Topic 2.1 The Nuclear Atom
... • this is NOT IB material until indicated • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
... • this is NOT IB material until indicated • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
Balancing Equations Notes
... Chemical Equation: a way to represent chemical reactions on paper. Animation http://www.chemistry.ohio-state.edu/betha/nealChemBal/ ...
... Chemical Equation: a way to represent chemical reactions on paper. Animation http://www.chemistry.ohio-state.edu/betha/nealChemBal/ ...
AM-1 Power point - Moline High School
... Mass number- the whole number based on the average atomic mass. Ex. Carbon would have the mass number of 12. It is equal to the number of protons + neutrons found in the nucleus. ...
... Mass number- the whole number based on the average atomic mass. Ex. Carbon would have the mass number of 12. It is equal to the number of protons + neutrons found in the nucleus. ...
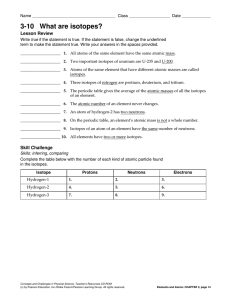
3-10 What are isotopes?
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
Section 6.2 Notes - oologah.k12.ok.us
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combin ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combin ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Notes
... Atoms of the same __________________ with ___________________ numbers Company,ofInc. ____________________________. ...
... Atoms of the same __________________ with ___________________ numbers Company,ofInc. ____________________________. ...
Name Test Review Chapters 4 and 25 Honors Chemistry 1. Fill in
... 11. What is the mass of a block of aluminum that has a volume of 22.4 cm3? (Density of Al = 2.70 g/cm3) 12. If a metal cylinder of copper (density = 8.9 g/cm3) has a mass of 45.4 grams, what is the volume of the cylinder? What is the cylinder’s diameter if it is 1.2 cm in height? 13. Convert 2950 m ...
... 11. What is the mass of a block of aluminum that has a volume of 22.4 cm3? (Density of Al = 2.70 g/cm3) 12. If a metal cylinder of copper (density = 8.9 g/cm3) has a mass of 45.4 grams, what is the volume of the cylinder? What is the cylinder’s diameter if it is 1.2 cm in height? 13. Convert 2950 m ...
Two valence electrons.
... atoms. When elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements with similar properties. ...
... atoms. When elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements with similar properties. ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... Law of DEFINITE PROPORTIONS: a chemical COMPOUND contains the SAME ELEMENTS in exactly the SAME PROPORTION by MASS regardless of the size of the sample or the source of the compound. ◦ it doesn’t matter how or where a pure chemical compound ...
... Law of DEFINITE PROPORTIONS: a chemical COMPOUND contains the SAME ELEMENTS in exactly the SAME PROPORTION by MASS regardless of the size of the sample or the source of the compound. ◦ it doesn’t matter how or where a pure chemical compound ...
atoms lesson
... All things on earth are made of ATOMS! OBJECTIVES • Know the three parts of an ATOM: the ELECTRON, PROTON, and NEUTRON. • Explain what makes ATOMS of one ELEMENT different from those of another ELEMENT. • Be able to calculate ATOMIC MASS and ATOMIC NUMBER. ...
... All things on earth are made of ATOMS! OBJECTIVES • Know the three parts of an ATOM: the ELECTRON, PROTON, and NEUTRON. • Explain what makes ATOMS of one ELEMENT different from those of another ELEMENT. • Be able to calculate ATOMIC MASS and ATOMIC NUMBER. ...
Name Test Review Chemistry Unit 2: The Atom 1. Fill in the blank
... 9. If a student weighs out 2.01 g of silicon, how many moles is that? 10. How many moles are there in 2.4010 x 1025 particles of gold? 11. What is the mass of a block of aluminum that has a volume of 22.4 cm3? (Density of Al = 2.70 g/cm3) ...
... 9. If a student weighs out 2.01 g of silicon, how many moles is that? 10. How many moles are there in 2.4010 x 1025 particles of gold? 11. What is the mass of a block of aluminum that has a volume of 22.4 cm3? (Density of Al = 2.70 g/cm3) ...
PowerPoint Overview for Introduction
... But do you recall munching some Molybdenum or snaking on Selenium? Some 60 chemical elements are found in the body, but what all of them are doing there is still unknown. Roughly 96 percent of the mass of the human body is made up of just four elements: Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen, with a ...
