* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HISTORY OF THE ATOM AND ATOMIC THEORY
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
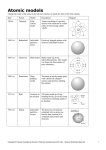
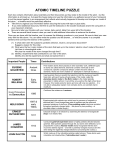
HISTORY OF THE ATOM AND ATOMIC THEORY ATOMS • The smallest part of an element that retains the properties of that element DEMOCRITUS • Greek philosopher • Came up with the word “atom” • Thought atoms were indivisible (couldn’t be broken down any further) JOHN DALTON • All atoms of an element are exactly alike. • Atoms of different elements combine to form compounds. • Law of Definite Proportions - those compounds always contain elements in the exact same proportions –Ex.; water is always H2O JJ Thomson • Discovered atoms were NOT indivisible… they could be divided into smaller parts • Discovered electrons – negatively charged particles within the atom • Plum-Pudding Model – said the electrons were spread throughout the atom ERNEST RUTHERFORD • Gold foil experiment – helped revise Thomson’s Plum-Pudding model – positively charged particles aimed at a thin sheet of gold foil. – thought most particles would travel straight through the foil, a few would be slightly deflected. – most went through, but some were deflected by a large amount – this indicated there was a positive charge in the center of the atom, and the center was small compared to the size of the atom GOLD-FOIL EXPERIMENT RUTHERFORD’S MODEL OF THE ATOM • Nucleus – center of the atom containing protons (positively charged) and neutrons (no charge) • Electrons – negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus NIELS BOHR • Suggested electrons are in certain energy levels surrounding the nucleus and they gain energy to move to higher levels or lose energy to move to lower levels MODERN ATOMIC THEORY • Nucleus of an atom is small, dense & in the center with protons and neutrons. • Electrons don’t occupy energy levels • Electrons behave more like waves than particles • It’s impossible to pinpoint the exact location of an electron • Orbital – region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be