Review for Bonding Test
... join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. Which of these is a compound? ...
... join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. Which of these is a compound? ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... the ATOMIC NUMBER is 11. The atom has a total ATOMIC MASS of approximately 23 – there must be neutrons along with the 11 protons to give a total mass of 23 amu (atomic mass ...
... the ATOMIC NUMBER is 11. The atom has a total ATOMIC MASS of approximately 23 – there must be neutrons along with the 11 protons to give a total mass of 23 amu (atomic mass ...
Atomic Structure Summary Sheet
... 1. If two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ra ...
... 1. If two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ra ...
physical earth science
... 3. Gold, silver and platinum are transition metals a. Located in groups 3-12 in periodic table b. Not found combined – found in nature pure c. Even less reactive d. Conduct heat/electricity e. Very useful in today’s society 4. Technetium and promethium are synthetic elements a. Synthetic – means man ...
... 3. Gold, silver and platinum are transition metals a. Located in groups 3-12 in periodic table b. Not found combined – found in nature pure c. Even less reactive d. Conduct heat/electricity e. Very useful in today’s society 4. Technetium and promethium are synthetic elements a. Synthetic – means man ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... properties that are different to those of the atoms of other elements. In a chemical reaction atoms are neither created, destroyed or charged into other atoms. Compounds are formed when two or more elements combine. When these postulates are combined they explain the earlier postulates that had been ...
... properties that are different to those of the atoms of other elements. In a chemical reaction atoms are neither created, destroyed or charged into other atoms. Compounds are formed when two or more elements combine. When these postulates are combined they explain the earlier postulates that had been ...
Unit 3 - Chemistry
... theories to explain his observations and came up with Dalton’s atomic theory. ...
... theories to explain his observations and came up with Dalton’s atomic theory. ...
HW-1-Ch1-Atomic-structure-W16
... 8. How long would it take for a sample of 222Rn that weighs 0.750 g to decay to 0.100 g? Assume a half-life for 222Rn of 3.823 days? ...
... 8. How long would it take for a sample of 222Rn that weighs 0.750 g to decay to 0.100 g? Assume a half-life for 222Rn of 3.823 days? ...
Chapter 11 and 12-2 Review/Study Guide for Test
... 5. What happens to the electrons in the atom when it becomes an ion? They are gained or lost to another atom. 6. What is an isotope? When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons from each other. 7. What determines the identity of an element? The number of protons in the nucleus ...
... 5. What happens to the electrons in the atom when it becomes an ion? They are gained or lost to another atom. 6. What is an isotope? When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons from each other. 7. What determines the identity of an element? The number of protons in the nucleus ...
Station 1 - The Periodic Table, Molecules and Molecular
... Station 2 – The Periodic Table and Naming 1. What is the distinction between atomic number and mass number? Between mass number and atomic mass? 2. Distinguish between the terms family and period in connection with the periodic table. For which of these is the term group also used. 3. When metals r ...
... Station 2 – The Periodic Table and Naming 1. What is the distinction between atomic number and mass number? Between mass number and atomic mass? 2. Distinguish between the terms family and period in connection with the periodic table. For which of these is the term group also used. 3. When metals r ...
Matter and Energy
... Properties of Matter Practice 1. Describe each of the following properties as physical or chemical: a. neon is a color gas at room temperature b. apple slices turn brown when exposed to air c. phosphorus will ignite when exposed to air d. at room temperature, mercury is a liquid e. propane gas is c ...
... Properties of Matter Practice 1. Describe each of the following properties as physical or chemical: a. neon is a color gas at room temperature b. apple slices turn brown when exposed to air c. phosphorus will ignite when exposed to air d. at room temperature, mercury is a liquid e. propane gas is c ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... More on the Atom • An atom is uniquely defined by #p+ = Z = atomic number (see Periodic Table) • In a neutral atom, #p+ = #e-; note that #n is not equal to #p+ nor #e-. • In an atomic ion, #p+ ≠ #e- resulting in a net nonzero charge on the species – Neutral atoms can lose electrons producing a posi ...
