Document
... radioactive elements have too many protons or neutrons. Carbon-14, a radioactive form of carbon, has too may neutrons and its nucleus is unstable. This unstable nucleus will vibrate and contort and attempt to become stable by ejecting particles and giving off energy. This is radioactive decay giving ...
... radioactive elements have too many protons or neutrons. Carbon-14, a radioactive form of carbon, has too may neutrons and its nucleus is unstable. This unstable nucleus will vibrate and contort and attempt to become stable by ejecting particles and giving off energy. This is radioactive decay giving ...
Atomic Theory
... The modern quantum model of the atom is quite abstract and math provides the best description. Between wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle, it is difficult to describe the nature of the atom without some strange analogies. In this course, when discussing “locations” of electrons what ...
... The modern quantum model of the atom is quite abstract and math provides the best description. Between wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle, it is difficult to describe the nature of the atom without some strange analogies. In this course, when discussing “locations” of electrons what ...
800 - Paint Valley Local Schools
... called these and are arranged in a manner that the elements in these columns have similar chemical and physical properties. ...
... called these and are arranged in a manner that the elements in these columns have similar chemical and physical properties. ...
sch3u unit 1 test: matter
... 20. When baking soda is heated, sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide gas are formed. This reaction can be classified as a.synthesis b.combustion c.decomposition d.single displacement ...
... 20. When baking soda is heated, sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide gas are formed. This reaction can be classified as a.synthesis b.combustion c.decomposition d.single displacement ...
Atomic Structure
... ________ The Alkali Earth with the smallest atomic radius. ________ Element number 14 (element with atomic number 14). ________ The second period noble gas. ________ The first metal in group 1. ________ An element that reacts like chlorine, but has a smaller atomic radius. ________ A third period el ...
... ________ The Alkali Earth with the smallest atomic radius. ________ Element number 14 (element with atomic number 14). ________ The second period noble gas. ________ The first metal in group 1. ________ An element that reacts like chlorine, but has a smaller atomic radius. ________ A third period el ...
What is the atom?
... back them up • Came up with Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms • Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different ...
... back them up • Came up with Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms • Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different ...
7A SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW - MERRICK 7th SCIENCE REVIEW
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
Atomic Size
... nonmetallic bonding types. Radii of the noble gas elements are estimates from those of nearby elements. ...
... nonmetallic bonding types. Radii of the noble gas elements are estimates from those of nearby elements. ...
chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... Periodic Table (Revisited) Vertical columns indicate number of electrons in outermost shell ...
... Periodic Table (Revisited) Vertical columns indicate number of electrons in outermost shell ...
Chapter 2 part 1
... Periodic Table (Revisited) Vertical columns indicate number of electrons in outermost shell ...
... Periodic Table (Revisited) Vertical columns indicate number of electrons in outermost shell ...
10/3/16 Intro Atomic Theories
... in which having more data makes it easier to make a prediction. ...
... in which having more data makes it easier to make a prediction. ...
J.J. Thomson and the Cathode Ray Tube 1897
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical, those of different atoms are different. 3. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed. ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical, those of different atoms are different. 3. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed. ...
1 - My eCoach
... 18. A sample of Strontium 90 undergoes radioactive decay by emitting an alpha particle. The remaining atom is: a. Yttrium 90 c. Rubidium 88 b. Krypton 86 d. Rubidium 86 ...
... 18. A sample of Strontium 90 undergoes radioactive decay by emitting an alpha particle. The remaining atom is: a. Yttrium 90 c. Rubidium 88 b. Krypton 86 d. Rubidium 86 ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
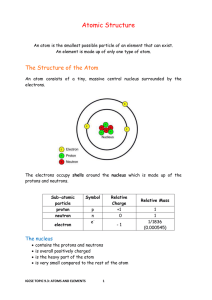
... 1. The Atomic Number of an atom = number of protons in the nucleus. 2. The Atomic Mass of an atom = number of Protons + Neutrons in the nucleus 3. The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. 4. Electrons orbit the nucleus in shells. 5. Each shell can only carry a set number of electrons. ...
