Chapter 2 Early philosophy of Matter Revolution
... approach to understanding was established • Over the next 150+ years Aristotle view of matter could not easily explain the observation being made ...
... approach to understanding was established • Over the next 150+ years Aristotle view of matter could not easily explain the observation being made ...
Notes on Atomic Structure Structure of Atoms Atoms are composed
... The periodic table is a list of the elements that make up matter. It is organized by increasing atomic number. The Atomic Number shows the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It identifies the type of atom/element. The atomic number also equals the number of electrons whenever the atom is n ...
... The periodic table is a list of the elements that make up matter. It is organized by increasing atomic number. The Atomic Number shows the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It identifies the type of atom/element. The atomic number also equals the number of electrons whenever the atom is n ...
Unit 2 Notes - School City of Hobart
... Nuclear reactions involve changes in atomic nuclei to generate energy. Nuclear Chemistry is the study of those reactions, with an emphasis on their uses in chemistry and their effects on biological systems 21.1 Radioactivity • Nucleon is simply another name for particles in the nucleus (proton/neutr ...
... Nuclear reactions involve changes in atomic nuclei to generate energy. Nuclear Chemistry is the study of those reactions, with an emphasis on their uses in chemistry and their effects on biological systems 21.1 Radioactivity • Nucleon is simply another name for particles in the nucleus (proton/neutr ...
Early Models of the Atom
... “Raison bun model” (plum pudding model) of the atom – positive charges all around (the bun) and negative pieces inside (the raisons) – everything was floating around in one big ball Analyzed uranium to see Becquerel rays Uranium was the source of the emission – later Marie gave these emissions the n ...
... “Raison bun model” (plum pudding model) of the atom – positive charges all around (the bun) and negative pieces inside (the raisons) – everything was floating around in one big ball Analyzed uranium to see Becquerel rays Uranium was the source of the emission – later Marie gave these emissions the n ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest particle of an element. Atomic number - The number of protons in the nucleus of an element Atomic mass – The average mass of one atom of an element Proton – A small positively particle in the nucleus Neutron – a small particle in the nucleu ...
... Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest particle of an element. Atomic number - The number of protons in the nucleus of an element Atomic mass – The average mass of one atom of an element Proton – A small positively particle in the nucleus Neutron – a small particle in the nucleu ...
Unit 10 Test Review
... b. movement of electrons from higher energy states to lower energy states. c. movement of electrons from lower energy states to higher energy states. d. movement of electrons as they fall into the nucleus. 11. How many neutrons are contained in an atom of strontium-88? 12. Which of the following rep ...
... b. movement of electrons from higher energy states to lower energy states. c. movement of electrons from lower energy states to higher energy states. d. movement of electrons as they fall into the nucleus. 11. How many neutrons are contained in an atom of strontium-88? 12. Which of the following rep ...
Chapter 3 - CCRI Faculty Web
... •Mass Number – The number of protons + the number of neutrons in an atom. For example: An atom with 5 protons and 7 neutrons •Mass # = 5p+ + 7n0 = 12 •This number is not unique for each element. All but one element have atoms with different numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers. ...
... •Mass Number – The number of protons + the number of neutrons in an atom. For example: An atom with 5 protons and 7 neutrons •Mass # = 5p+ + 7n0 = 12 •This number is not unique for each element. All but one element have atoms with different numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers. ...
Atoms and Atomic Structure
... – Evidenced by line spectra (figs 3.11 and 3.12) – Transition between ground and excited states…energy considerations ...
... – Evidenced by line spectra (figs 3.11 and 3.12) – Transition between ground and excited states…energy considerations ...
Note-taking Strategy Your notes should contain a title with
... Summary: The idea of the atom was proposed over 2500 years ago. Democritus taught that the atom was the tiniest particle of matter. He thought of it as a tiny, indivisible, indestructible particle. However, his ideas were not based on any scientific experimenting. 2000 years later in England, John ...
... Summary: The idea of the atom was proposed over 2500 years ago. Democritus taught that the atom was the tiniest particle of matter. He thought of it as a tiny, indivisible, indestructible particle. However, his ideas were not based on any scientific experimenting. 2000 years later in England, John ...
Concepts of Physical Science
... and neutrons 6. A substance with a pH more than 7 that turns litmus paper blue 7. a chemical bond in which atoms are held together by their mutual attraction for two electrons they share 8. Atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons and therefore, different masses 9. An ato ...
... and neutrons 6. A substance with a pH more than 7 that turns litmus paper blue 7. a chemical bond in which atoms are held together by their mutual attraction for two electrons they share 8. Atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons and therefore, different masses 9. An ato ...
ps-5-1-and-5-2-ws
... Introduction to Atoms 5.1 & 5.2 1. What three particles are found in an atom? 2. Which two particles are found in an atom’s nucleus? 3. Explain why scientists use models to study atoms. ...
... Introduction to Atoms 5.1 & 5.2 1. What three particles are found in an atom? 2. Which two particles are found in an atom’s nucleus? 3. Explain why scientists use models to study atoms. ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
Lecture 2
... An element is defined its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more ...
... An element is defined its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more ...
Chemistry Midterm Exam 2015 (Study Guide) Unit 1: Measurement
... b. Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons d. F, 19 protons, 19 electrons ...
... b. Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons d. F, 19 protons, 19 electrons ...
Comprehensive Science 3 Module 4 Practice Test
... Different elements are made up of different atoms Atoms of different elements combine to make different compounds 5. The elements listed at the far right side of the periodic table are _______. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Transitional Metals ...
... Different elements are made up of different atoms Atoms of different elements combine to make different compounds 5. The elements listed at the far right side of the periodic table are _______. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Transitional Metals ...
Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom An atom is the smallest particle of an
... __________; in particular, they all have the same _________. 3. Atoms of different elements are ____________; in particular, they have different masses. 4. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements in the compound are j ...
... __________; in particular, they all have the same _________. 3. Atoms of different elements are ____________; in particular, they have different masses. 4. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements in the compound are j ...
The Atomic Theory of Matter
... other properties. Atoms of one element are different from that of another element. • Atoms are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither changed nor destroyed during chemical reactions. ...
... other properties. Atoms of one element are different from that of another element. • Atoms are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither changed nor destroyed during chemical reactions. ...
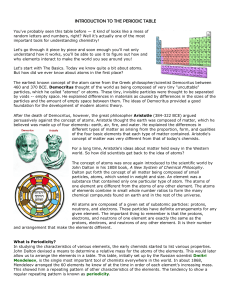
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
... of the element. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom may also be changed to create various isotopes of an element (some more stable than others). But add or subtract even one proton from an atom of any element and you no longer have the original element in any form. Now you have a differ ...
... of the element. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom may also be changed to create various isotopes of an element (some more stable than others). But add or subtract even one proton from an atom of any element and you no longer have the original element in any form. Now you have a differ ...