and then attacking the Union right at Culp’s and East Cemetery Hills with Ewell’s divisions. By evening, the Federals retained Little Round Top and had repulsed most of Ewell’s men. During the morning of July 3, the Confederate infantry were dri ...
Important People of the Civil War
... the 1st Republican President – Southern states almost immediately began to secede. Issued the Emancipation Proclamation in 1863, which freed slaves in the Confederate states that had not rejoined the Union-could not be enforced, but it did allow freed slaves to join the Union Army. He hoped to giv ...
... the 1st Republican President – Southern states almost immediately began to secede. Issued the Emancipation Proclamation in 1863, which freed slaves in the Confederate states that had not rejoined the Union-could not be enforced, but it did allow freed slaves to join the Union Army. He hoped to giv ...
Name_______________________________________DUE
... ● George McClellan commander of the Union army in the east early in the Civil War. ● Ulysses S. Grant Union general who won battles in the west. He was eventually promoted to command the Army of the Potomac. ● Battle of Shiloh bloody battle in Tennessee won by Grant. ● William Tecumseh Sherman U ...
... ● George McClellan commander of the Union army in the east early in the Civil War. ● Ulysses S. Grant Union general who won battles in the west. He was eventually promoted to command the Army of the Potomac. ● Battle of Shiloh bloody battle in Tennessee won by Grant. ● William Tecumseh Sherman U ...
Small and interesting facts about the Civil War
... Confederate, Private Abraham Lincoln of Co. F 1st VA Cavalry. He was reported as a deserter in 1864, so the North ended up with both of them. The 126th New York was the YMCA Regiment. Though more then 27,000 were casualties of the battle of Chickamauga, and 4,000 were killed, only one soldier is kno ...
... Confederate, Private Abraham Lincoln of Co. F 1st VA Cavalry. He was reported as a deserter in 1864, so the North ended up with both of them. The 126th New York was the YMCA Regiment. Though more then 27,000 were casualties of the battle of Chickamauga, and 4,000 were killed, only one soldier is kno ...
Grant - Images
... ___________ is a draft that forced men to serve in the army. She cared for the wounded and sick & eventually founded the Red Cross. In order to pay for the war in the North Congress decided to collect ________ ...
... ___________ is a draft that forced men to serve in the army. She cared for the wounded and sick & eventually founded the Red Cross. In order to pay for the war in the North Congress decided to collect ________ ...
Battles of the End of the Civil War
... 3. Label and use different colors to show the paths of the following: A) Sherman’s “March to the sea” and on through South and North Carolina B) Grant’s pursuit of Lee through Virginia ...
... 3. Label and use different colors to show the paths of the following: A) Sherman’s “March to the sea” and on through South and North Carolina B) Grant’s pursuit of Lee through Virginia ...
Vol. 1, Issue 1
... largest Confederate unit there, the 26th North Carolina Infantry, of more than 700 men. Both units suffered 80% casualties in the battle.) Four or 5 regiments (or more later in the war as the regiments suffered greater loses) made up a brigade commanded by a brigadier (1 star) general (or temporaril ...
... largest Confederate unit there, the 26th North Carolina Infantry, of more than 700 men. Both units suffered 80% casualties in the battle.) Four or 5 regiments (or more later in the war as the regiments suffered greater loses) made up a brigade commanded by a brigadier (1 star) general (or temporaril ...
Fort Sumter, in Charleston Harbor (one of the most important federal
... Ft. Sumter • April 6, 1861 – President Lincoln announces that he is re-supplying Union troops at Fort Sumter, in Charleston Harbor (one of the most important federal posts that controlled the entrance to Charleston Harbor). • Confederate leaders decided to attack Fort Sumter before the ships arrive ...
... Ft. Sumter • April 6, 1861 – President Lincoln announces that he is re-supplying Union troops at Fort Sumter, in Charleston Harbor (one of the most important federal posts that controlled the entrance to Charleston Harbor). • Confederate leaders decided to attack Fort Sumter before the ships arrive ...
The Cultural Landscape of the Colony of Virginia
... Carolina. As the North and South prepared for the bloodiest and most tragic war ever fought by American soldiers, Virginia’s men and women took sides in the fighting. ...
... Carolina. As the North and South prepared for the bloodiest and most tragic war ever fought by American soldiers, Virginia’s men and women took sides in the fighting. ...
Civil War
... 1863: Lee invades the North Fights the Army of the Potomac TURNING POINT: South would never again invade the North ...
