Reconstruction - 7th Grade Texas History
... Changing Role of Women • During the Civil War, women’s roles changed: – Women did more farm work – Many women served as nurses for troops – They made uniforms and other clothing for soldiers – They took jobs as teachers, shopkeepers, and drivers, usually performed by men ...
... Changing Role of Women • During the Civil War, women’s roles changed: – Women did more farm work – Many women served as nurses for troops – They made uniforms and other clothing for soldiers – They took jobs as teachers, shopkeepers, and drivers, usually performed by men ...
The Civil War – Fact Sheet
... • In two days at Shiloh on the banks of the Tennessee River, more Americans fell than in all previous American wars combined. • During the Battle of Antietam, 12,401 Union men were killed, missing or wounded; double the casualties of D-Day, 82 years later. With a total of 23,000 casualties on both s ...
... • In two days at Shiloh on the banks of the Tennessee River, more Americans fell than in all previous American wars combined. • During the Battle of Antietam, 12,401 Union men were killed, missing or wounded; double the casualties of D-Day, 82 years later. With a total of 23,000 casualties on both s ...
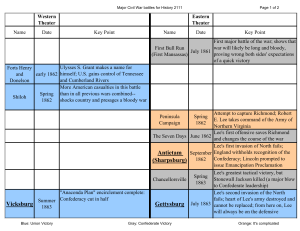
Major Battles of the Civil War
... Wilderness Campaign • Union army relies on manpower and industry to win • Confederates on the defensive – They don’t have the troops or weapons to replace their losses – Forced to rely on trenches and terrain to make up for their smaller army ...
... Wilderness Campaign • Union army relies on manpower and industry to win • Confederates on the defensive – They don’t have the troops or weapons to replace their losses – Forced to rely on trenches and terrain to make up for their smaller army ...
Civil War Timeline
... • The Rebel siege of Chattanooga ends as Union forces under Grant defeat the siege army of Gen. Braxton Bragg. During the battle, one of the most dramatic moments of the war occurs. Yelling "Chickamauga! Chickamauga!" Union troops avenge their previous defeat at Chickamauga by storming up the face o ...
... • The Rebel siege of Chattanooga ends as Union forces under Grant defeat the siege army of Gen. Braxton Bragg. During the battle, one of the most dramatic moments of the war occurs. Yelling "Chickamauga! Chickamauga!" Union troops avenge their previous defeat at Chickamauga by storming up the face o ...
Exploring the Americas
... Seymour landed troops in Jacksonville that were to be used to march on Tallahassee, but were stopped in Baker County by Joseph Finnegan. Confederate forces did not pursue the retreating Union army due to the heroism of the 54th Massachusetts and the 35th US Colored regiments. Was the largest Civil W ...
... Seymour landed troops in Jacksonville that were to be used to march on Tallahassee, but were stopped in Baker County by Joseph Finnegan. Confederate forces did not pursue the retreating Union army due to the heroism of the 54th Massachusetts and the 35th US Colored regiments. Was the largest Civil W ...
Chapter 11 Section 1
... First Battle of Bull Run • 1st major battle of the Civil War • 35,000 soldiers involved • 2,900 union casualties • Confederates suffered fewer than 2,000 casualties • Confederate victory ...
... First Battle of Bull Run • 1st major battle of the Civil War • 35,000 soldiers involved • 2,900 union casualties • Confederates suffered fewer than 2,000 casualties • Confederate victory ...
Civil War Study Guide KEY
... Chickamauga, but failed to finish them off. Union general Grant returned with more troops and drove Bragg and his troops further south into Georgia. Pierre Beauregard – Confederate general from South Carolina who ordered the rebels to fire on Ft. Sumter, thus starting the Civil War. Battles To Know: ...
... Chickamauga, but failed to finish them off. Union general Grant returned with more troops and drove Bragg and his troops further south into Georgia. Pierre Beauregard – Confederate general from South Carolina who ordered the rebels to fire on Ft. Sumter, thus starting the Civil War. Battles To Know: ...
Civil War Timeline - York Region District School Board
... South Carolina feared a trick in Lincoln’s plan Robert Anderson was asked to surrender Anderson’s sets up a proposition to surrender only after his supplies have run out Proposition is rejected Shots were fired on the Fort Civil War began on April 12 Fort Sumter was surrendered to South Carolina ...
... South Carolina feared a trick in Lincoln’s plan Robert Anderson was asked to surrender Anderson’s sets up a proposition to surrender only after his supplies have run out Proposition is rejected Shots were fired on the Fort Civil War began on April 12 Fort Sumter was surrendered to South Carolina ...
The Battle of Shiloh
... • His Army attacked on April 6, near Shiloh Church. He was successful, at first, in pushing Gen. William T. Sherman’s men back to an area called the Crossroads. • The Hornet’s Nest, just north of this point, saw the bloodiest fighting. ...
... • His Army attacked on April 6, near Shiloh Church. He was successful, at first, in pushing Gen. William T. Sherman’s men back to an area called the Crossroads. • The Hornet’s Nest, just north of this point, saw the bloodiest fighting. ...
Chapter 12 Key Terms – Road to Civil War
... 21. Battle of Bull Run: ________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ 22. Battle of Shiloh: __________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ 23. Battle of Antietam: ________________ ________________________________ ____________ ...
... 21. Battle of Bull Run: ________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ 22. Battle of Shiloh: __________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ 23. Battle of Antietam: ________________ ________________________________ ____________ ...
