sites of protein synthesis in nucleoli of root meristematic cells of
... Light microscopy. A. cepa is a diploid species with a single pair of nucleolar chromosomes (Heitz, 1931). Two nucleoli, therefore, are formed at telophase and these, during interphase, may remain distinct (Fig. 1) or adhere to form a dumbbell-shaped structure, or fuse into a large spherical organell ...
... Light microscopy. A. cepa is a diploid species with a single pair of nucleolar chromosomes (Heitz, 1931). Two nucleoli, therefore, are formed at telophase and these, during interphase, may remain distinct (Fig. 1) or adhere to form a dumbbell-shaped structure, or fuse into a large spherical organell ...
Immunity Hemopoiesis and Cellular Drosophila
... its expression is necessary for cell maintenance during development (12, 13). The Drosophila genome encodes three RUNX transcription factors, of which Lozenge (Lz) is involved in hemopoiesis. Initially, it was observed that in a lozenge (lz) lossof-function mutant no crystal cells are formed (11). L ...
... its expression is necessary for cell maintenance during development (12, 13). The Drosophila genome encodes three RUNX transcription factors, of which Lozenge (Lz) is involved in hemopoiesis. Initially, it was observed that in a lozenge (lz) lossof-function mutant no crystal cells are formed (11). L ...
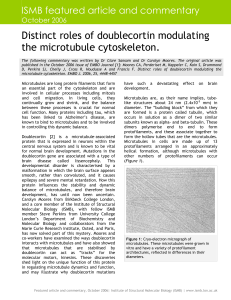
Distinct roles of doublecortin modulating the microtubule cytoskeleton.
... between protofilaments and that it might therefore impede kinesin movement along the microtubules. Moores and co-workers therefore examined kinesin motion along doublecortinstabilised tracks and found, surprisingly, that doublecortin binding did not prevent walking by kinesin motors. This means that ...
... between protofilaments and that it might therefore impede kinesin movement along the microtubules. Moores and co-workers therefore examined kinesin motion along doublecortinstabilised tracks and found, surprisingly, that doublecortin binding did not prevent walking by kinesin motors. This means that ...
Secreted Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Polypeptides Are Derived from
... (gp27s) are the major proteins in the virion outer coat. In the virus particle, this coat envelopes a nucleocapsid composed of a partially double-stranded DNA genome surrounded by core proteins. One of the remarkable features of HBsAg is that, unlike most viral envelope glycoproteins, both p24s and ...
... (gp27s) are the major proteins in the virion outer coat. In the virus particle, this coat envelopes a nucleocapsid composed of a partially double-stranded DNA genome surrounded by core proteins. One of the remarkable features of HBsAg is that, unlike most viral envelope glycoproteins, both p24s and ...
A. Penicillins
... the number of resistant strains, especially in S. aureus. The main mechanism of resistance is the production and secretion of β-lactamase enzyme. β-lactamase is a mutated version of transpeptidase which is closely related in structure, especially in the active site. This means that β-lactamase w ...
... the number of resistant strains, especially in S. aureus. The main mechanism of resistance is the production and secretion of β-lactamase enzyme. β-lactamase is a mutated version of transpeptidase which is closely related in structure, especially in the active site. This means that β-lactamase w ...
Gram Stain - American Proficiency Institute
... Common modifications of the classic Gram stain procedure involve variations in fixation method, reagents, and timing. Fixation, which attaches the specimen to the slide before staining, can be done with heat or methanol. In heat fixation, the slide is gently warmed so that all moisture evaporates fr ...
... Common modifications of the classic Gram stain procedure involve variations in fixation method, reagents, and timing. Fixation, which attaches the specimen to the slide before staining, can be done with heat or methanol. In heat fixation, the slide is gently warmed so that all moisture evaporates fr ...
The Drosophila wing differentiation factor Vestigial
... mediated via activation of the expression of dE2F transcription factor and its target genes, RNR2 and stg. However, ectopic vg, but not dE2F, is able to activate DHFR expression in the wing disc, raising the possibility that vg could control genes involved in DNA replication independently of dE2F. I ...
... mediated via activation of the expression of dE2F transcription factor and its target genes, RNR2 and stg. However, ectopic vg, but not dE2F, is able to activate DHFR expression in the wing disc, raising the possibility that vg could control genes involved in DNA replication independently of dE2F. I ...
The argos Gene Encodes a Diffusible Factor
... 1987). In afgos w7’ discs it appears that many of the mystery cells inappropriately start differentiating as neurons and never leave the developing ommatidia. Occasionally, extra neural cells are detected between ommatidia, rather than associated with a specific cluster. It is not known whether thes ...
