MrsB-Chemistry
... B. A scientist thought that matter could not be divided into smaller pieces because chemical reactions only combine elements. They don’t cause elements to change into other elements. C. Alpha particles were used like bullets, and small, positively charged particles shot out from the center of the at ...
... B. A scientist thought that matter could not be divided into smaller pieces because chemical reactions only combine elements. They don’t cause elements to change into other elements. C. Alpha particles were used like bullets, and small, positively charged particles shot out from the center of the at ...
Isotopes, Ions Worksheet
... 20. a) Do different atoms of the same element have different half-life (t ½ )? NO Different atoms of the same element have the SAME half-life. b) Do different isotopes have different half-lifes (t ½ )? YES Different isotopes have a different neutron number which results in different half-life 21. Li ...
... 20. a) Do different atoms of the same element have different half-life (t ½ )? NO Different atoms of the same element have the SAME half-life. b) Do different isotopes have different half-lifes (t ½ )? YES Different isotopes have a different neutron number which results in different half-life 21. Li ...
2-1 Chemistry of life
... When we total the monetary value of the elements in our bodies and the value of the average person's skin, we arrive at a net worth of $4.50 Our most valuable asset is our skin. The method the Imperial State Institute for Nutrition at Tokyo developed for measuring the amount of a person's skin is to ...
... When we total the monetary value of the elements in our bodies and the value of the average person's skin, we arrive at a net worth of $4.50 Our most valuable asset is our skin. The method the Imperial State Institute for Nutrition at Tokyo developed for measuring the amount of a person's skin is to ...
File - Mr. Gittermann
... • The number of protons in a nucleus; all atoms of any given element have the same atomic number; because an uncharged atom has the same number of protons and electrons, typically the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number ...
... • The number of protons in a nucleus; all atoms of any given element have the same atomic number; because an uncharged atom has the same number of protons and electrons, typically the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number ...
Atoms pg. 102
... Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons. Isotopes are identified by its mass. ...
... Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons. Isotopes are identified by its mass. ...
Classifying Matter
... neutrons. The electrons are always found whizzing around the center in areas called shells or orbitals. Electrons have a negative charge and protons have a positive charge whereas neutrons have no charge. They are neutral. Due to the presence of equal number of negative electrons and positive proton ...
... neutrons. The electrons are always found whizzing around the center in areas called shells or orbitals. Electrons have a negative charge and protons have a positive charge whereas neutrons have no charge. They are neutral. Due to the presence of equal number of negative electrons and positive proton ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions - GW
... • An ion composed of two or more elementsbehaves as a unit with a set positive or negative charge ...
... • An ion composed of two or more elementsbehaves as a unit with a set positive or negative charge ...
atomic structure (see second part of ppt)
... nucleus could only be located in specific paths called orbitals. This was supported by the line spectra of atoms His model is called the planetary model ...
... nucleus could only be located in specific paths called orbitals. This was supported by the line spectra of atoms His model is called the planetary model ...
Protons neutrons electrons Charge Positive neutral negative Mass
... • Small tiny sphere = atom • Atoms of the same element are all alike • Atoms of different elements are different from each other • Atoms of different elements can combine to form compounds • Billiard ball model ...
... • Small tiny sphere = atom • Atoms of the same element are all alike • Atoms of different elements are different from each other • Atoms of different elements can combine to form compounds • Billiard ball model ...
Ch. 5 Outline Notes
... a. Hypothesized _________________ using experiments B. __________________ Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of ________________ 2. Atoms are _______________________ and cannot be __________________ into smaller particles (later proved _______________) 3. All atoms of one element are exactly ______ ...
... a. Hypothesized _________________ using experiments B. __________________ Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of ________________ 2. Atoms are _______________________ and cannot be __________________ into smaller particles (later proved _______________) 3. All atoms of one element are exactly ______ ...
Chemistry Exam Review
... around the nucleus. • Elements in the 1st column all have 1 electron in their outer (valence) orbit. ...
... around the nucleus. • Elements in the 1st column all have 1 electron in their outer (valence) orbit. ...
Pre-AP Chemistry
... Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. (1e) Students know some naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioa ...
... Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. (1e) Students know some naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioa ...
C1.1 The fundamental ideas in chemistry
... formed from metals and non-metals consist of ions. Compounds formed from nonmetals consist of molecules. In molecules the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. Further details of the types of bonding are not required. Candidates should know that metals lose electrons to form positive ions, wher ...
... formed from metals and non-metals consist of ions. Compounds formed from nonmetals consist of molecules. In molecules the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. Further details of the types of bonding are not required. Candidates should know that metals lose electrons to form positive ions, wher ...
Atom Building blocks of matter Proton Sub
... Sub-atomic particle with positive (+) charge; located in nucleus of atom; determines identity of element ...
... Sub-atomic particle with positive (+) charge; located in nucleus of atom; determines identity of element ...
PS.Ch6.Test.95
... 2 Atoms and Elements P R A C T I C E 1. Certain properties are characteristic of metals. Which property means that you can pound the ...
... 2 Atoms and Elements P R A C T I C E 1. Certain properties are characteristic of metals. Which property means that you can pound the ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... 2 Atoms and Elements P R A C T I C E 1. Certain properties are characteristic of metals. Which property means that you can pound the ...
... 2 Atoms and Elements P R A C T I C E 1. Certain properties are characteristic of metals. Which property means that you can pound the ...
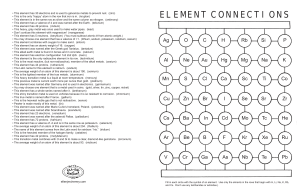
element connections
... • This element has 5 neutrons. (beryllium) (You must subtract atomic # from atomic weight.) • You may choose one element that has a valence of +1. (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium) • This element combines with oxygen to make sand. (silicon) • This element has an atomic weight of 16. (ox ...
... • This element has 5 neutrons. (beryllium) (You must subtract atomic # from atomic weight.) • You may choose one element that has a valence of +1. (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium) • This element combines with oxygen to make sand. (silicon) • This element has an atomic weight of 16. (ox ...
PS-CC-2test - Edquest Science
... B. iron and copper C. aluminum and carbon D. lead and zinc 13. The periodic table is organized by the patterns of the properties of the elements. The rows in the periodic table vary with the amount of elements they contain. These rows are called … A. groups B. families C. periods D. metals ...
... B. iron and copper C. aluminum and carbon D. lead and zinc 13. The periodic table is organized by the patterns of the properties of the elements. The rows in the periodic table vary with the amount of elements they contain. These rows are called … A. groups B. families C. periods D. metals ...
Chemistry 101 Chapter 4 Elements, Atoms, and Ions = =
... Note: for the main-group elements, the elements of the each group have the same chemical and physical properties. Note: from up to down in a column and from right to left across a row the metallic property of elements increases. Alkali metals (1A): Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr. They are very reactive a ...
... Note: for the main-group elements, the elements of the each group have the same chemical and physical properties. Note: from up to down in a column and from right to left across a row the metallic property of elements increases. Alkali metals (1A): Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr. They are very reactive a ...
Lecture notes chapter 4
... Note: for the main-group elements, the elements of the each group have the same chemical and physical properties. Note: from up to down in a column and from right to left across a row the metallic property of elements increases. Alkali metals (1A): Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr. They are very reactive a ...
... Note: for the main-group elements, the elements of the each group have the same chemical and physical properties. Note: from up to down in a column and from right to left across a row the metallic property of elements increases. Alkali metals (1A): Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr. They are very reactive a ...
Unit Map Chemistry I Unit III
... Solve problems involving mass Lab in grams, amount in moles, and number of atoms of an element. The Mole Lab ...
... Solve problems involving mass Lab in grams, amount in moles, and number of atoms of an element. The Mole Lab ...
Chapter 4
... aver of the masses of all the atoms in the sample. ~mass # - atomic# = #of neutrons ...
... aver of the masses of all the atoms in the sample. ~mass # - atomic# = #of neutrons ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Chapter 2 Handout 1 The Atom Dalton`s
... 1. Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all the other elements. 3. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chem ...
... 1. Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all the other elements. 3. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chem ...