isotopes
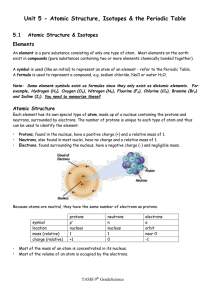
... writing isotopes represent? • The mass number • total number of protons and neutrons in a specific nucleus of an atom. • The atomic number • always refers to the total number of protons in an atom. ...
... writing isotopes represent? • The mass number • total number of protons and neutrons in a specific nucleus of an atom. • The atomic number • always refers to the total number of protons in an atom. ...
ATOM ATOMIC SYMBOL ATOMIC NUMBER
... Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number Number of Electrons = Number of Protons Ions: Add or subtract an electron from the element Isotope: Add or subtract a neutron from the element ...
... Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number Number of Electrons = Number of Protons Ions: Add or subtract an electron from the element Isotope: Add or subtract a neutron from the element ...
Chapter 4 Cornell Notes
... ____________________ of large atoms into smaller pieces) and nuclear ____________________ (the ____________________ of small atoms into one large one), but on earth these reactions do not occur naturally. 2) Naturally occurring nuclear reactions result from the unusual number of neutrons of an isoto ...
... ____________________ of large atoms into smaller pieces) and nuclear ____________________ (the ____________________ of small atoms into one large one), but on earth these reactions do not occur naturally. 2) Naturally occurring nuclear reactions result from the unusual number of neutrons of an isoto ...
Atomic Structure of hydrogen
... Cancer treatment – A weak beam of radiation will kill cancer cells more readily than healthy cells. Carbon dating – All living things contain a known proportion of radioactive carbon-14 atoms. When an organism dies it stops taking in new carbon atoms so the proportion of carbon-14 atoms slowly drops ...
... Cancer treatment – A weak beam of radiation will kill cancer cells more readily than healthy cells. Carbon dating – All living things contain a known proportion of radioactive carbon-14 atoms. When an organism dies it stops taking in new carbon atoms so the proportion of carbon-14 atoms slowly drops ...
Particular particle knowledge
... 15. By looking for the same number of protons - in this case V and Z both have 47. 16. It is an unstable isotope. 17. Emits nuclear radiation. Radioactive decay. 18. alpha (), beta particles (), gamma radiation ( ) 19. Beta particle. 20. Formed in nucleus when a neutron changes to a proton (n p+ ...
... 15. By looking for the same number of protons - in this case V and Z both have 47. 16. It is an unstable isotope. 17. Emits nuclear radiation. Radioactive decay. 18. alpha (), beta particles (), gamma radiation ( ) 19. Beta particle. 20. Formed in nucleus when a neutron changes to a proton (n p+ ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
Canyon High School Chemistry
... 33. By which common decay mode does an atom lose the greatest mass? The least? V. Nuclear Stability, Half-Life, Reactions and Health Considerations 34. What force holds protons together in the nucleus? 35. Define Half-Life. How is it useful? 36. A piece of wood found in an ancient burial chamber con ...
... 33. By which common decay mode does an atom lose the greatest mass? The least? V. Nuclear Stability, Half-Life, Reactions and Health Considerations 34. What force holds protons together in the nucleus? 35. Define Half-Life. How is it useful? 36. A piece of wood found in an ancient burial chamber con ...
4.1 & 4.2 LDP and R.A.M
... -Now, Dalton used hydrogen first because it was the lightest element and gave it a mass of 1. -he compared all the other element to this value For ex. : when Dalton looked at water, he saw thta 1 g of hydrogen combined with 8 g oxygen -so he gave oxygen a mass of 8 -this was a mistake since 2 atoms ...
... -Now, Dalton used hydrogen first because it was the lightest element and gave it a mass of 1. -he compared all the other element to this value For ex. : when Dalton looked at water, he saw thta 1 g of hydrogen combined with 8 g oxygen -so he gave oxygen a mass of 8 -this was a mistake since 2 atoms ...
WHAT IS THE BASIC STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... positive cathode in a tube that was a near vacuum. 2. The remaining gas would glow and the beam was capable of moving a small paddle wheel. 3. This suggested the cathode ray consists of small individual particles. 4. J.J. Thomson studied the cathode ray. He discovered magnetic and electrical fields ...
... positive cathode in a tube that was a near vacuum. 2. The remaining gas would glow and the beam was capable of moving a small paddle wheel. 3. This suggested the cathode ray consists of small individual particles. 4. J.J. Thomson studied the cathode ray. He discovered magnetic and electrical fields ...
ALL MATTER IS MADE UP OF TINY PARTICLES CALLED “ATOMOS”
... – mass cannot be created nor destroyed – For example, if you were told that 4 grams of hydrogen reacted with some oxygen to make 36 grams of water then you could figure out how much oxygen must have been used by applying the law of conservation of mass. ...
... – mass cannot be created nor destroyed – For example, if you were told that 4 grams of hydrogen reacted with some oxygen to make 36 grams of water then you could figure out how much oxygen must have been used by applying the law of conservation of mass. ...
Chapter 5
... Most of the mass and all of the positive charge is in a very small region in the center of the atom, the nucleus Very little of the mass, and all of the negative charge occupies most of the volume of the atom, outside of the nucleus. ...
