on the ecological roles of salamanders
... Burton & Likens (1975a,b) first quantified both density and biomass of a salamander guild at a watershed scale. Working in the Hubbard Brook experimental forest of New Hampshire, they estimated that five salamander species had a combined average density of 2950 salamanders/ha (0.29/m2) and a biomass ...
... Burton & Likens (1975a,b) first quantified both density and biomass of a salamander guild at a watershed scale. Working in the Hubbard Brook experimental forest of New Hampshire, they estimated that five salamander species had a combined average density of 2950 salamanders/ha (0.29/m2) and a biomass ...
Evolutionary branching and sympatric speciation
... Evolutionary branching has been found in a number of models including models for the evolution of dispersal rates (Doebeli and Ruxton 1997, Parvinen 1999) and for the evolution of seed size (Geritz et al. 1999), in host-parasite models (Koella and Doebeli 1999, Boots and Haraguchi 1999), in models f ...
... Evolutionary branching has been found in a number of models including models for the evolution of dispersal rates (Doebeli and Ruxton 1997, Parvinen 1999) and for the evolution of seed size (Geritz et al. 1999), in host-parasite models (Koella and Doebeli 1999, Boots and Haraguchi 1999), in models f ...
Towards a framework for assessment and management of
... Ecosystems are affected by multiple human threats simultaneously (Halpern et al. 2008a). Recently, there has been increased emphasis on ecosystem-based management (EBM) approaches to address this challenge. EBM aims to sustain ecosystems and their services to humans considering the complexity of hum ...
... Ecosystems are affected by multiple human threats simultaneously (Halpern et al. 2008a). Recently, there has been increased emphasis on ecosystem-based management (EBM) approaches to address this challenge. EBM aims to sustain ecosystems and their services to humans considering the complexity of hum ...
Habitat degradation and fishing effects on the size structure of coral
... composition and structure of the benthic community. This is an unusual case study, as burgeoning populations on most tropical coasts increase the demands for marine resources and fishing intensity. However the current scenario in the Lau Islands is analogous to management strategies that endeavor to ...
... composition and structure of the benthic community. This is an unusual case study, as burgeoning populations on most tropical coasts increase the demands for marine resources and fishing intensity. However the current scenario in the Lau Islands is analogous to management strategies that endeavor to ...
Understanding the evolution and function of entomopathogenic fungi
... primarily transmitted horizontally, and produce infective stages which are released into the environment when the host dies. The infection cycle is continued when a new susceptible host acquires the infective stages from the environment. The efficiency of transmission in this system is affected very ...
... primarily transmitted horizontally, and produce infective stages which are released into the environment when the host dies. The infection cycle is continued when a new susceptible host acquires the infective stages from the environment. The efficiency of transmission in this system is affected very ...
A gentle depilation of the niche: Dicean
... particle size would have been represented more appropriately by employing several axes. One axis might scale mean particle size, another might scale variance of particle size, and others might scale other parameters of food particle size-frequency distributions. In that way, at each point in the nic ...
... particle size would have been represented more appropriately by employing several axes. One axis might scale mean particle size, another might scale variance of particle size, and others might scale other parameters of food particle size-frequency distributions. In that way, at each point in the nic ...
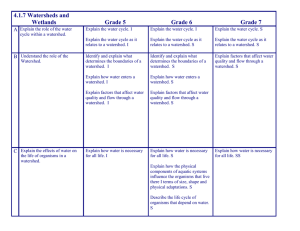
4.1.7 Watersheds and Wetlands
... predator/prey relationship and components. (S) how it maintains the balances within ecosystems. (S) Explain energy flow through a food web.(S) Explain the importance of the predator/prey relationship and how it maintains the balance within ecosystems. (S) Understand the limiting factors and predict ...
... predator/prey relationship and components. (S) how it maintains the balances within ecosystems. (S) Explain energy flow through a food web.(S) Explain the importance of the predator/prey relationship and how it maintains the balance within ecosystems. (S) Understand the limiting factors and predict ...
Scheldt Estuary Evaluation Methodology Phase 2
... securing economic, safety and wildlife interests, the Netherlands and Flanders jointly designed an integrated approach, viz. the Long-Term Vision (LTV), from which developed the Scheldt Estuary Development Outline 2010. In this context it was decided to set up the joint monitoring programme MONEOS. ...
... securing economic, safety and wildlife interests, the Netherlands and Flanders jointly designed an integrated approach, viz. the Long-Term Vision (LTV), from which developed the Scheldt Estuary Development Outline 2010. In this context it was decided to set up the joint monitoring programme MONEOS. ...
Patterns and Consequences of Interspecific Competition
... (individual or population; see below for explanation), the duration of the experiment, the number of sites and years in which the experiment was repeated, the number of different target and neighbor species or groups, the type of any additional treatments that were performed (e.g., herbivore protect ...
... (individual or population; see below for explanation), the duration of the experiment, the number of sites and years in which the experiment was repeated, the number of different target and neighbor species or groups, the type of any additional treatments that were performed (e.g., herbivore protect ...
Collection of Bait Organisms in Estuaries
... periods’ and provided reasons for its absence from these systems. More recent focus on the larval life history strategies has now shown that mud prawn larvae require an obligatory marine phase of development. First-stage larvae migrate from the estuary in highest numbers on the crepuscular ebb tide. ...
