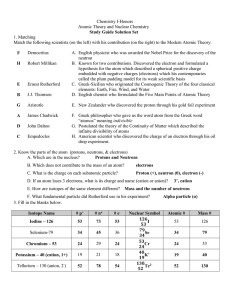
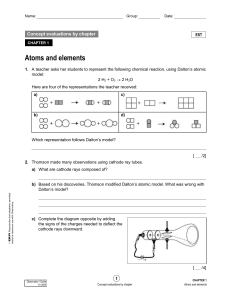
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure
... Early Models of Atoms • Democritus (460-400B.C.) first suggested the existence of these particles, which he called “atoms” for the Greek word for “uncuttable”. They lacked experimental support due to the lack of scientific testing at the time. • John Dalton (1766-1844) performed experiments to stud ...
... Early Models of Atoms • Democritus (460-400B.C.) first suggested the existence of these particles, which he called “atoms” for the Greek word for “uncuttable”. They lacked experimental support due to the lack of scientific testing at the time. • John Dalton (1766-1844) performed experiments to stud ...
Types of Measurement
... 1. Ionic: made up of ions of opposite charge A. strong electrostatic force of attraction; ionic bond B. electrons are transferred 2. Covalent: made up of two or more nonmetals A. electrons are shared ...
... 1. Ionic: made up of ions of opposite charge A. strong electrostatic force of attraction; ionic bond B. electrons are transferred 2. Covalent: made up of two or more nonmetals A. electrons are shared ...
Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. The v ...
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. The v ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... 2. All ______________of a given ______________are ___________but atoms of any one element are __________________ from the atoms of every other element. 3. ___________________are formed when _____________of different elements unite in ...
... 2. All ______________of a given ______________are ___________but atoms of any one element are __________________ from the atoms of every other element. 3. ___________________are formed when _____________of different elements unite in ...
Chapter 3: Atomic Structure
... concentrated into a very small volume in comparison to the rest of the atom Electrons circling around the nucleus like planets around the sun. A lot of empty space ...
... concentrated into a very small volume in comparison to the rest of the atom Electrons circling around the nucleus like planets around the sun. A lot of empty space ...
Identifying Elements LAB
... A Greek philosopher named Democritus, who lived over 2000 years ago, taught people that all things were made of grains which could not be divided. He called these grains atomos because in Greek atomos means “uncuttable”. Today, atom is the common name for the tiny particles of matter that cannot be ...
... A Greek philosopher named Democritus, who lived over 2000 years ago, taught people that all things were made of grains which could not be divided. He called these grains atomos because in Greek atomos means “uncuttable”. Today, atom is the common name for the tiny particles of matter that cannot be ...
e - Central Lyon CSD
... Democritus and Aristotle ◦ Democritus thought all matter consisted of extremely tiny particles that could not be divided. (Cut aluminum foil in half) ◦ Also thought matter in liquids was round and smooth; in solids rough and prickly ◦ Aristotle thought there was no limit to the number of times matte ...
... Democritus and Aristotle ◦ Democritus thought all matter consisted of extremely tiny particles that could not be divided. (Cut aluminum foil in half) ◦ Also thought matter in liquids was round and smooth; in solids rough and prickly ◦ Aristotle thought there was no limit to the number of times matte ...
Postulates of Dalton`s atomic theory - Chemwiki
... Atoms of same element can combine in more than one ratio to form two or more compounds. The atom is the smallest unit of matter that can take part in a chemical reaction. ...
... Atoms of same element can combine in more than one ratio to form two or more compounds. The atom is the smallest unit of matter that can take part in a chemical reaction. ...
Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... Millikan’s Oil Drop Experiment showing the charge of the electron and its uniformity. Discovery of Radioactivity: Henri Becquerel’s experiment, nature of alpha, beta and gamma radiation. Discovery of the Nucleus: Plum Pudding atomic model. Ernest Rutherford’s experiment showing small size, hardness ...
