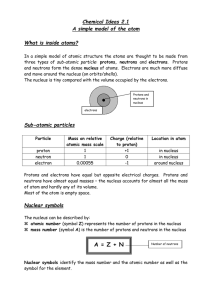
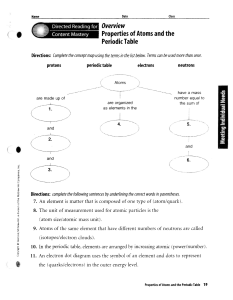
Chapter 5 – Atomic Structure
... identical. The atoms of one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. The atoms of one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Chapter 2 - U of L Class Index
... The # protons defines the element. If the # protons changes, then it is not the same element. eg. The carbon atom has 6 protons in the nucleus. If you remove 1 proton from the carbon nucleus, you change the nature of the element. C - p → B if you add 1 proton to the carbon nucleus you get nitrogen. ...
... The # protons defines the element. If the # protons changes, then it is not the same element. eg. The carbon atom has 6 protons in the nucleus. If you remove 1 proton from the carbon nucleus, you change the nature of the element. C - p → B if you add 1 proton to the carbon nucleus you get nitrogen. ...
atomic theory quiz II review
... We will have a quiz over the information you have learned about the atomic theory. Please actively study (sing, dance, act, draw, write) the following info: ...
... We will have a quiz over the information you have learned about the atomic theory. Please actively study (sing, dance, act, draw, write) the following info: ...
Atomictheory
... Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be divided. • All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. • An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of different elements. At ...
... Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be divided. • All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. • An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of different elements. At ...
Name
... 5. What is the charge of an atom and why? Atoms are neutral because the positive protons cancel the negative electrons. 6. Summarize the main concepts of Dalton’s Atomic Theory. 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical AND at ...
... 5. What is the charge of an atom and why? Atoms are neutral because the positive protons cancel the negative electrons. 6. Summarize the main concepts of Dalton’s Atomic Theory. 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical AND at ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Electron Cloud – area around nucleus where electrons spend most of their time - makes up most of the size of an atom - mostly empty space ...
... Electron Cloud – area around nucleus where electrons spend most of their time - makes up most of the size of an atom - mostly empty space ...
CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS AND ATOMS
... CHEMICAL ELEMENT • a substance that cannot be further decomposed into simpler substances by chemical or physical means. • consists of atoms that all have the same atomic number. • approximately 115 elements are known. • 88 elements occur naturally. • microscopic--single atom of an element. • macros ...
... CHEMICAL ELEMENT • a substance that cannot be further decomposed into simpler substances by chemical or physical means. • consists of atoms that all have the same atomic number. • approximately 115 elements are known. • 88 elements occur naturally. • microscopic--single atom of an element. • macros ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... _________ 16. Of the following particles, those not found in the nucleus of an atom are a. protons. b. neutrons. c. electrons. d. protons and neutrons. _________ 17. Different atoms of the same element may have different a. numbers of protons. b. atomic numbers. c. atomic masses. d. numbers of elect ...
... _________ 16. Of the following particles, those not found in the nucleus of an atom are a. protons. b. neutrons. c. electrons. d. protons and neutrons. _________ 17. Different atoms of the same element may have different a. numbers of protons. b. atomic numbers. c. atomic masses. d. numbers of elect ...
Document
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
Atomic Structure
... Atomos – smallest unit of matter Dalton’s Theory 1) Elements composed of tiny indivisible (not invisible) particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical 3) Atoms of different elements can chemically combine with one another in simple whole number ratios (compounds) 4) In ...
... Atomos – smallest unit of matter Dalton’s Theory 1) Elements composed of tiny indivisible (not invisible) particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical 3) Atoms of different elements can chemically combine with one another in simple whole number ratios (compounds) 4) In ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Fusion processes in stars have been shown to form nuclei up to 26 protons and 30 neutrons (5626Fe). ...
... Fusion processes in stars have been shown to form nuclei up to 26 protons and 30 neutrons (5626Fe). ...
Matter and Energy
... ◦ Protons – found in nucleus, + charge, 1 AMU ◦ Neutrons – found in nucleus, no charge, 1 AMU ◦ Electrons – found orbiting nucleus, - charge, approximately 1/1836 AMU ...
