Chapter 5 “Atomic Structure and the Periodic table”
... 2)Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3)Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4)In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed ...
... 2)Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3)Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4)In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... 2. Democritus and Aristotle, around 420 B.C. suggested that matter could be broken down into smaller and smaller components. 3. They coined the term “atoms”, which is Greek for “indivisible”. 4. Atoms were considered tiny particles that could not be seen. B. Quantitative Studies 1. Law of Conservati ...
... 2. Democritus and Aristotle, around 420 B.C. suggested that matter could be broken down into smaller and smaller components. 3. They coined the term “atoms”, which is Greek for “indivisible”. 4. Atoms were considered tiny particles that could not be seen. B. Quantitative Studies 1. Law of Conservati ...
Models Atoms - Hardy Science
... Models Atoms Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. ___ The positively charged particle in an atom’s nucleus is the ...
... Models Atoms Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. ___ The positively charged particle in an atom’s nucleus is the ...
AM-1 Power point - Moline High School
... • John Dalton in 1808 1. Atoms can not be divided 2. All atoms of a given element were exactly the same 3. Atoms of different elements could join to form compounds ...
... • John Dalton in 1808 1. Atoms can not be divided 2. All atoms of a given element were exactly the same 3. Atoms of different elements could join to form compounds ...
Matter and Atoms - davis.k12.ut.us
... element is made up of one kind of atom. Atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still have the properties of that element. Molecule is two or more atoms put together that still have the properties of a particular substance. ...
... element is made up of one kind of atom. Atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still have the properties of that element. Molecule is two or more atoms put together that still have the properties of a particular substance. ...
Chapter 4: Atomic Structure
... the region the nucleus. (a tiny central core of an atom and is composed of protons and neutrons) Rutherford’s atomic model is known as the nuclear atom. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all of ...
... the region the nucleus. (a tiny central core of an atom and is composed of protons and neutrons) Rutherford’s atomic model is known as the nuclear atom. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all of ...
Answers
... (c) Lithium would float on water, [1] producing gas steadily. [1] (d) Potassium would melt to a silvery ball [1] which moves about very quickly on the water surface, [1] producing a hissing sound, [1] burning spontaneously with a lilac flame [1] before finally disappearing completely. [1] (e) It wou ...
... (c) Lithium would float on water, [1] producing gas steadily. [1] (d) Potassium would melt to a silvery ball [1] which moves about very quickly on the water surface, [1] producing a hissing sound, [1] burning spontaneously with a lilac flame [1] before finally disappearing completely. [1] (e) It wou ...
BillNyeAtoms
... What is all matter in the universe made of? _________________ What does the word ‘atom’ mean? _________________________ Which particles in an atom are ‘heavy’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Which particles in an atom are ‘ ...
... What is all matter in the universe made of? _________________ What does the word ‘atom’ mean? _________________________ Which particles in an atom are ‘heavy’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Which particles in an atom are ‘ ...
Practice Test #2 - smhs
... The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to be 16.00% abundant, what is the percent abundance of the heaviest isotope? The average atomic mass ...
... The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to be 16.00% abundant, what is the percent abundance of the heaviest isotope? The average atomic mass ...
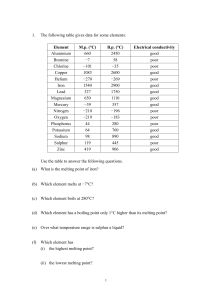
What does an elements atomic # tell us about the element?
... Smallest part of a compound that still has all the properties of that compound Compound can have properties entirely unlike the elements of which it is made ...
... Smallest part of a compound that still has all the properties of that compound Compound can have properties entirely unlike the elements of which it is made ...
Power point on the Periodic Table
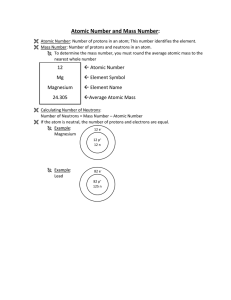
... Number of protons is equal to number of electrons Number of protons that an atom of any element has is called the atomic number The sum of the protons and neutrons is called the mass number Protons and neutrons make up nearly all the mass of an atom ...
... Number of protons is equal to number of electrons Number of protons that an atom of any element has is called the atomic number The sum of the protons and neutrons is called the mass number Protons and neutrons make up nearly all the mass of an atom ...
The four elements: fire, water, wind, and earth.
... •ATOM: smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical identity of the element ...
... •ATOM: smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical identity of the element ...
Document
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
The Nature of Molecules
... • Diagram of typical atomic structure: • Atomic #/mass of: H, He, C, O, N, S, P, Ne ...
... • Diagram of typical atomic structure: • Atomic #/mass of: H, He, C, O, N, S, P, Ne ...
Matter
... • I can recognize that there are more than 100 different elements that make up all living and nonliving things. • I can identify atoms as the simplest form of each element and the building blocks of all matter. ...
... • I can recognize that there are more than 100 different elements that make up all living and nonliving things. • I can identify atoms as the simplest form of each element and the building blocks of all matter. ...
2.2 Periodic Trends
... What are the trends that occur in the periodic table by organizing elements by their atomic number? Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic t ...
... What are the trends that occur in the periodic table by organizing elements by their atomic number? Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic t ...
Name Period _____ Chemistry Review
... ____ 14. A(n) pure substance is made of only one kind of matter and has definite properties. _________________________ ____ 15. A substance that undergoes a chemical change is still the same substance after the change. _________________________ ____ 16. A(n) mixture is made of two or more substances ...
... ____ 14. A(n) pure substance is made of only one kind of matter and has definite properties. _________________________ ____ 15. A substance that undergoes a chemical change is still the same substance after the change. _________________________ ____ 16. A(n) mixture is made of two or more substances ...
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure
... • Democritus (460-400B.C.) first suggested the existence of these particles, which he called “atoms” for the Greek word for “uncuttable”. They lacked experimental support due to the lack of scientific testing at the time. • John Dalton (1766-1844) performed experiments to study the ratios in which e ...
... • Democritus (460-400B.C.) first suggested the existence of these particles, which he called “atoms” for the Greek word for “uncuttable”. They lacked experimental support due to the lack of scientific testing at the time. • John Dalton (1766-1844) performed experiments to study the ratios in which e ...
Chapter 3 study guide answers
... Oxygen can combine with carbon to form two compounds, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The ratio of the masses of oxygen that combine with a given mass of carbon is 1:2. This is an example of ...
... Oxygen can combine with carbon to form two compounds, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The ratio of the masses of oxygen that combine with a given mass of carbon is 1:2. This is an example of ...
study guide - atomic srtucture/_classification of matter
... Nuclear symbol: Show the element’s symbol, the atomic mass & the atomic number. Mass goes on the top left of the symbol, number goes on the bottom left of the symbol. mass#atomic number X Bohr Model: Shows number of electrons in each energy level around the nucleus. Mixtures vs. Substances ...
... Nuclear symbol: Show the element’s symbol, the atomic mass & the atomic number. Mass goes on the top left of the symbol, number goes on the bottom left of the symbol. mass#atomic number X Bohr Model: Shows number of electrons in each energy level around the nucleus. Mixtures vs. Substances ...