... More on the Atom • An atom is uniquely defined by #p+ = Z = atomic number (see Periodic Table) • In a neutral atom, #p+ = #e-; note that #n is not equal to #p+ nor #e-. • In an atomic ion, #p+ ≠ #e- resulting in a net nonzero charge on the species – Neutral atoms can lose electrons producing a posi ...
CH.2
... determine the atomic number, atomic mass, the number of protons, and the number of electrons of any atom of a particular element using a periodic table. (B5) determine the number of neutrons in an isotope given its mass number. (B5) perform calculations to determine the “weighted” average atomic ...
... determine the atomic number, atomic mass, the number of protons, and the number of electrons of any atom of a particular element using a periodic table. (B5) determine the number of neutrons in an isotope given its mass number. (B5) perform calculations to determine the “weighted” average atomic ...
Atoms and Their Electrons
... number of protons and the neutrons of an atom together. An element must have a certain number of protons but it can have a range of numbers of neutrons i.e. hydrogen can have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons to go with its 1 proton. These are called isotopes of hydrogen In real life there may be a number of diff ...
... number of protons and the neutrons of an atom together. An element must have a certain number of protons but it can have a range of numbers of neutrons i.e. hydrogen can have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons to go with its 1 proton. These are called isotopes of hydrogen In real life there may be a number of diff ...
Eighth Grade Review - PAMS-Doyle
... Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. ...
... Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes Q- Sometimes an isotope is written ...
... numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes Q- Sometimes an isotope is written ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes Q- Sometimes an isotope is written ...
... numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes Q- Sometimes an isotope is written ...
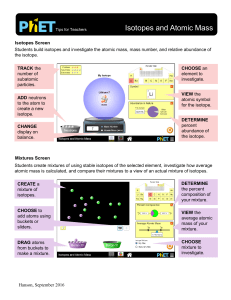
Isotopes and Atomic Mass
... • Calculate the mass number and write the name and atomic symbol for these isotopes of hydrogen: protium (0 neutrons), deuterium (1 neutron), and tritium (2 neutrons). • Your friend claims, “The chance of finding a specific isotope of an element is the same for all isotopes of that element”. Explain ...
... • Calculate the mass number and write the name and atomic symbol for these isotopes of hydrogen: protium (0 neutrons), deuterium (1 neutron), and tritium (2 neutrons). • Your friend claims, “The chance of finding a specific isotope of an element is the same for all isotopes of that element”. Explain ...
Friday, Feb 3, 2006
... neutron—no charge, relative mass = 1 11) Thomson passed an electric current through sealed glass tubes filled with gases The resulting glowing beam consisted of tiny negatively charged particles moving at high speed. Thomson concluded that electrons must be parts of the atoms of all elements. Millik ...
... neutron—no charge, relative mass = 1 11) Thomson passed an electric current through sealed glass tubes filled with gases The resulting glowing beam consisted of tiny negatively charged particles moving at high speed. Thomson concluded that electrons must be parts of the atoms of all elements. Millik ...
Page | 1 MATS1101 Chemistry notes semester 2 2012 TOPIC 1
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
Ch. 2 Chemical Basis of the Body (pp. 26-33)
... Health clinic: Clinical use of atomic particles * Isotopes are same atoms but have different number of neutrons *EX. Hydrogen usually has 1 proton and 0 neutrons. This is what water is made from. However, when hydrogen has 1 proton and 1 neutron, it is an isotope called deuterium or heavy water. ...
... Health clinic: Clinical use of atomic particles * Isotopes are same atoms but have different number of neutrons *EX. Hydrogen usually has 1 proton and 0 neutrons. This is what water is made from. However, when hydrogen has 1 proton and 1 neutron, it is an isotope called deuterium or heavy water. ...
Chapter 6: Chemistry in Biology
... When molecules come close together, the attractive forces between slightly positive and negative regions pull on the molecules and hold them together. ...
... When molecules come close together, the attractive forces between slightly positive and negative regions pull on the molecules and hold them together. ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... The pH of a substance can be determined using ____________________ paper Neutral substances have a pH of __________. An example of a common neutral substance is ____________. Acids- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range fo ...
... The pH of a substance can be determined using ____________________ paper Neutral substances have a pH of __________. An example of a common neutral substance is ____________. Acids- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range fo ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.