... Most of the mass and all of the positive charge is in a very small region in the center of the atom, the nucleus Very little of the mass, and all of the negative charge occupies most of the volume of the atom, outside of the nucleus. ...
CHEM 1305 - HCC Learning Web
... -------5. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of silver-107? A) 47 B) 60 C) 107 D) 154 ------6. What is the name of the family of elements in Group IIA/ 2? A) Alkali metals B) Alkaline earth metals C) Halogens D) Noble gases -------7. Which fifth period representative element has the hig ...
... -------5. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of silver-107? A) 47 B) 60 C) 107 D) 154 ------6. What is the name of the family of elements in Group IIA/ 2? A) Alkali metals B) Alkaline earth metals C) Halogens D) Noble gases -------7. Which fifth period representative element has the hig ...
03.03a Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... ____________________ - smallest particle of an element that retains the ____________________ of that element. ____________________ is the man credited with the discovery of the electrons in the late _____, using cathode ray tubes. ____________________ discovered the mass of the electron. Knowledge o ...
... ____________________ - smallest particle of an element that retains the ____________________ of that element. ____________________ is the man credited with the discovery of the electrons in the late _____, using cathode ray tubes. ____________________ discovered the mass of the electron. Knowledge o ...
The History of the Atom Carousel Who-What-When
... conflicting theories of matter. Aristotle believed in the then current thought that there were four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. To this he added ‘Aether’ meaning outer space and the planets. Democritus believed matter was composed of many tiny pieces and the smallest were indivisible. He ...
... conflicting theories of matter. Aristotle believed in the then current thought that there were four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. To this he added ‘Aether’ meaning outer space and the planets. Democritus believed matter was composed of many tiny pieces and the smallest were indivisible. He ...
Chemistry: Unit Organizer Name 6-__ Matter has physical properties
... Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Compound: 2 or more elements combined to make something new, Ex. Na (sodium) + Cl (chlorine) = NaCl (salt) Density:The measurement of how much mass of a substance is co ...
... Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Compound: 2 or more elements combined to make something new, Ex. Na (sodium) + Cl (chlorine) = NaCl (salt) Density:The measurement of how much mass of a substance is co ...
Unit B - Topic 2.0 Notes
... Element Symbol and Name • a capital letter followed by a lower case letter, usually an abbreviation of the element’s name. • Some elements have a Latin name (potassium’s Latin name is kalium, so its symbol is K). • Other elements are named after the location in which they were discovered (californi ...
... Element Symbol and Name • a capital letter followed by a lower case letter, usually an abbreviation of the element’s name. • Some elements have a Latin name (potassium’s Latin name is kalium, so its symbol is K). • Other elements are named after the location in which they were discovered (californi ...
Chem 112 The Atom Power Point
... Matter is composed of empty space through which atoms move Different kinds of atoms come in different sizes and shapes The differing properties of atoms are due to the size, shape, and movement of atoms – Dalton Different atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds ...
... Matter is composed of empty space through which atoms move Different kinds of atoms come in different sizes and shapes The differing properties of atoms are due to the size, shape, and movement of atoms – Dalton Different atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds ...
atoms - cloudfront.net
... elements to sort them into groups. • In 1829 J. W. Dobereiner arranged elements into triads – groups of three elements with similar properties – One element in each triad had properties intermediate of the other two elements ...
... elements to sort them into groups. • In 1829 J. W. Dobereiner arranged elements into triads – groups of three elements with similar properties – One element in each triad had properties intermediate of the other two elements ...
Getting to know and love our atoms, more and more each day
... The elements 1. The elements in Mendeleev’s periodic table are arranged in rows (left to right) called ___________. These rows are arranged in order of __________________ atomic mass. 2. The elements are also arranged into columns (up and down) called _____________ or ______________. The elements wi ...
... The elements 1. The elements in Mendeleev’s periodic table are arranged in rows (left to right) called ___________. These rows are arranged in order of __________________ atomic mass. 2. The elements are also arranged into columns (up and down) called _____________ or ______________. The elements wi ...
Key - Seattle Central College
... – Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals, make up <0.005% of Earth's crust – Actinide series: Th-Lr, also called transuranium elements, generally all man-made and exist for only very short periods of time before decaying to other elements Periodic Law: ...
... – Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals, make up <0.005% of Earth's crust – Actinide series: Th-Lr, also called transuranium elements, generally all man-made and exist for only very short periods of time before decaying to other elements Periodic Law: ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
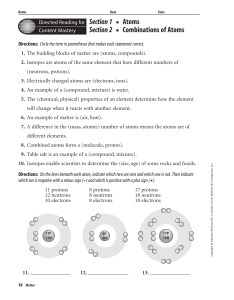
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
Matter
... Elements can join together to form all the different types of matter. That is why they are called the building blocks of matter. Elements can join together chemically to form compounds. Compounds are substances made of 2 or more elements which combine in a chemical reaction. The smallest unit of a c ...
... Elements can join together to form all the different types of matter. That is why they are called the building blocks of matter. Elements can join together chemically to form compounds. Compounds are substances made of 2 or more elements which combine in a chemical reaction. The smallest unit of a c ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.