... 1987). In afgos w7’ discs it appears that many of the mystery cells inappropriately start differentiating as neurons and never leave the developing ommatidia. Occasionally, extra neural cells are detected between ommatidia, rather than associated with a specific cluster. It is not known whether thes ...
Interesting Facts - Raleigh Charter High School
... Two paramecium bind forming a cytoplasmic bridge between them. Then the micronucleus of the paramecium undergoes meiosis. Four nuclei are formed, three disintegrate and the other duplicates by mitosis. The daughter nucleus moves across the bridge and fuses with the other daughter nucleus to for a di ...
... Two paramecium bind forming a cytoplasmic bridge between them. Then the micronucleus of the paramecium undergoes meiosis. Four nuclei are formed, three disintegrate and the other duplicates by mitosis. The daughter nucleus moves across the bridge and fuses with the other daughter nucleus to for a di ...
James G. Heys , 363 (2013); DOI: 10.1126/science.1233831
... Fig. 3. Membrane potential sag is weaker and slower in bat neurons. (A) Voltage responses measured at steady-state membrane potentials of –80 (left), –75 (middle), and –70 mV (right). Sag ratios (B) and time constants (C) in bat (blue) and rat (green) neurons at –80 (left), –75 (middle), and –70 mV ...
... Fig. 3. Membrane potential sag is weaker and slower in bat neurons. (A) Voltage responses measured at steady-state membrane potentials of –80 (left), –75 (middle), and –70 mV (right). Sag ratios (B) and time constants (C) in bat (blue) and rat (green) neurons at –80 (left), –75 (middle), and –70 mV ...
Bioelectricity Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential The postsynaptic cell
... The postsynaptic cell can either hyperpolarize or hypopolarize in response to the transmitter substance. It is possible to study the postsynaptic events by puncturing the soma of a cell with a microelectrode to pick up the changes in membrane potential that result from activity in a presynaptic axon ...
... The postsynaptic cell can either hyperpolarize or hypopolarize in response to the transmitter substance. It is possible to study the postsynaptic events by puncturing the soma of a cell with a microelectrode to pick up the changes in membrane potential that result from activity in a presynaptic axon ...
FIP2 and Rip11 specify Rab11a-mediated cellular
... [13] and functions as an adapter protein for the direct interaction of Rab11a with the motor protein myosin-Vb [14]. A second interesting member of the class I FIPs is Rip11 which also co-localises with Rab11a in endosomal membranes [15]. To investigate the functional role of Rab11a and its effector ...
... [13] and functions as an adapter protein for the direct interaction of Rab11a with the motor protein myosin-Vb [14]. A second interesting member of the class I FIPs is Rip11 which also co-localises with Rab11a in endosomal membranes [15]. To investigate the functional role of Rab11a and its effector ...
A Cellular Adventure
... Lysosome: Yeah, I do get very full. Sometimes I feel like I’m going to burst. All of the organelles mumble “Oh, no… don’t burst!” Ryan: Well, what’s wrong with that? Lysosome: Remember when I said that I was full of digestive enzymes? Ryan: Yeah, but what does that have to do with anything? Lysosom ...
... Lysosome: Yeah, I do get very full. Sometimes I feel like I’m going to burst. All of the organelles mumble “Oh, no… don’t burst!” Ryan: Well, what’s wrong with that? Lysosome: Remember when I said that I was full of digestive enzymes? Ryan: Yeah, but what does that have to do with anything? Lysosom ...
Quaternary ammonium surfactant structure determines selective
... attractive and cheap topical prophylactic options for sexually transmitted infections and perinatal vertically transmitted urogenital infections. Although attributed to their high affinity for biological membranes, the mechanisms behind QAS microbicidal activity are not fully understood. We evaluate ...
... attractive and cheap topical prophylactic options for sexually transmitted infections and perinatal vertically transmitted urogenital infections. Although attributed to their high affinity for biological membranes, the mechanisms behind QAS microbicidal activity are not fully understood. We evaluate ...
Dendritic cells in humans—from fetus to adult
... factors regulating myeloid development in humans are gradually being revealed [reviewed by Doulatov et al. (56)]. A number of transcription factors (TFs), including C/EBPα, IRF8, IRF4 and GATA2, are implicated in the regulation of myeloid cell generation; the most convincing evidence for the fundame ...
... factors regulating myeloid development in humans are gradually being revealed [reviewed by Doulatov et al. (56)]. A number of transcription factors (TFs), including C/EBPα, IRF8, IRF4 and GATA2, are implicated in the regulation of myeloid cell generation; the most convincing evidence for the fundame ...
The Role of Cytoskeletal Elements in Shaping Bacterial Cells
... kinases, and hsp70. Their search predicted three bacterial proteins (FtsA, MreB, and ParM (SbtA)) as additional members of the actin/sugar kinase/Hsp70 superfamiliy. FtsA is a division protein identified from the fts (filamentation temperature sensitive) screen for division-defective mutants of E. c ...
