Another look at chemical reactions HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WATER
... Atomic terms - ATOMIC NUMBER: The number of protons in the atomic nucleus. Each ELEMENT has the SAME NUMBER OF PROTONS in every nucleus. In neutral atoms, the number of ELECTRONS is also equal to the atomic number. Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its ...
... Atomic terms - ATOMIC NUMBER: The number of protons in the atomic nucleus. Each ELEMENT has the SAME NUMBER OF PROTONS in every nucleus. In neutral atoms, the number of ELECTRONS is also equal to the atomic number. Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its ...
Periodic Table ppt
... The number of Protons in atom is also the Atomic number, so therefore the Atomic number also represents the amount of Protons in the nucleus of that Atom. ...
... The number of Protons in atom is also the Atomic number, so therefore the Atomic number also represents the amount of Protons in the nucleus of that Atom. ...
Elements02
... In 1781 Antoine Lavoisier explained how to tell elements from non-elements and over the next 30 years many new elements were discovered by scientists such as Englishman John Dalton. Dalton is also famous for his 1808 theory, which explained why elements differ from each other and non-elements. His t ...
... In 1781 Antoine Lavoisier explained how to tell elements from non-elements and over the next 30 years many new elements were discovered by scientists such as Englishman John Dalton. Dalton is also famous for his 1808 theory, which explained why elements differ from each other and non-elements. His t ...
Modern Atomic Theory - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... •All elements are composed of atoms. •All atoms of the same element are identical – in particular they have the same mass. •The atoms of one kind of element are different from the atoms of all other elements - in particular the atoms of one element have a different mass than those of other elements. ...
... •All elements are composed of atoms. •All atoms of the same element are identical – in particular they have the same mass. •The atoms of one kind of element are different from the atoms of all other elements - in particular the atoms of one element have a different mass than those of other elements. ...
History of Atomic Theory • Democritus: Atom meaning “unable to
... different elements are different. o Atoms join together with other atoms to make new substances. JJ Thomson: “Plum pudding” Model (1897) o Discovered the electron. Rutherford: “Gold foil” experiment (1911) o Atom has a positive center (nucleus). o Atoms are made up of mostly empty space. Niels ...
... different elements are different. o Atoms join together with other atoms to make new substances. JJ Thomson: “Plum pudding” Model (1897) o Discovered the electron. Rutherford: “Gold foil” experiment (1911) o Atom has a positive center (nucleus). o Atoms are made up of mostly empty space. Niels ...
Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... produces smaller and smaller groups of atoms, until you come to a single gold atom. Dividing that atom into two parts produces fragments that no longer have the properties of gold. ...
... produces smaller and smaller groups of atoms, until you come to a single gold atom. Dividing that atom into two parts produces fragments that no longer have the properties of gold. ...
Integrated Science 3
... 19. What is true about the element immediately below the element that has an atomic number 17 in the periodic table. a) 17 electrons in its outer most level c) 17 protons in nucleus b) 7 electrons in its outermost level d) 7 protons in its nucleus 20. Two atoms that are isotopes have the same number ...
... 19. What is true about the element immediately below the element that has an atomic number 17 in the periodic table. a) 17 electrons in its outer most level c) 17 protons in nucleus b) 7 electrons in its outermost level d) 7 protons in its nucleus 20. Two atoms that are isotopes have the same number ...
Atomic Structure Notes Atoms
... Electron cloud or energy rings -Atoms are made of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, & electrons ...
... Electron cloud or energy rings -Atoms are made of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, & electrons ...
Nickel 28 Ni 58.693
... Matter can be broken down into its simple parts called __________. Each element on the periodic table has its own ___________. How many elements can be found naturally? ...
... Matter can be broken down into its simple parts called __________. Each element on the periodic table has its own ___________. How many elements can be found naturally? ...
Isotope Worksheet
... atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, ! ...
... atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, ! ...
Isotope Worksheet
... In other words, isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Since any atom having 9 protons (Z = 9) must be an atom of fluorine, we can omit the Z-value and just use the symbol F for many purposes, i.e., we can write 19F instead of 19F. ...
