File
... - Discovered that protons are located in a central nucleus. Atoms had too much mass - Scientists had discovered that atoms weighed more than they should if there was only protons and electrons. - There were also isotopes of elements that weighed different amounts but had the same charge as a regular ...
... - Discovered that protons are located in a central nucleus. Atoms had too much mass - Scientists had discovered that atoms weighed more than they should if there was only protons and electrons. - There were also isotopes of elements that weighed different amounts but had the same charge as a regular ...
Distinguishing Between Atoms
... 2. If the mass of 293Nv is 293.15 amu (red)and that of 295Nv is 295.15 amu (blue), what is the atomic mass of Nv? ...
... 2. If the mass of 293Nv is 293.15 amu (red)and that of 295Nv is 295.15 amu (blue), what is the atomic mass of Nv? ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... 19th Century) – When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratio of the masses of the second element that combine with 1g of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. The ratio of the masses of oxygen in H2O and H2O2 will be a small whole number (“2”). ...
... 19th Century) – When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratio of the masses of the second element that combine with 1g of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. The ratio of the masses of oxygen in H2O and H2O2 will be a small whole number (“2”). ...
Chapter 2 2012
... carbon by multiplying each isotope by its relative abundance and summing the two values. There are only two terms (isotopes) in ...
... carbon by multiplying each isotope by its relative abundance and summing the two values. There are only two terms (isotopes) in ...
20040702 - canteach
... lithium. The symbols Li-6 and Li-7 represent them. Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons in their atoms but varying numbers of neutrons. All isotopes of a given element have similar chemical and physical properties but may show very large variations in nuclear properties (in lighter ...
... lithium. The symbols Li-6 and Li-7 represent them. Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons in their atoms but varying numbers of neutrons. All isotopes of a given element have similar chemical and physical properties but may show very large variations in nuclear properties (in lighter ...
CHEM 1 0 1 - Near East University
... indicating mass on an atomic scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12. C-12 isotope with 6 proton and 6 neutron has a mass exactly 12amu Relative atomic masses ; . H: 1.008amu . He: 4.003amu . O: 16.00amu . Fe: 55.85amu ...
... indicating mass on an atomic scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12. C-12 isotope with 6 proton and 6 neutron has a mass exactly 12amu Relative atomic masses ; . H: 1.008amu . He: 4.003amu . O: 16.00amu . Fe: 55.85amu ...
Isotopes and Mass Number
... Calculating Atomic Mass Atomic Mass is the average of all an element’s masses You need two values ...
... Calculating Atomic Mass Atomic Mass is the average of all an element’s masses You need two values ...
Do Now - March [4-2], 2009 - stroh
... • An atom is the smallest particle of an element that has all the properties of that element – Electrically neutral (no charge) – Spherically shaped (like a ball) – Composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons ...
... • An atom is the smallest particle of an element that has all the properties of that element – Electrically neutral (no charge) – Spherically shaped (like a ball) – Composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons ...
Chapter 5: The periodic table is a tool for organizing
... Atoms of different elements have different properties. All matter is made of small, individual particles called atoms. Atoms of different elements can combine to form new substances. ...
... Atoms of different elements have different properties. All matter is made of small, individual particles called atoms. Atoms of different elements can combine to form new substances. ...
Physical Science 1st Semester final Review
... 7. Classify the matter below as either a pure substance or a mixture. If you believe that it is a pure substance, write down whether it is an element or a compound. If you believe that it is a mixture, write down whether or not is homogeneous or heterogeneous. a. Table salt (NaCl) ...
... 7. Classify the matter below as either a pure substance or a mixture. If you believe that it is a pure substance, write down whether it is an element or a compound. If you believe that it is a mixture, write down whether or not is homogeneous or heterogeneous. a. Table salt (NaCl) ...
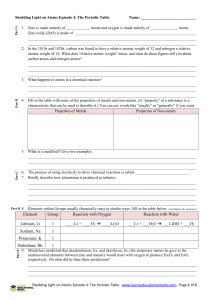
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... atomic weight of 14. What does “relative atomic weight” mean, and what do these figures tell you about carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms? ______________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
... atomic weight of 14. What does “relative atomic weight” mean, and what do these figures tell you about carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms? ______________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
Ch 4 - USD305.com
... • Groups 1 and 2, same # of electrons as group #, 312 have 2 or more, 13-18 same as group # -10 except for helium (only has 2) • Metals – Alkali, alkaline-earth, transition, others ...