... Millikan’s Oil Drop Experiment showing the charge of the electron and its uniformity. Discovery of Radioactivity: Henri Becquerel’s experiment, nature of alpha, beta and gamma radiation. Discovery of the Nucleus: Plum Pudding atomic model. Ernest Rutherford’s experiment showing small size, hardness ...
Packet
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
Atomic Model Power Point
... • Atomic mass unit is defined as one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. • The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. • To calculate the atomic mass of an element, multiply the mass by its natural abundance and then ad ...
... • Atomic mass unit is defined as one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. • The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. • To calculate the atomic mass of an element, multiply the mass by its natural abundance and then ad ...
Review Packet
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
rocks and minerals quiz
... An atom is mostly empty space between the electrons and the nucleus. This presents a conceptual problem: How do atoms form solids with all this empty space? ATOMIC STRUCTURE ANALOGY Imagine a jungle gym on a children’s playground. If you are a bug up close, you would see a large jungle gym with plen ...
... An atom is mostly empty space between the electrons and the nucleus. This presents a conceptual problem: How do atoms form solids with all this empty space? ATOMIC STRUCTURE ANALOGY Imagine a jungle gym on a children’s playground. If you are a bug up close, you would see a large jungle gym with plen ...
File
... electron. The electron is released with a large amount of energy. The proton stays in the nucleus. ...
... electron. The electron is released with a large amount of energy. The proton stays in the nucleus. ...
electron
... mass 10.012 amu and a relative abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
... mass 10.012 amu and a relative abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
Notes ch 3.2 - Douglas County
... Today • Daltons basic ideas survive. • We now know there are versions of elements (isotopes) • We now know that atoms can be subdivided. (They have parts p, n, e) ...
... Today • Daltons basic ideas survive. • We now know there are versions of elements (isotopes) • We now know that atoms can be subdivided. (They have parts p, n, e) ...
Physical Science EOCT Review Domain 1: Chemistry
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses, due to varying numbers of neutrons. Isotope ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses, due to varying numbers of neutrons. Isotope ...
A`r ji r/ Ii
... a. the total number of protons and neulrons in the nucleus of an atom b. the weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element c. 1/12 the mass of a carboni2 atom d. the number of protons in the nucleus of an element e. atoms with the same number of protons but differe ...
... a. the total number of protons and neulrons in the nucleus of an atom b. the weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element c. 1/12 the mass of a carboni2 atom d. the number of protons in the nucleus of an element e. atoms with the same number of protons but differe ...
Study Guide - Honors Chemistry
... by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may or may not be ...
... by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may or may not be ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... in a tiny, dense, positively-charged nucleus. similar to a small solar system with the electrons circling a tiny, dense, nucleus. ...
... in a tiny, dense, positively-charged nucleus. similar to a small solar system with the electrons circling a tiny, dense, nucleus. ...
Chemistry Study Guide What is matter made of? Matter is anything
... Elements are unique, pure substances. Elements and the Periodic Table Elements are arranged in order of their atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Every element has its own atomic number. The periodic table has horizontal ...
... Elements are unique, pure substances. Elements and the Periodic Table Elements are arranged in order of their atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Every element has its own atomic number. The periodic table has horizontal ...
atomic structure discoveries/experiments conclusions
... Electrons and other discoveries: Electric charges: static electricity Electrolysis: Faraday's work on the chemical reaction produced when an electric current passes through a liquid resulted in the laws of electrolysis. The discovery of Electrons: Cathode ray tube (Thomson, 1897) On April 30, 1897, ...
... Electrons and other discoveries: Electric charges: static electricity Electrolysis: Faraday's work on the chemical reaction produced when an electric current passes through a liquid resulted in the laws of electrolysis. The discovery of Electrons: Cathode ray tube (Thomson, 1897) On April 30, 1897, ...
11129_evl_ch1_ste_eleve (3)
... EST 12. Which of the following elements are isotopes of the same element? Explain your answer. ...
... EST 12. Which of the following elements are isotopes of the same element? Explain your answer. ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.