What is the Matter?
... Properties of Matter •Matter has volume Matter has mass Matter has weight ...
... Properties of Matter •Matter has volume Matter has mass Matter has weight ...
Chapter 3 – Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter - Hatboro
... ______________. It says that if ______ or more different _______ are made of the same 2 elements, the ratio of the ________ element combined with a fixed mass of the 1st element is always a ________ of small ___________ numbers multiple proportions 2nd whole ...
... ______________. It says that if ______ or more different _______ are made of the same 2 elements, the ratio of the ________ element combined with a fixed mass of the 1st element is always a ________ of small ___________ numbers multiple proportions 2nd whole ...
atomic number - geraldinescience
... atom is the mass number. • The mass of a subatomic particle is too small to be expressed easily in grams, so a special unit called the atomic mass unit (amu) is used. • Protons and neutrons each have an atomic mass close to 1 amu. • Electrons have much less mass than protons or neutrons do. The mass ...
... atom is the mass number. • The mass of a subatomic particle is too small to be expressed easily in grams, so a special unit called the atomic mass unit (amu) is used. • Protons and neutrons each have an atomic mass close to 1 amu. • Electrons have much less mass than protons or neutrons do. The mass ...
Atomic mass
... that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample. Law of Multiple Proportions states that If two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, the masses of the second element combined with a certain ...
... that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample. Law of Multiple Proportions states that If two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, the masses of the second element combined with a certain ...
Elements and Atoms
... • To make molecules, you must have elements. • Elements are made of atoms. While the atoms may have different weights and organization, they are all built in the same way. ...
... • To make molecules, you must have elements. • Elements are made of atoms. While the atoms may have different weights and organization, they are all built in the same way. ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... have 7 valence electrons are active nonmetals usually combined w/ other elements * Know that there is a difference between fission and fusion: fusion- put atoms together with enormous amounts of energy released fission- splitting atoms- energy released- not as much as fusion- may occur in a chain re ...
... have 7 valence electrons are active nonmetals usually combined w/ other elements * Know that there is a difference between fission and fusion: fusion- put atoms together with enormous amounts of energy released fission- splitting atoms- energy released- not as much as fusion- may occur in a chain re ...
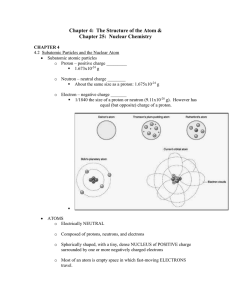
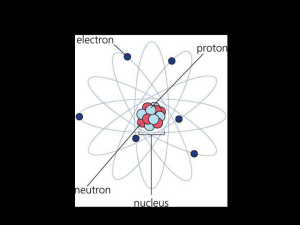
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... o Above the band of stability – too many _____________; Below the band of stability – too many _______________ or too few ______________ o BETA DECAY: For elements above the band of stability (too many neutrons) A NEUTRON will decay into a PROTON (stays in the nucleus) and an ELECTRON (leaves the ...
... o Above the band of stability – too many _____________; Below the band of stability – too many _______________ or too few ______________ o BETA DECAY: For elements above the band of stability (too many neutrons) A NEUTRON will decay into a PROTON (stays in the nucleus) and an ELECTRON (leaves the ...
genchm 113 - Angelfire
... John Dalton formulated a precise definition of the indivisible building blocks of matter called atoms. “Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter.” ...
... John Dalton formulated a precise definition of the indivisible building blocks of matter called atoms. “Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter.” ...
Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... Organisms eat plants, break down the sugars, and release energy along with CO 2 & H2O Exergonic reactions involve a net release of energy; while endergonic reactions involve a net absorption of energy Energy must be added to the reactants for most chemical reactions to occur; called activation energ ...
... Organisms eat plants, break down the sugars, and release energy along with CO 2 & H2O Exergonic reactions involve a net release of energy; while endergonic reactions involve a net absorption of energy Energy must be added to the reactants for most chemical reactions to occur; called activation energ ...
Chap 1-3 Review
... Draw the Bohr model diagrams for the following species (**watch the charge**) ...
... Draw the Bohr model diagrams for the following species (**watch the charge**) ...
The Size of the Atom Atomic Numbers Atomic Mass Numbers
... If all atoms are composed of the same particles, how can there be more than 100 different elements? The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, called the atomic number. Every hydrogen atom—atomic number 1—has exactly one proton in its nucleus. Every gold atom has ...
... If all atoms are composed of the same particles, how can there be more than 100 different elements? The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, called the atomic number. Every hydrogen atom—atomic number 1—has exactly one proton in its nucleus. Every gold atom has ...
The atomic number tells how many protons Protons make an atom
... Atoms of the same element with different atomic masses are called isotopes Gold has a mass of 196.97 That means MOST gold atoms have 197 p+ and no, but some rare atoms will have only 196. They ALL have 79 p+. Most have 118no, but a few may have 117 no. ...