Unit 3 A Nation Divided Chapter 10 Section 3 The Civil War 1861
... The Mississippi River could no longer be a ____supply route___for the South. However, the North could not use the river safely either. The Union needed to capture ___________________________________ to be in control of the entire river. After six weeks, Union forces under General Grant won at ______ ...
... The Mississippi River could no longer be a ____supply route___for the South. However, the North could not use the river safely either. The Union needed to capture ___________________________________ to be in control of the entire river. After six weeks, Union forces under General Grant won at ______ ...
THE CIVIL WAR 05_06 Pt I
... the Civil War •Insisted that the Union be held together, by force if necessary. ...
... the Civil War •Insisted that the Union be held together, by force if necessary. ...
CIVIL WAR UNIT STUDY GUIDE
... Gettysburg: turning point of the war, the North gained victory and began to win the Civil War The Atlanta Campaign: Vital industrial and railway supply center in the south. The Union was able to cut supply routes to Confederate troops. Sherman’s March to the Sea: After capturing Atlanta, William T. ...
... Gettysburg: turning point of the war, the North gained victory and began to win the Civil War The Atlanta Campaign: Vital industrial and railway supply center in the south. The Union was able to cut supply routes to Confederate troops. Sherman’s March to the Sea: After capturing Atlanta, William T. ...
The Furnace of Civil War
... Confederate unit and hey expected one big battle and a quick victory for the war • However, after initial success by the Union, Confederate reinforcements arrived and, coupled with Stonewall Jackson’s line holding, sent the Union soldiers into disarray • The Battle of Bull Run showed the North that ...
... Confederate unit and hey expected one big battle and a quick victory for the war • However, after initial success by the Union, Confederate reinforcements arrived and, coupled with Stonewall Jackson’s line holding, sent the Union soldiers into disarray • The Battle of Bull Run showed the North that ...
The Union Wins Reading and Questions
... military division of the Mississippi. These two appointments would change the course of the war. Old friends and comrades in arms, both men believed in waging total war. They reasoned that it was the strength of the people’s will that was keeping the war going. If the Union could destroy the Souther ...
... military division of the Mississippi. These two appointments would change the course of the war. Old friends and comrades in arms, both men believed in waging total war. They reasoned that it was the strength of the people’s will that was keeping the war going. If the Union could destroy the Souther ...
Chapter 11-4: The War Continues
... – Cherokee leader Stand Watie was the last Confederate general to surrender at war’s end. ...
... – Cherokee leader Stand Watie was the last Confederate general to surrender at war’s end. ...
Chapter Seventeen Structured Notes
... position and blockading or bombarding it order to force them to surrender The Union won the victory at Vicksburg and Gettysburg The Confederacy suffered heavy losses at the Battle of Gettysburg The last Confederacy charge against the Union was at Pickett’s Charge President gave his Gettysbur ...
... position and blockading or bombarding it order to force them to surrender The Union won the victory at Vicksburg and Gettysburg The Confederacy suffered heavy losses at the Battle of Gettysburg The last Confederacy charge against the Union was at Pickett’s Charge President gave his Gettysbur ...
Powerpoint 24
... War in the Eastern States While the two sides fought for control of the Tennessee and the Mississippi River, The Union was trying to capture the Confederate capital at Richmond Virginia, close to the Union. Why would each side want control of the Mississippi River? What did it have to offer? (Turn ...
... War in the Eastern States While the two sides fought for control of the Tennessee and the Mississippi River, The Union was trying to capture the Confederate capital at Richmond Virginia, close to the Union. Why would each side want control of the Mississippi River? What did it have to offer? (Turn ...
Civil War Battles - United States History
... Sherman was determined to cut the heart out of the Southerners’ support for the Confederacy. As Sherman’s troops marched, they set fire to the land and destroyed all that they came across (after taking what they could). – 60 mile-wide path of destruction ...
... Sherman was determined to cut the heart out of the Southerners’ support for the Confederacy. As Sherman’s troops marched, they set fire to the land and destroyed all that they came across (after taking what they could). – 60 mile-wide path of destruction ...
Chapter 15-5 Notes: Decisive Battles
... o July 1 – 3, about 75,000 Confederates battled about 85,000 Union soldiers Union army held Cemetery Ridge; Confederates on Seminary Ridge attacked the ends of the Union lines July 3rd, Lee attacked the center of the Union line, led by General George Pickett and 15,000 Confederates through about ...
... o July 1 – 3, about 75,000 Confederates battled about 85,000 Union soldiers Union army held Cemetery Ridge; Confederates on Seminary Ridge attacked the ends of the Union lines July 3rd, Lee attacked the center of the Union line, led by General George Pickett and 15,000 Confederates through about ...
The Civil War
... The North and South started a bloody Civil War The North and South fought in the most important battle in Gettysburg. The purpose was that the North and South disagreed that slaves should be allowed in new territories and states. ...
... The North and South started a bloody Civil War The North and South fought in the most important battle in Gettysburg. The purpose was that the North and South disagreed that slaves should be allowed in new territories and states. ...
What was NC`s role in the Civil War efforts?
... a rich man's war but a fight in his place and therefore not have to fight poor man's fight"? South - people who owned 20+ slaves were not required to join. Many slaves joined their owners to fight or take care of their masters. Both- Men btwn 17-50 were conscripted ...
... a rich man's war but a fight in his place and therefore not have to fight poor man's fight"? South - people who owned 20+ slaves were not required to join. Many slaves joined their owners to fight or take care of their masters. Both- Men btwn 17-50 were conscripted ...