... ◦ Protons – found in nucleus, + charge, 1 AMU ◦ Neutrons – found in nucleus, no charge, 1 AMU ◦ Electrons – found orbiting nucleus, - charge, approximately 1/1836 AMU ...
The Atom Part 1 Notes
... back them up • Came up with Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms • Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different ...
... back them up • Came up with Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms • Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different ...
® Atoms ® Make up all matter ® Made up of smaller particles called
... Sum of protons and neutrons Written as; carbon12 carbon-14, carbon-13 Even with different isotopes they react the same chemically ...
... Sum of protons and neutrons Written as; carbon12 carbon-14, carbon-13 Even with different isotopes they react the same chemically ...
The Atom: Idea to Theory
... – Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element Mullis ...
... – Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element Mullis ...
Chapter 3 - mrgoosby
... The inner ring, #1, can only have 2 electrons The second ring can have up to 8 electrons The third ring can have up to 18 electrons The fourth ring can have up to 32 electrons All rings up to ring #7, the last ring, can have up to 32 electrons KEY VOCAB: Energy Level – the rings containing electrons ...
... The inner ring, #1, can only have 2 electrons The second ring can have up to 8 electrons The third ring can have up to 18 electrons The fourth ring can have up to 32 electrons All rings up to ring #7, the last ring, can have up to 32 electrons KEY VOCAB: Energy Level – the rings containing electrons ...
Structure of the Atom JJ Thomson- discovered the electron in late
... as protons are found to be at the center of this nucleus. James Chadwick- discovers the NEUTRON in 1932. The neutron is located in the nucleus and has NO CHARGE. The following table summarizes the subatomic particles listed in order of discovery: ...
... as protons are found to be at the center of this nucleus. James Chadwick- discovers the NEUTRON in 1932. The neutron is located in the nucleus and has NO CHARGE. The following table summarizes the subatomic particles listed in order of discovery: ...
Atoms - SD308.org
... He never developed a theory because he did not have experimental support nor did he explain chemical behavior. It took 2000 years after Democritus for the real nature of atoms and events at the atomic level to be established ...
... He never developed a theory because he did not have experimental support nor did he explain chemical behavior. It took 2000 years after Democritus for the real nature of atoms and events at the atomic level to be established ...
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... atom of carbon must contain 18. - - - - - - - but some contain six neutrons and others have eight neutrons. ...
... atom of carbon must contain 18. - - - - - - - but some contain six neutrons and others have eight neutrons. ...
Early Models of the Atom
... atom: smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical identity of the element Three laws giving elements of atoms: 1. Law of conservation of matter: matter cannot be created or destroyed 2. Law of constant composition: the ratio must always be preserved (ex. H2 O 2 H’s & 1 O) 3. Law of mu ...
... atom: smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical identity of the element Three laws giving elements of atoms: 1. Law of conservation of matter: matter cannot be created or destroyed 2. Law of constant composition: the ratio must always be preserved (ex. H2 O 2 H’s & 1 O) 3. Law of mu ...
Elements and Compounds checklist for web
... Explain why internationally recognised symbols are used for elements Research task: What's in a name? • Outline the contributions of Marie Curie, Albert Einstein, Glenn Seaborg and Niels Bohr to our understa ...
... Explain why internationally recognised symbols are used for elements Research task: What's in a name? • Outline the contributions of Marie Curie, Albert Einstein, Glenn Seaborg and Niels Bohr to our understa ...
Atomic Theory
... by Lavoisier and many other scientists. • Dalton proposed his atomic theory of matter in 1803. ...
... by Lavoisier and many other scientists. • Dalton proposed his atomic theory of matter in 1803. ...
Zn 8 p + 8 p + 30 p + 8 n 8 n 35 n 8 e
... but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers Isotopes of chlorine 35Cl ...
... but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers Isotopes of chlorine 35Cl ...
chapter 2
... 13. What two things are classified as pure substances?___ compounds _____ and ____ elements ______ 14. What is the difference between a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture? _____________________ __ HO – looks uniform in composition; HE – you can see different parts ____________ 15. Describe each o ...
... 13. What two things are classified as pure substances?___ compounds _____ and ____ elements ______ 14. What is the difference between a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture? _____________________ __ HO – looks uniform in composition; HE – you can see different parts ____________ 15. Describe each o ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.