... Atoms of the same element with different atomic masses are called isotopes Gold has a mass of 196.97 That means MOST gold atoms have 197 p+ and no, but some rare atoms will have only 196. They ALL have 79 p+. Most have 118no, but a few may have 117 no. ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Waterford Public Schools
... • Metals are located on the left hand side of the Periodic Table • Most of the elements are metals • The metals include all of the transition metals as well as post transition metals • Metals are solids (except mercury), conduct electricity, are ductile, are malleable and can form alloys • Non-metal ...
... • Metals are located on the left hand side of the Periodic Table • Most of the elements are metals • The metals include all of the transition metals as well as post transition metals • Metals are solids (except mercury), conduct electricity, are ductile, are malleable and can form alloys • Non-metal ...
Chemistry - Chapter 2 - WSCC Biology Tutoring
... Phosphorus, and Sulfer, also known as CHNOPS. These elements make up about 95% of the body weight of all organisms. ...
... Phosphorus, and Sulfer, also known as CHNOPS. These elements make up about 95% of the body weight of all organisms. ...
Atoms and Elements
... suggested the material world when broken down to the extreme would consist of tiny particles called atomos, meaning indivisible. Alchemists through the middle ages physically experimented with matter aiming to create gold from base metals and an elixir for everlasting life. Englishman Robert Boyle ( ...
... suggested the material world when broken down to the extreme would consist of tiny particles called atomos, meaning indivisible. Alchemists through the middle ages physically experimented with matter aiming to create gold from base metals and an elixir for everlasting life. Englishman Robert Boyle ( ...
GOB 3ed Chapter 2 part 1
... • Metals are shiny solids at room temperature, except for mercury (Hg), which is a liquid. ...
... • Metals are shiny solids at room temperature, except for mercury (Hg), which is a liquid. ...
atomic structure intro - Hood River County School District
... 3. What do isotopes of the same element have in common? How do isotopes of the same element differ? ...
... 3. What do isotopes of the same element have in common? How do isotopes of the same element differ? ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 9. How many protons, neutron, and electrons does U-234 have? P=92, n= 142, e=92 10. How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of one proton or one neutron? Approx. 2000 11. What element has 21 protons and 24 neutrons? Scandium-45 12. An atom of potassium has 19 protons and 20 neutrons. What ...
... 9. How many protons, neutron, and electrons does U-234 have? P=92, n= 142, e=92 10. How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of one proton or one neutron? Approx. 2000 11. What element has 21 protons and 24 neutrons? Scandium-45 12. An atom of potassium has 19 protons and 20 neutrons. What ...
2010 Physical Science Comprehensive Test REVIEW Ch 0.3 Sig
... 52. An example of a metalloid, elements with properties between metals and non-metals, is (be able to locate all of these.) 53. Evidence that a chemical change has occurred would include: 54. The atomic mass of a helium atom is: 55. According to the periodic table which group are the chemical elemen ...
... 52. An example of a metalloid, elements with properties between metals and non-metals, is (be able to locate all of these.) 53. Evidence that a chemical change has occurred would include: 54. The atomic mass of a helium atom is: 55. According to the periodic table which group are the chemical elemen ...
Practice Test #2 - smhs
... Nuclear mass defect is equivalent, by conversion, to: A) atomic mass; force; C) energy of a chemical reaction; D) binding energy. ...
... Nuclear mass defect is equivalent, by conversion, to: A) atomic mass; force; C) energy of a chemical reaction; D) binding energy. ...
+ mass isotope 2
... surface of the milk. Do not put a drop of food coloring in the center. Repeat steps 3 and 4. ...
... surface of the milk. Do not put a drop of food coloring in the center. Repeat steps 3 and 4. ...
Review Stations - ANSWER KEY - Liberty Union High School District
... 1. What is the difference between Democritus’ and Dalton’s Model of the Atom? Very similar – both thought that atoms made up everything and were very small. Democritus named them, atomos, and Dalton said they were indivisible. 2. How did Rutherford build on Thomson’s discovery? Describe each of thei ...
... 1. What is the difference between Democritus’ and Dalton’s Model of the Atom? Very similar – both thought that atoms made up everything and were very small. Democritus named them, atomos, and Dalton said they were indivisible. 2. How did Rutherford build on Thomson’s discovery? Describe each of thei ...
Types of Measurement
... 1. Ionic: made up of ions of opposite charge A. strong electrostatic force of attraction; ionic bond B. electrons are transferred 2. Covalent: made up of two or more nonmetals A. electrons are shared ...
... 1. Ionic: made up of ions of opposite charge A. strong electrostatic force of attraction; ionic bond B. electrons are transferred 2. Covalent: made up of two or more nonmetals A. electrons are shared ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.