... But do you recall munching some Molybdenum or snaking on Selenium? Some 60 chemical elements are found in the body, but what all of them are doing there is still unknown. Roughly 96 percent of the mass of the human body is made up of just four elements: Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen, with a ...
Learning Targets Chapter 4
... relative mass of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom. I can calculate the number of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom using the atomic number, mass number and overall charge of the atom or a periodic table provided. I can describe the similarity and di ...
... relative mass of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom. I can calculate the number of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom using the atomic number, mass number and overall charge of the atom or a periodic table provided. I can describe the similarity and di ...
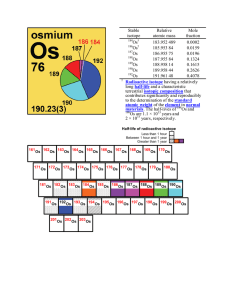
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (positive or negative electrons), gamma radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a fina ...
... number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (positive or negative electrons), gamma radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a fina ...
ISOTOPES
... of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number of protons, electrons, and neutrons as every other atom of the element. Thus the atomic mass of every atom of an element would be the same. In the early twentieth century, scientists ...
... of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number of protons, electrons, and neutrons as every other atom of the element. Thus the atomic mass of every atom of an element would be the same. In the early twentieth century, scientists ...
Lesson x- Review W14 answers
... 21) A student runs an experiment testing the effect of different amounts of salt on the boiling point temperature of water. In pot A she adds no salt (NaCl) to the water, in pot B she adds 20 g of NaCl, and in pot C she adds 40 g of NaCl. She boils each and finds that pot A boiled at 100 °C, pot B ...
... 21) A student runs an experiment testing the effect of different amounts of salt on the boiling point temperature of water. In pot A she adds no salt (NaCl) to the water, in pot B she adds 20 g of NaCl, and in pot C she adds 40 g of NaCl. She boils each and finds that pot A boiled at 100 °C, pot B ...
Compounds Booklet Companion New 2013
... A form of an atom that has a different number of neutrons than the common form of that atom. Ex. The most common form of hydrogen has 1 proton and 1 electron but 0 neutrons. A small percentage of hydrogen atoms have 1 proton, 1 electron, and1 neutron. An even smaller percentage of hydrogen atoms hav ...
... A form of an atom that has a different number of neutrons than the common form of that atom. Ex. The most common form of hydrogen has 1 proton and 1 electron but 0 neutrons. A small percentage of hydrogen atoms have 1 proton, 1 electron, and1 neutron. An even smaller percentage of hydrogen atoms hav ...
Parts of an Atom
... The period an element is in is equal to the number of energy levels it has. (see the column of numbers in the upper right hand corner of each box) Properties change slowly from one end of each row to the other. Groups: Vertical columns of elements All elements in a group have similar propertie ...
... The period an element is in is equal to the number of energy levels it has. (see the column of numbers in the upper right hand corner of each box) Properties change slowly from one end of each row to the other. Groups: Vertical columns of elements All elements in a group have similar propertie ...
- St. Aidan School
... atoms that cannot be divided ii. All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. iii. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. They can not be created of destroyed in any ...
... atoms that cannot be divided ii. All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. iii. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. They can not be created of destroyed in any ...
COS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3
... determines atom’s chemical properties participate in chemical bonding Every atom has between one and eight ...
... determines atom’s chemical properties participate in chemical bonding Every atom has between one and eight ...
CHAPTER 3, ATOMS: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF MATTER
... The law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed during ordinary chemical reactions or physical changes. The law of definite proportions states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
... The law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed during ordinary chemical reactions or physical changes. The law of definite proportions states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
worksheet #1 - chemistryrocks.net
... number of ______________________ in a neutral atom of that element. The atomic number gives the “identity “of an element as well as its location on the Periodic Table. No two different elements will have the ______________________ atomic number. [4] The ______________________ of an element is the av ...
... number of ______________________ in a neutral atom of that element. The atomic number gives the “identity “of an element as well as its location on the Periodic Table. No two different elements will have the ______________________ atomic number. [4] The ______________________ of an element is the av ...
Review for Bonding Test
... join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. Which of these is a compound? ...
... join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. Which of these is a compound? ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.