Mitosis - World of Teaching
... • Chromatid - one strand of DNA; after replication, a chromosome is made up of two identical chromatids • Daughter cells - new cells produced by cell division • Cytokinesis – a division of the cytoplasm of one parent cell into 2 daughter cells ...
... • Chromatid - one strand of DNA; after replication, a chromosome is made up of two identical chromatids • Daughter cells - new cells produced by cell division • Cytokinesis – a division of the cytoplasm of one parent cell into 2 daughter cells ...
IRM CHAP 09
... 3. Explain the necessity of maintaining the same number of chromosomes per cell after cell division. 4. Understand what is meant by cell cycle and be able to visualize where mitosis fits into the cell cycle. 5. Be able to characterize each phase of mitosis. 6. Explain how the cytoplasm is apportione ...
... 3. Explain the necessity of maintaining the same number of chromosomes per cell after cell division. 4. Understand what is meant by cell cycle and be able to visualize where mitosis fits into the cell cycle. 5. Be able to characterize each phase of mitosis. 6. Explain how the cytoplasm is apportione ...
Mitosis *. Part II
... In animal cells, cytokinesis results when a fiber ring composed of a protein called actin around the center of the cell contracts pinching the cell into two daughter cells, each with one nucleus. In plant cells, the rigid wall requires that a cell plate be synthesized between the two daughter cells. ...
... In animal cells, cytokinesis results when a fiber ring composed of a protein called actin around the center of the cell contracts pinching the cell into two daughter cells, each with one nucleus. In plant cells, the rigid wall requires that a cell plate be synthesized between the two daughter cells. ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 1. What phase duplicates the cytoplasmic organelles? 2. What phase duplicates the DNA? 3. What phase checks that duplication is completed? 4. What do we need to do to grow bigger? 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During proph ...
... 1. What phase duplicates the cytoplasmic organelles? 2. What phase duplicates the DNA? 3. What phase checks that duplication is completed? 4. What do we need to do to grow bigger? 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During proph ...
Mitosis, Cell division and aging
... 3. Which stage or phase of the cell cycle corresponds to each of the descriptions below? a) A new cell wall begins to form. cytokinesis b) The membrane of the nucleus dissolves. prophase (starts to dissolve), metaphase (finished) c) Daughter chromosomes begin to separate. anaphase d) Thick chromosom ...
... 3. Which stage or phase of the cell cycle corresponds to each of the descriptions below? a) A new cell wall begins to form. cytokinesis b) The membrane of the nucleus dissolves. prophase (starts to dissolve), metaphase (finished) c) Daughter chromosomes begin to separate. anaphase d) Thick chromosom ...
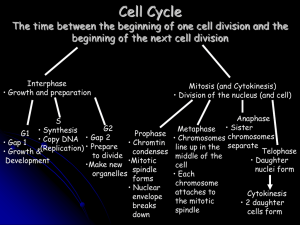
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A cell, whether it is one part of a larger
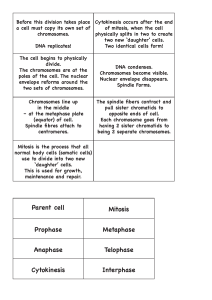
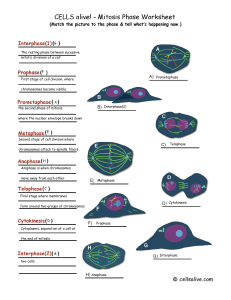
... divide it undergoes a process called MITOSIS, which is division of the nucleus. This is followed by division of the cytoplasm, which is called CYTOKINESIS. The entire process is best studied in stages, but remember they are a continual process! IPMAT - an anagram for remembering the stages. ...
... divide it undergoes a process called MITOSIS, which is division of the nucleus. This is followed by division of the cytoplasm, which is called CYTOKINESIS. The entire process is best studied in stages, but remember they are a continual process! IPMAT - an anagram for remembering the stages. ...
Check answers
... Growth; Cell is doing its job Includes G1, S, G2 Nuclear envelope/nucleoli are visible DNA is less condensed as chromatin S- DNA makes copy G2- Make organelles needed for new cell (EX: Centrosomes/centrioles are copied ) PROPHASE (1st dividing phase) Chromatin condenses; Chromosomes first visible Nu ...
... Growth; Cell is doing its job Includes G1, S, G2 Nuclear envelope/nucleoli are visible DNA is less condensed as chromatin S- DNA makes copy G2- Make organelles needed for new cell (EX: Centrosomes/centrioles are copied ) PROPHASE (1st dividing phase) Chromatin condenses; Chromosomes first visible Nu ...
Mitosis Notes
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move ...
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move ...
MS Word worksheet
... How does the nature of chromatin change at the end of the mitotic phase (extent of packing)? ...
... How does the nature of chromatin change at the end of the mitotic phase (extent of packing)? ...
How Do Cells Divide? 1. Regarding the mitotic phase of the cell
... How does its length compare to the S phase of the cycle? What are the two major events that occur during the mitotic phase? What "choices" does a cell have at the end of the mitotic phase? How does the nature of chromatin change at the end of the mitotic phase (extent of packing)? 2. Indicate the lo ...
... How does its length compare to the S phase of the cycle? What are the two major events that occur during the mitotic phase? What "choices" does a cell have at the end of the mitotic phase? How does the nature of chromatin change at the end of the mitotic phase (extent of packing)? 2. Indicate the lo ...
name
... 4. After the chromosomes replicate and condense they become visible during Prophase. Label this diagram of a doubled chromosome: ...
... 4. After the chromosomes replicate and condense they become visible during Prophase. Label this diagram of a doubled chromosome: ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
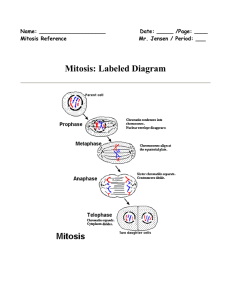
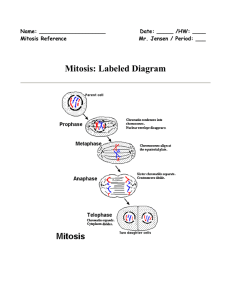
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.