... 1. The Atomic Number of an atom = number of protons in the nucleus. 2. The Atomic Mass of an atom = number of Protons + Neutrons in the nucleus 3. The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. 4. Electrons orbit the nucleus in shells. 5. Each shell can only carry a set number of electrons. ...
Name Date Class Period ______
... Name ______________________________________ Date __________________ Class Period _________ Atoms, Elements, and Compound Test Study Guide I. ...
... Name ______________________________________ Date __________________ Class Period _________ Atoms, Elements, and Compound Test Study Guide I. ...
Basic Atomic Structure and Isotope Symbols
... Atomic Number - is the number of protons in the atom. If the atom is neutral the atomic number is also the number of electrons in the atom. Mass Number - is the number of protons + neutrons in the atom. Both of these numbers will be parts of the Isotope Symbol. Both of these numbers are found by cou ...
... Atomic Number - is the number of protons in the atom. If the atom is neutral the atomic number is also the number of electrons in the atom. Mass Number - is the number of protons + neutrons in the atom. Both of these numbers will be parts of the Isotope Symbol. Both of these numbers are found by cou ...
unit 4 * organization of matter
... in our language that are formed from the 26 letters of the alphabet The atoms are like letters of the alphabet : they allow to form any substances which exist ...
... in our language that are formed from the 26 letters of the alphabet The atoms are like letters of the alphabet : they allow to form any substances which exist ...
Groups of the Periodic Table
... • Have some properties of metals AND some of non-metals • Some are very good conductors, others are very poor – used as semiconductors in circuits and lasers ...
... • Have some properties of metals AND some of non-metals • Some are very good conductors, others are very poor – used as semiconductors in circuits and lasers ...
9.3 Atoms and Elements notes
... each shell can only contain a fixed number of electrons. Once a shell is full, any remaining electrons must go into the next shell. Atoms of different elements contain different numbers of protons. If two atoms have the same number of protons then they must be atoms of the same element. Atoms have ...
... each shell can only contain a fixed number of electrons. Once a shell is full, any remaining electrons must go into the next shell. Atoms of different elements contain different numbers of protons. If two atoms have the same number of protons then they must be atoms of the same element. Atoms have ...
Chemistry 30A Chapter 2- Atoms and the Periodic Table Laney
... Back to elements: An element is characterized by its atomic number which is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. Thus the nucleus of lead contains 82 protons and the nucleus of iron contains 26 protons. The other number found alongside each element of the Periodic Table is the atomic mass ...
... Back to elements: An element is characterized by its atomic number which is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. Thus the nucleus of lead contains 82 protons and the nucleus of iron contains 26 protons. The other number found alongside each element of the Periodic Table is the atomic mass ...
study guide for atoms/periodic table quiz
... Energy Level A specific amount of energy related to the movement of electrons in atoms. Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons, but have the same number of protons. Periodic Table A chart which organizes elements into periods and families to help chemists understand them. Pe ...
... Energy Level A specific amount of energy related to the movement of electrons in atoms. Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons, but have the same number of protons. Periodic Table A chart which organizes elements into periods and families to help chemists understand them. Pe ...
Unit III * Introduction to Atomic Theory
... Summarize Dalton’s atomic theory. Distinguish among protons, electrons, and neutrons in terms of mass and charge. Describe the structure of the atom. ...
... Summarize Dalton’s atomic theory. Distinguish among protons, electrons, and neutrons in terms of mass and charge. Describe the structure of the atom. ...
Chapter 2 Outline 3rd PERIOD
... Elements are unique substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical methods Examples: oxygen, carbon, gold, copper, and iron Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen make up 96% of body weight All elements are shown on the periodic table Atoms are the building blocks ...
... Elements are unique substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical methods Examples: oxygen, carbon, gold, copper, and iron Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen make up 96% of body weight All elements are shown on the periodic table Atoms are the building blocks ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Study Guide
... 2) Complete the table below then use the diagram to compare and contrast the subatomic particles. Protons ...
... 2) Complete the table below then use the diagram to compare and contrast the subatomic particles. Protons ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.