Unit 4 Test REVIEW
... 4. How do you calculate the number of neutrons in an atom? 5. One atomic mass unit is equal to __________ the mass of once carbon-12 atom. 6. Isotopes of the same element have different numbers of ________________. 7. Dalton theorized that atoms are indivisible and that all atoms of an element are i ...
... 4. How do you calculate the number of neutrons in an atom? 5. One atomic mass unit is equal to __________ the mass of once carbon-12 atom. 6. Isotopes of the same element have different numbers of ________________. 7. Dalton theorized that atoms are indivisible and that all atoms of an element are i ...
How to write up a practical: General review
... electrons and neutrons and some of their properties TO BE ABLE draw the basic structure of the atom. TO UNDERSTAND how these particles are physically arranged in relation to each other. ...
... electrons and neutrons and some of their properties TO BE ABLE draw the basic structure of the atom. TO UNDERSTAND how these particles are physically arranged in relation to each other. ...
Review Packet
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
Atomic Timeline - Ms Brown`s Chemistry Page
... • John Dalton formulated the Atomic Theory which states that: atoms of an element are different than atoms of other elements; atoms of one element are the same; that atoms of different elements can be combined; that atoms cannot be divided or separated; and that elements are made of tiny particles c ...
... • John Dalton formulated the Atomic Theory which states that: atoms of an element are different than atoms of other elements; atoms of one element are the same; that atoms of different elements can be combined; that atoms cannot be divided or separated; and that elements are made of tiny particles c ...
File - Mrs. Riggs Online
... Electrons arranged in concentric layers that surround the nucleus called electron shells/energy levels/clouds/orbitals: ...
... Electrons arranged in concentric layers that surround the nucleus called electron shells/energy levels/clouds/orbitals: ...
ChLM Final Review Name: Period: Base Knowledge 1. Classify the
... 1. Classify the following as observations or inferences a) The liquid is green because food coloring was added. b) The beaker has green liquid in it. c) The beaker can hold up to 250 mL. d) The beaker will be the best tool for this lab. 2. Measure the following, circle your estimated digit and inclu ...
... 1. Classify the following as observations or inferences a) The liquid is green because food coloring was added. b) The beaker has green liquid in it. c) The beaker can hold up to 250 mL. d) The beaker will be the best tool for this lab. 2. Measure the following, circle your estimated digit and inclu ...
Bohr Models and Lewis Dot Structures
... • Proposed by Niels Bohr in 1915 • Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that have a set size and energy. • The energy of the orbit is related to its size. • The lowest energy is found in the smallest orbit. ...
... • Proposed by Niels Bohr in 1915 • Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that have a set size and energy. • The energy of the orbit is related to its size. • The lowest energy is found in the smallest orbit. ...
Chemistry for Changing Times
... • Elements might combine in more than one set of proportions – Each set makes up a new compound ...
... • Elements might combine in more than one set of proportions – Each set makes up a new compound ...
Word format
... Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called the _________________. Ions Ions are what we get when the electrons partnered with one ...
... Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called the _________________. Ions Ions are what we get when the electrons partnered with one ...
pdf format
... Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called the _________________. Ions Ions are what we get when the electrons partnered with one ...
... Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called the _________________. Ions Ions are what we get when the electrons partnered with one ...
document
... Alkali Metals – (Group 1) are the most reactive of all metals; don’t occur in nature in their element form Alkaline Earth Metals – (Group 2) shiny, ductile and malleable; combine readily with other elements Transition Elements – (Group 3 – 12) most familiar metals because they often occur in nature ...
... Alkali Metals – (Group 1) are the most reactive of all metals; don’t occur in nature in their element form Alkaline Earth Metals – (Group 2) shiny, ductile and malleable; combine readily with other elements Transition Elements – (Group 3 – 12) most familiar metals because they often occur in nature ...
elements_and_the_periodic_table_2011
... Some symbols come from their Greek or Latin name: Mercury (Hg) comes from Greek ...
... Some symbols come from their Greek or Latin name: Mercury (Hg) comes from Greek ...
atoms and elements
... An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still maintain the properties of that element. All elements are made of atoms. So what’s an element? What makes one element different from another? Let’s find out! Vocabulary: First things first, let’s look at the structure of ...
... An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still maintain the properties of that element. All elements are made of atoms. So what’s an element? What makes one element different from another? Let’s find out! Vocabulary: First things first, let’s look at the structure of ...