... kinases, and hsp70. Their search predicted three bacterial proteins (FtsA, MreB, and ParM (SbtA)) as additional members of the actin/sugar kinase/Hsp70 superfamiliy. FtsA is a division protein identified from the fts (filamentation temperature sensitive) screen for division-defective mutants of E. c ...
The Mechanisms and Mechanics of Archenteron Elongation during
... walls, and which have a relatively short distance to traverse during secondary invagination. The first result of the mechanical simulations is that when such shapes are modeled as elastic structures solely under the influence of filopodial pulling, the correct morphology cannot be obtained (Figs. Za ...
... walls, and which have a relatively short distance to traverse during secondary invagination. The first result of the mechanical simulations is that when such shapes are modeled as elastic structures solely under the influence of filopodial pulling, the correct morphology cannot be obtained (Figs. Za ...
Extracellular matrix stiffness in regulation of intestinal stem cell
... separate stem cells from other cell types. First, stem cells are undifferentiated. Due to their lack of tissue-specific features, stem cells are not able to carry out specialized functions. Second, unspecialized stem cells can divide without limits and renew themselves for long periods by replicatin ...
... separate stem cells from other cell types. First, stem cells are undifferentiated. Due to their lack of tissue-specific features, stem cells are not able to carry out specialized functions. Second, unspecialized stem cells can divide without limits and renew themselves for long periods by replicatin ...
Spatial Relationship between Transcription Sites and Chromosome
... with respect to the structural organization of interphase chromosomes is of functional significance for gene control. The aim of the present study is to elucidate whether transcription sites have a distinct spatial distribution in relation to the organization of chromosome territories and chromatin. ...
... with respect to the structural organization of interphase chromosomes is of functional significance for gene control. The aim of the present study is to elucidate whether transcription sites have a distinct spatial distribution in relation to the organization of chromosome territories and chromatin. ...
GNOM-LIKE1/ERMO1 and SEC24a/ERMO2 Are
... and Walz, 2001). The outer nuclear envelope is continuous with the rough ER, and the rough ER is distinguished from smooth ER by the presence of ribosomes on the cytosolic side of the membrane. The ER forms a dynamic polygonal network composed of tubules, sheets, and three-way junctions. In addition ...
... and Walz, 2001). The outer nuclear envelope is continuous with the rough ER, and the rough ER is distinguished from smooth ER by the presence of ribosomes on the cytosolic side of the membrane. The ER forms a dynamic polygonal network composed of tubules, sheets, and three-way junctions. In addition ...
Commentary in EMBO Journal
... autophagy protein LC3 in preparation for fusion of the double-membrane autophagosome to lysosomes. Lipidation of LC3 is a signature autophagic event, and it became apparent early on that autophagy was not solely a nutrient scavenging pathway, but one that also efficiently clears damaged organelles f ...
... autophagy protein LC3 in preparation for fusion of the double-membrane autophagosome to lysosomes. Lipidation of LC3 is a signature autophagic event, and it became apparent early on that autophagy was not solely a nutrient scavenging pathway, but one that also efficiently clears damaged organelles f ...
Peeping in on the cytoskeleton: light microscopy
... noise. Both these contribute to the greatly enhanced depth penetration achieved by TPCM. In addition, the longer red-shifted wavelengths are inherently less damaging to biological specimens than the more energetic shorter wavelengths. The other advantages of TPCM include the lack of pinholes and ass ...
... noise. Both these contribute to the greatly enhanced depth penetration achieved by TPCM. In addition, the longer red-shifted wavelengths are inherently less damaging to biological specimens than the more energetic shorter wavelengths. The other advantages of TPCM include the lack of pinholes and ass ...
Diatoms
... Most of the time, diatoms reproduce asexually by mitotic cell divisions. Each daughter cell receives half the cell wall of the original diatom and then regenerates the other half. They also reproduce sexually. ...
... Most of the time, diatoms reproduce asexually by mitotic cell divisions. Each daughter cell receives half the cell wall of the original diatom and then regenerates the other half. They also reproduce sexually. ...
Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor Signaling in
... background level of differentiation, which is only slightly above the level of differentiation of the parental cell line (or H19-7 cells transduced with the empty vector). Fig. 1B shows that all cell lines fail to grow and actually decrease in number in N2 SFM. Only H19-7/ IGF-IR cells grow at 34°C, ...
... background level of differentiation, which is only slightly above the level of differentiation of the parental cell line (or H19-7 cells transduced with the empty vector). Fig. 1B shows that all cell lines fail to grow and actually decrease in number in N2 SFM. Only H19-7/ IGF-IR cells grow at 34°C, ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.