... 1863: Lee invades the North Fights the Army of the Potomac TURNING POINT: South would never again invade the North ...
Time line power point
... Confederates attack union Federal forces almost defeated until later in the night when reinforcements arrive, finally confederated forces retreated, casualties were high on both sides. ...
... Confederates attack union Federal forces almost defeated until later in the night when reinforcements arrive, finally confederated forces retreated, casualties were high on both sides. ...
The War Continues - CEC American History
... Lee decides to invade the North again Lincoln replaces Hooker with Gen. Meade Confederate general heard of shoe supply This begins the battle of Gettysburg on July 1 -begins north of the town; end of day Union forces are pushed to some hills south of town Lee & Meade arrive for the 2nd day of battle ...
... Lee decides to invade the North again Lincoln replaces Hooker with Gen. Meade Confederate general heard of shoe supply This begins the battle of Gettysburg on July 1 -begins north of the town; end of day Union forces are pushed to some hills south of town Lee & Meade arrive for the 2nd day of battle ...
“The War Ends
... • Robert E Lee again went on the offensive. He planned to attack Pennsylvania and then Washington DC. On his way to Pennsylvania, he met a northern army at the town of Gettysburg. Even though the south made several aggressive charges, they were not able to break through the union position. The sou ...
... • Robert E Lee again went on the offensive. He planned to attack Pennsylvania and then Washington DC. On his way to Pennsylvania, he met a northern army at the town of Gettysburg. Even though the south made several aggressive charges, they were not able to break through the union position. The sou ...
William Tecumseh Sherman
... • Lee wanted to win international support, demoralize the Union, and force an end to the war. He decided to invade the North. In June 1863, his army entered Pennsylvania. Under General George Meade, Union forces met the Confederates on July 1st in Gettysburg Pennsylvania. The Battle of Gettysburg r ...
... • Lee wanted to win international support, demoralize the Union, and force an end to the war. He decided to invade the North. In June 1863, his army entered Pennsylvania. Under General George Meade, Union forces met the Confederates on July 1st in Gettysburg Pennsylvania. The Battle of Gettysburg r ...
battle of chickamauga - Flushing Community Schools
... Graduated 5 th in his class at West Point Loses his command after this battle Retired from the military in March 1867 Elected to the House of Representatives in 1880 Died in California on March 11, 1898 ...
... Graduated 5 th in his class at West Point Loses his command after this battle Retired from the military in March 1867 Elected to the House of Representatives in 1880 Died in California on March 11, 1898 ...
Name American History Period
... 12. Who led the charge as the Confederates marched slowly up toward Cemetery Ridge? ______________________________________ 13. How many men did the Confederates lose on this charge? __________________ 14. On the fourth day, Lee began to _________________ to Virginia. In all, nearly _________ Confede ...
... 12. Who led the charge as the Confederates marched slowly up toward Cemetery Ridge? ______________________________________ 13. How many men did the Confederates lose on this charge? __________________ 14. On the fourth day, Lee began to _________________ to Virginia. In all, nearly _________ Confede ...
Leaders of the Civil War
... One of the greatest generals of all time ◦ Less soldiers and supplies than the North but wins many key battles ...
... One of the greatest generals of all time ◦ Less soldiers and supplies than the North but wins many key battles ...
July 1862
... Between June 26 and July 2, Union and Confederate forces fought a series of battles: Mechanicsville (June 26-27), Gaines's Mill (June 27), Savage's Station (June 29), Frayser's Farm (June 30), and Malvern Hill (July 1). On July 2, the Confederates withdrew to Richmond, ending the Peninsular Campaign ...
... Between June 26 and July 2, Union and Confederate forces fought a series of battles: Mechanicsville (June 26-27), Gaines's Mill (June 27), Savage's Station (June 29), Frayser's Farm (June 30), and Malvern Hill (July 1). On July 2, the Confederates withdrew to Richmond, ending the Peninsular Campaign ...
The Civil War Begins
... The War for the Capitals Union forces led by McClellan headed toward Richmond, VA. After a series of battles the confederate general was wounded and command of the army passed to Robert E. Lee. Lee drove McClellan away from Richmond. ...
... The War for the Capitals Union forces led by McClellan headed toward Richmond, VA. After a series of battles the confederate general was wounded and command of the army passed to Robert E. Lee. Lee drove McClellan away from Richmond. ...