Reading Quiz
... Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons. An atom that loses an electron becomes a positive ion (CATION) An atom that gains an electron becomes a negative ion (ANION) ...
... Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons. An atom that loses an electron becomes a positive ion (CATION) An atom that gains an electron becomes a negative ion (ANION) ...
Chapter 2choutline - Madison County Schools
... number (chlorine has ______neutrons) Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in __________________ and number of neutrons (they have the same number of protons) Isotopes are identified by writing the name or symbol of element followed by its ___________ ____________ (Cl-37 or chlorine-37) ...
... number (chlorine has ______neutrons) Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in __________________ and number of neutrons (they have the same number of protons) Isotopes are identified by writing the name or symbol of element followed by its ___________ ____________ (Cl-37 or chlorine-37) ...
and the atomic
... • this is NOT IB material until Rutherford • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
... • this is NOT IB material until Rutherford • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
Chapter 3 pages 65
... tube. He called these particles corpuscles but today we call them electrons. This finding is important because it was the first finding that showed particles of the atom had charges. Discovery of the atomic nucleus Scientist Ernest Rutherford conducted an experiment in which he bombarded a thin shee ...
... tube. He called these particles corpuscles but today we call them electrons. This finding is important because it was the first finding that showed particles of the atom had charges. Discovery of the atomic nucleus Scientist Ernest Rutherford conducted an experiment in which he bombarded a thin shee ...
study guide for atoms/periodic table quiz
... Period ROWS in the Periodic Table are called periods. The elements in a period have very different properties. Family/Group COLUMNS in the Periodic Table represent groups or families. Elements in the same family have similar properties. Bohr Diagram A drawing which shows electrons in their energy le ...
... Period ROWS in the Periodic Table are called periods. The elements in a period have very different properties. Family/Group COLUMNS in the Periodic Table represent groups or families. Elements in the same family have similar properties. Bohr Diagram A drawing which shows electrons in their energy le ...
Atomic Structure_Tre..
... increase producing a greater force of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons. This increase in attraction pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus - causing the atomic radii to decrease. ...
... increase producing a greater force of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons. This increase in attraction pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus - causing the atomic radii to decrease. ...
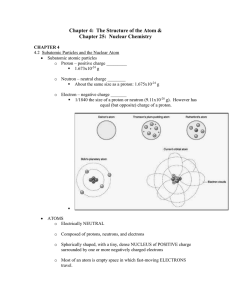
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... Nuclear equations are used to show the radioactive decay process o Mass number and Atomic number are CONSERVED ...
... Nuclear equations are used to show the radioactive decay process o Mass number and Atomic number are CONSERVED ...
EXPERIMENT
... Within the atom, the protons and neutrons are tightly packed in the nucleus and called nucleons. Fastmoving electrons occupy the rest of the atom, which is mostly empty space. Electrons are so small that their mass is considered to be negligible compared to the mass of a proton or neutron. Every ato ...
... Within the atom, the protons and neutrons are tightly packed in the nucleus and called nucleons. Fastmoving electrons occupy the rest of the atom, which is mostly empty space. Electrons are so small that their mass is considered to be negligible compared to the mass of a proton or neutron. Every ato ...
14_1_atoms and isotopes FPS3
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
CHAPTER 18 NOTES
... • Area around the nucleus of an atom where its electrons are most likely found • Farther an electron is from the nucleus, the more energy • Electrons with lower amount of energy are in the first level • 1st – 2 electrons 2nd – 8 electrons 3rd – 18 electrons 4th – 32 electrons ...
... • Area around the nucleus of an atom where its electrons are most likely found • Farther an electron is from the nucleus, the more energy • Electrons with lower amount of energy are in the first level • 1st – 2 electrons 2nd – 8 electrons 3rd – 18 electrons 4th – 32 electrons ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... orbital diagrams of the elements (5.3) Relate valence electrons to Lewis (electron dot) structures (5.3) Describe the ground-state arrangement of electrons in atoms of any element using orbital notation, electron configuration, and Lewis structures (5.3) Identify electron configuration that co ...
... orbital diagrams of the elements (5.3) Relate valence electrons to Lewis (electron dot) structures (5.3) Describe the ground-state arrangement of electrons in atoms of any element using orbital notation, electron configuration, and Lewis structures (5.3) Identify electron configuration that co ...