... In other words, isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Since any atom having 9 protons (Z = 9) must be an atom of fluorine, we can omit the Z-value and just use the symbol F for many purposes, i.e., we can write 19F instead of 19F. ...
Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonding
... eight electrons in their outer energy level or, in the case of elements 1-5, two in their outer shell level. ...
... eight electrons in their outer energy level or, in the case of elements 1-5, two in their outer shell level. ...
Atomic Structure
... a proton, but unlike the proton, has no charge. k. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons (hence …different mass numbers) l. This part of the atom houses protons and neutrons. ...
... a proton, but unlike the proton, has no charge. k. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons (hence …different mass numbers) l. This part of the atom houses protons and neutrons. ...
IPS Unit 2 Worksheet Packet
... ____ 11. An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which scientists can predict where an electron is likely to be found. ____ 12. An atom is made of positively charged, pudding like material through which negatively charged particles are scattered. ____ 13. In a ...
... ____ 11. An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which scientists can predict where an electron is likely to be found. ____ 12. An atom is made of positively charged, pudding like material through which negatively charged particles are scattered. ____ 13. In a ...
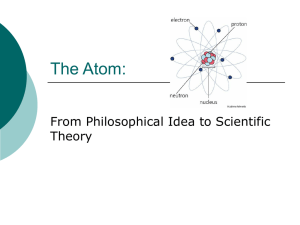
HISTORY OF THE ATOM AND ATOMIC THEORY
... through the foil, a few would be slightly deflected. – most went through, but some were deflected by a large amount – this indicated there was a positive charge in the center of the atom, and the center was small compared to the size of the atom ...
... through the foil, a few would be slightly deflected. – most went through, but some were deflected by a large amount – this indicated there was a positive charge in the center of the atom, and the center was small compared to the size of the atom ...
CS 211 – Spring 2017 Lab 4: Molar Mass
... Also note on rows 6-10, the Element is BLANK, and so the Atomic Weight and Subtotals are EMPTY. When the user selects another atom in A6-10, Columns C and D should be populated. The second example is for Ethanol (C2H6O). ...
... Also note on rows 6-10, the Element is BLANK, and so the Atomic Weight and Subtotals are EMPTY. When the user selects another atom in A6-10, Columns C and D should be populated. The second example is for Ethanol (C2H6O). ...
2.9 Use the helium-4 isotope to define atomic number and mass
... 2.34 Give two examples of each of the following: (a) a diatomic molecule containing atoms of the same element, (b) a diatomic molecule containing atoms of different elements, (c) polyatomic molecule containing atoms of the same element, (d) a polyatomic molecule containing atoms of different element ...
... 2.34 Give two examples of each of the following: (a) a diatomic molecule containing atoms of the same element, (b) a diatomic molecule containing atoms of different elements, (c) polyatomic molecule containing atoms of the same element, (d) a polyatomic molecule containing atoms of different element ...
Elements, Isotopes and Ions
... 2. 1 Calcium atom has 22 neutrons and another Calcium atom has 24 neutrons. Why are these both Calcium atoms even though they have a different # of neutrons? ...
... 2. 1 Calcium atom has 22 neutrons and another Calcium atom has 24 neutrons. Why are these both Calcium atoms even though they have a different # of neutrons? ...
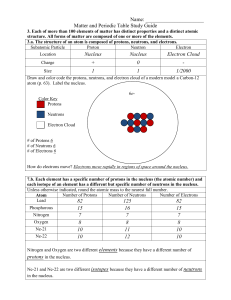
Matter and the Periodic Table Study Guide Answer Key
... 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound List the number of each type of atom making up the compound NH4 1 Nit ...
... 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound List the number of each type of atom making up the compound NH4 1 Nit ...
the # protons is not equal to the # neutrons
... number of valence electrons. The difference is in how stable the nucleus is. The general rule is that the isotope will be radioactive if the # protons is not equal to the # neutrons. ...
... number of valence electrons. The difference is in how stable the nucleus is. The general rule is that the isotope will be radioactive if the # protons is not equal to the # neutrons. ...
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
The Atom - Williamstown Independent Schools
... are composed of the same two elements then ratios of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... are composed of the same two elements then ratios of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. ...