+ 2 HCL(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
... Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements. Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how many electrons an element has g ...
... Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements. Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how many electrons an element has g ...
Chemistry Midterm Exam 2015 (Study Guide) Unit 1: Measurement
... a. Ionic= made of metals & non-metals/exchanges or transfers electrons/ cation & anions/ strong bond/ high melting pts & boiling pts/ crystal structures/ can conduct electricity when dissolved in water/ called formula units b. Covalent- made of all non-metals/ shares electrons/ no charges/ weak bond ...
... a. Ionic= made of metals & non-metals/exchanges or transfers electrons/ cation & anions/ strong bond/ high melting pts & boiling pts/ crystal structures/ can conduct electricity when dissolved in water/ called formula units b. Covalent- made of all non-metals/ shares electrons/ no charges/ weak bond ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet Refer to your periodic table to fill in the
... Atomic Structure Worksheet Refer to your periodic table to fill in the table. Name: ____________________________________ The periodic table can give you a great deal of information about the composition of an atom. • The atomic number is equal to the number of protons. • The atomic mass is equal to ...
... Atomic Structure Worksheet Refer to your periodic table to fill in the table. Name: ____________________________________ The periodic table can give you a great deal of information about the composition of an atom. • The atomic number is equal to the number of protons. • The atomic mass is equal to ...
atomic number - Net Start Class
... the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. • An atom with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are called isotopes. • Isotopes are chemically alike, because it is the protons which are responsible for the chemical behavior. ...
... the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. • An atom with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are called isotopes. • Isotopes are chemically alike, because it is the protons which are responsible for the chemical behavior. ...
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
... 3. You will refer back to this page several times as you view this presentation. ...
... 3. You will refer back to this page several times as you view this presentation. ...
Basic Atomic Theory
... • The energy is therefore “quantized” – Only certain orbits with certain radii are possible – Orbits in between discrete value not possible ...
... • The energy is therefore “quantized” – Only certain orbits with certain radii are possible – Orbits in between discrete value not possible ...
File
... _____ 6. If two or more compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element that is combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. This statement is called the law of a. definite proportions. b. conservation ...
... _____ 6. If two or more compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element that is combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. This statement is called the law of a. definite proportions. b. conservation ...
Chap 11 Sect 1 Notes Atomic Theory
... •Electrons were free to rotate within the cloud of positive substance. ...
... •Electrons were free to rotate within the cloud of positive substance. ...
Honors Chemistry Name Julien Period _____ Date Atoms and
... b. All atoms of a given element are identical to one another and different from atoms of other elements. c. Atoms of two or more different elements combine to form compounds. A particular compound is always made up of the same kinds of atoms and the same number of each kind of atom. d. A chemical r ...
... b. All atoms of a given element are identical to one another and different from atoms of other elements. c. Atoms of two or more different elements combine to form compounds. A particular compound is always made up of the same kinds of atoms and the same number of each kind of atom. d. A chemical r ...
chem 1 TIFF new.indd
... atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons, so this number is also the number of electrons in an atom. For example, the smallest element is hydrogen. It has an atomic number of 1, which means it has only one proton. It also has only one electron, since the number of protons equals th ...
... atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons, so this number is also the number of electrons in an atom. For example, the smallest element is hydrogen. It has an atomic number of 1, which means it has only one proton. It also has only one electron, since the number of protons equals th ...
atomic number - Teacher Pages
... Group 18 is known as the Nobel Gases. These elements do not ordinarily form compounds, because the Nobel gases do not share or gain electrons. ...
... Group 18 is known as the Nobel Gases. These elements do not ordinarily form compounds, because the Nobel gases do not share or gain electrons. ...
Models of the Atom: A Historical perspective
... Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
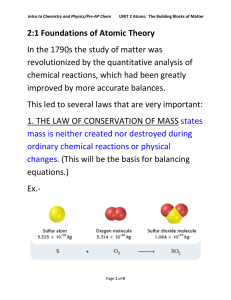
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... is used as fuel for nuclear power plants has a mass number of 235 and is known as uranium235 in hyphen notation. Isotopes can also be written with nuclear symbols in which the superscript indicates the mass number (protons+neutrons) and the subscript indicates the atomic number (number of protons). ...
... is used as fuel for nuclear power plants has a mass number of 235 and is known as uranium235 in hyphen notation. Isotopes can also be written with nuclear symbols in which the superscript indicates the mass number (protons+neutrons) and the subscript indicates the atomic number (number of protons). ...
Midterm Review File
... 17. Write the orbital diagram (arrow) for the following elements. You may use the noble gas base if you’d like. a. Oxygen b. Argon c. Barium ...
... 17. Write the orbital diagram (arrow) for the following elements. You may use the noble gas base if you’d like. a. Oxygen b. Argon c. Barium ...
Atomic Structure
... An atom is the smallest building block of matter. Atoms are made of neutrons, protons and electrons. The nucleus of an atom is extremely small in comparison to the atom. If an atom was the size of the Houston Astrodome, then its nucleus would be the size of a pea. Scientists use the Periodic Table i ...
... An atom is the smallest building block of matter. Atoms are made of neutrons, protons and electrons. The nucleus of an atom is extremely small in comparison to the atom. If an atom was the size of the Houston Astrodome, then its nucleus would be the size of a pea. Scientists use the Periodic Table i ...
File - 7th Grade Science
... Neutrons and Isotopes • Isotopes – atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Mass number – the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom ...
... Neutrons and Isotopes • Isotopes – atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Mass number – the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom ...
Periodic Table Jeopardy
... A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. All atoms in this substance have the same atomic #. ...
... A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. All atoms in this substance have the same atomic #. ...
Atomic Model
... cannot be pinpointed – Electrons are particles and waves at the same time – Developed quantum numbers based on theories of Einstein and Planck ...
... cannot be pinpointed – Electrons are particles and waves at the same time – Developed quantum numbers based on theories of Einstein and Planck ...
Electrons
... number of protons but different numbers of neutrons • Most elements in the first two rows of the periodic table have at least 2 isotopes with one being more common than the other • In nature, elements are almost always found as a mixture of isotopes ...
... number of protons but different numbers of neutrons • Most elements in the first two rows of the periodic table have at least 2 isotopes with one being more common than the other • In nature, elements are almost always found as a mixture of isotopes ...
Models of the Atom
... • Different types of matter are combinations of these basic elements • Based on philosophy, not experiment • Model accepted for 2000 years. ...
... • Different types of matter are combinations of these basic elements • Based on philosophy, not experiment • Model accepted for 2000 years. ...
Please use your NUMERICAL RESPONSE SHEET to answer the
... Use the following diagram to answer then next 4 questions Zarley was studying the periodic table and looking for any patterns in the arrangement of the elements. ...
... Use the following diagram to answer then next 4 questions Zarley was studying the periodic table and looking for any patterns in the arrangement of the elements. ...
Atomic Structure Notes File
... Since + and - charges are equal in atoms, it is also the number of electrons ...
... Since + and - charges are equal in atoms, it is also the number of electrons ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.