... • Groups 1 and 2, same # of electrons as group #, 312 have 2 or more, 13-18 same as group # -10 except for helium (only has 2) • Metals – Alkali, alkaline-earth, transition, others ...
Atomic number
... 4.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms All atoms of a given element are identical The atoms of a given are different from those of any other ...
... 4.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms All atoms of a given element are identical The atoms of a given are different from those of any other ...
Chemistry
... Types of sub-atomic particles Neutron does not have an electrical charge called a neutral charge Neutrons and protons are almost exactly the same size but much larger than electrons ...
... Types of sub-atomic particles Neutron does not have an electrical charge called a neutral charge Neutrons and protons are almost exactly the same size but much larger than electrons ...
Matter
... A few elements, such as silicon, have some of the properties of metals and some of the properties of nonmetals. Since they are not clearly one or the other, they are called metalloids, or semimetals. They are used in making semiconductors – materials which can conduct some electricity better than an ...
... A few elements, such as silicon, have some of the properties of metals and some of the properties of nonmetals. Since they are not clearly one or the other, they are called metalloids, or semimetals. They are used in making semiconductors – materials which can conduct some electricity better than an ...
Teacher timeline events
... nucleus into smaller parts. This ejects more neutrons and continues the fission change reaction. 1941 - 51: Glenn Seaborg was able to actually artificially synthesize 6 transuranium elements. With the creation of these elements, the periodic table had to be changed to include them. 1942: Enrico Ferm ...
... nucleus into smaller parts. This ejects more neutrons and continues the fission change reaction. 1941 - 51: Glenn Seaborg was able to actually artificially synthesize 6 transuranium elements. With the creation of these elements, the periodic table had to be changed to include them. 1942: Enrico Ferm ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... in the B families. These are the metals you are probably most familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... in the B families. These are the metals you are probably most familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
study guide - atomic srtucture/_classification of matter
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
Atomic Structure and Isotopes
... > Atoms of the same elements are the same. > Atoms of different elements can combine together to make compounds. > Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. ...
... > Atoms of the same elements are the same. > Atoms of different elements can combine together to make compounds. > Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. ...
chapter 7 quiz
... J) 9.__G__The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. K) electron 10._T__The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus L) cathode of an atom. M) electron cloud 11._Y__Discovered radioactivity. N) Darth Vader 12._C__Discovered three types of radiation. O) chemical symbol 13._J__The charge on ...
... J) 9.__G__The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. K) electron 10._T__The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus L) cathode of an atom. M) electron cloud 11._Y__Discovered radioactivity. N) Darth Vader 12._C__Discovered three types of radiation. O) chemical symbol 13._J__The charge on ...
Unit 2 Test Review - Liberty High School
... 5. If sodium melts at 97.72° C and boils at 882.8°C, what is its physical state at 80°C? At 250°C? 6. What is a pure substance made up of more than one kind of atom called? 7. Describe the difference between a compound and an element. Give two examples of each. 8. How can a solution be distinguished ...
... 5. If sodium melts at 97.72° C and boils at 882.8°C, what is its physical state at 80°C? At 250°C? 6. What is a pure substance made up of more than one kind of atom called? 7. Describe the difference between a compound and an element. Give two examples of each. 8. How can a solution be distinguished ...
chapter 19 - Celina City Schools
... REFER to the National Geographic section entitled, “Visualizing the Atomic Model” (p.582) Section 2 – Masses of Atoms I. Atomic ____________ A) Atomic ____________ The number of protons (p+) in an atom Protons identify an ____________ B) Mass ____________ The sum of the number of protons and ...
... REFER to the National Geographic section entitled, “Visualizing the Atomic Model” (p.582) Section 2 – Masses of Atoms I. Atomic ____________ A) Atomic ____________ The number of protons (p+) in an atom Protons identify an ____________ B) Mass ____________ The sum of the number of protons and ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.









![Do Now - March [4-2], 2009 - stroh](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008519532_1-cab23fd6aae248311f653b62e7fe2161-300x300.png)