* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Elements and Compounds checklist for web
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
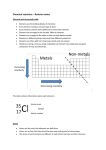
Year 8: Chemical World-‐ Elements, compounds and mixtures Check Date Revise assumed knowledge: ST3-‐12MW identifies the observable properties of solids, liquids and gases, and that changes made to materials are reversible or irreversible □ ST3-‐13MW describes how the properties of materials determine their use for specific purposes CW2 Scientific knowledge and developments in technology have changed our understanding of the structure and properties of matter. ELEMENTS 4CW2a. describe the properties and uses of some common elements, including metals and non-‐metals 4CW2d. explain why internationally recognised symbols are used for common elements Literacy activity (ESL focus): Define and describe. □ atom, element, metal, non-‐metal Identify general patterns in the periodic table. Eg. metals and non-‐metals □ □ Video: Metal reactivity Watch Richard Hammond’s ‘metals in a bath tub’ youtube. □ Identify the symbols for the first 20 elements in the periodic table □ □ □ □ Recap the particle theory of matter Explain why internationally recognised symbols are used for elements Research task: What's in a name? • Outline the contributions of Marie Curie, Albert Einstein, Glenn Seaborg and Niels Bohr to our understanding of the structure of atoms. • Identify the elements named after the above scientists. • Identify as many elements named after other scientists or places. Extension work: -‐ Define and describe protons, neutrons, electrons, atomic number, atomic mass -‐ Describe the basic structure of an atom (protons, neutrons and electrons -‐ Define atomic number and atomic mass -‐ Compare the atomic number and atomic mass of different elements -‐ Construct a model of an atom. Use any materials that you like. Your model must have a key. Distinguish between physical and chemical properties, using examples. • physical -‐ solid, liquid or gas -‐ boiling and melting point -‐ electrical conductivity -‐ heat conductivity -‐ density -‐ strength -‐ ductility -‐ malleability • chemical -‐ reactivity -‐ corrosiveness -‐ flammability -‐ solubility -‐ toxicity Compile a table comparing the above physical and chemical properties of metals □ and non-‐metals. Extension work: Relate the atomic number and atomic mass of different elements to their properties □ and uses first-‐hand investigation(s): Simple circuits □ Compare a range of metals and non-‐metals for their ability to conduct electricity. Research task: Research the history and uses of 5 metals and 5 non-‐metals used in everyday □ situations ICT exercise/Research task: Collect information about the boiling and melting points of some common elements □ (metal and non-‐metal) -‐ Use a spreadsheet application to plot a column graph of the data. 4CW2b. identify how our understanding of the structure and properties of elements has changed as a result of some technological devices Research task or teacher delivered • Outline the work performed by and models proposed by Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr □ • Include modern quantum cloud model, CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research and hadron collider project • Construct a scaled timeline of findings Research task: Discovery of elements Research four elements that required technology for them to be discovered. □ Describe the technology and outline why it was necessary for the element to be discovered. Assessment: Oxford online test-‐ Elements □ Students to achieve 100% in Support and Consolidate OR Consolidate and Extend COMPOUNDS AND MIXTURES 4CW2c. identify some examples of common compounds Literacy activity (ESL focus): Define and describe. □ Compound, mixture Identify a range of common compounds eg. H2O, CO2, NaCl, Fe2O3 □ first-‐hand investigation(s): Molymod kits I Construct common compounds using the kit. □ first-‐hand investigation(s): Making a compound from its elements. • Burn magnesium in a crucible first-‐hand investigation(s): Isolating elements from compounds Electrolysis of water first-‐hand investigation(s): Decomposing a compound Copper carbonate (Oxford pg181) first-‐hand investigation(s): Student designed task Compare chemical and physical properties of copper (element) and copper sulfate (compound). (Oxford pg182) • conductivity • reactivity with silver nitrate • addition to water • Melting and boiling points (how will you determine this?) Compare compounds and mixtures (table, diagram, flow chart) Distinguish between homogenous and heterogeneous mixtures □ □ □ □ □ □ □ first-‐hand investigation(s): Molymod kits II Model the following • An monatomic element • a diatomic element • a compound made of two elements • a compound made of four elements • a mixture containing at least two different substances – Take a photo of each and prepare an annotated slideshow demonstration – Describe at a particle level the difference between elements, compounds and mixtures, including the type and arrangement of particles Literacy activity: COSMOS. □ Students research for a related article. Students then write a series of questions that MUST include 5 multiple choice, 2 identify, 2 describe, 1 explain and either 1 assess or evaluate. Assessment: Oxford online test-‐ Compounds and mixtures □ Students to achieve 100% in Support and Consolidate OR Consolidate and Extend THE IMPACT OF ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS ON SOCIETY 4CW2f. investigate how people in different cultures in the past have applied their knowledge of the properties of elements and compounds to their use in everyday life, eg utensils, weapons and tools Research task: Contributions of cultures Research each of the following ‘ages’. Outline why they occurred in this specific order and provide details about the cultures and their contributions to each. • Copper age • Bronze age • Iron age • Industrial age Construct a scaled timeline of above first-‐hand investigation(s): Isolating elements from compounds I • Extract copper from copper oxide first-‐hand investigation(s): Isolating elements from compounds II • Extract copper from copper sulfate using electrolysis (Oxford pg194) Outline the uses of different elements and compounds in everyday life eg. Iron, Aluminium, carbon dioxide, Sulfuric acid Describe uses of elements and compounds by Aboriginals • Tools and weapons • carriers (nets, baskets, bags) • Ceremonials ochres Assessment: Oxford online test-‐ The impact of elements and compounds on society Students to achieve 100% in Support and Consolidate OR Consolidate and Extend 4CWadd3 investigate the nature of mineral crystals Describe crystal shapes of common minerals □ □ □ □ □ □ □ 4CWadd4 outline how some historical developments have contributed to evidence that has advanced our understanding of the particle model of matter Research task: Structure of the atom □ Research the history of the atom. Include all scientists and the technologies they used to increase our understanding of the structure and properties of elements has changed as a result of some technological devices. Construct a scaled timeline.