... periods’ and provided reasons for its absence from these systems. More recent focus on the larval life history strategies has now shown that mud prawn larvae require an obligatory marine phase of development. First-stage larvae migrate from the estuary in highest numbers on the crepuscular ebb tide. ...
Lack of relationship between below
... plants alter relative allocation to roots vs. shoots in response to below-ground competition, and whether the mass of a species’ root system accounts for interspecific differences in below-ground competitive response. 2 Seedlings of each of 10 native species were transplanted into the naturally occu ...
... plants alter relative allocation to roots vs. shoots in response to below-ground competition, and whether the mass of a species’ root system accounts for interspecific differences in below-ground competitive response. 2 Seedlings of each of 10 native species were transplanted into the naturally occu ...
EUR 22550 EN
... it is indeed necessary to state their clear goals. It should be avoided to use the general, broad term ‘biodiversity’ as it results in the lack of identification with the goal among the stakeholders, especially farmers, who fail to see its immediate impact on their own activities. The scale of AEM a ...
... it is indeed necessary to state their clear goals. It should be avoided to use the general, broad term ‘biodiversity’ as it results in the lack of identification with the goal among the stakeholders, especially farmers, who fail to see its immediate impact on their own activities. The scale of AEM a ...
Name Date: Per.: Score: ECOLOGY UNIT 6 Blended Learning Guide
... As you read the text, complete the following: 1. All ecosystems are made of _______________________ and ____________________components. 2. _________________factors are living things, such as _________________or ________________and include things that were once alive. 3. _________________factors are ...
... As you read the text, complete the following: 1. All ecosystems are made of _______________________ and ____________________components. 2. _________________factors are living things, such as _________________or ________________and include things that were once alive. 3. _________________factors are ...
Mutualisms in a changing world: an evolutionary
... drought episodes causing morphological and physiological changes that increase pathogenicity. Alternatively, shifts to antagonism could be heritable, with drought episodes favouring more thermophilic, increasingly pathogenic genotypes (Moricca & Ragazzi 2008). Finally, extreme and variable weather c ...
... drought episodes causing morphological and physiological changes that increase pathogenicity. Alternatively, shifts to antagonism could be heritable, with drought episodes favouring more thermophilic, increasingly pathogenic genotypes (Moricca & Ragazzi 2008). Finally, extreme and variable weather c ...
Energy flow of a boreal intertidal ecosystem, the Sylt
... First we compiled a holistic description of the standing stocks of the major communities and species in the Bight and of the interactions between them by means of a quantitative food web model that illustrated the rate of energy uptake, dissipation and transfer between the components of the system. ...
... First we compiled a holistic description of the standing stocks of the major communities and species in the Bight and of the interactions between them by means of a quantitative food web model that illustrated the rate of energy uptake, dissipation and transfer between the components of the system. ...
The intraspecific scaling of metabolic rate with body mass in fishes
... for animals and plants, both within and between species (Bokma 2004; Glazier 2005; White et al. 2006; Seibel 2007; Makarieva et al. 2008). A key question is to what extent is this variation just statistical ÔnoiseÕ about an average scaling relationship, compared with systematic variation that could ...
... for animals and plants, both within and between species (Bokma 2004; Glazier 2005; White et al. 2006; Seibel 2007; Makarieva et al. 2008). A key question is to what extent is this variation just statistical ÔnoiseÕ about an average scaling relationship, compared with systematic variation that could ...
DDT Persuasive Essay - APES -
... that animals such as lizards have no purpose in Borneo’s ecosystem. In reality, they controlled the caterpillar population, which bring us to the second point, survival of species is needed to maintain the equilibrium of an ecosystem. DDT causes damage to the environment and people by creating fluc ...
... that animals such as lizards have no purpose in Borneo’s ecosystem. In reality, they controlled the caterpillar population, which bring us to the second point, survival of species is needed to maintain the equilibrium of an ecosystem. DDT causes damage to the environment and people by creating fluc ...
The role of mixotrophic protists in the biological
... marked shift in the way that aquatic protists are popularly characterized and subdivided. Instead of the traditional “black-and-white” view that characterizes typical marine microbial protists as being either phototrophic “phytoplankton” or phagotrophic “microzooplankton”, they argued that a signifi ...
... marked shift in the way that aquatic protists are popularly characterized and subdivided. Instead of the traditional “black-and-white” view that characterizes typical marine microbial protists as being either phototrophic “phytoplankton” or phagotrophic “microzooplankton”, they argued that a signifi ...
limiting resources and the regulation of diversity in phytoplankton
... system as a model to look for community-level responses to resource availability via an index of diversity. Hutchinson (1961) noted that species richness and diversity of phytoplankton communities are often greater than the number of measured limiting resources even when conditions are apparently cl ...
... system as a model to look for community-level responses to resource availability via an index of diversity. Hutchinson (1961) noted that species richness and diversity of phytoplankton communities are often greater than the number of measured limiting resources even when conditions are apparently cl ...
BAILS et al 2005 Prescription for Great Lakes Ecosystem Protection and Restoration
... There is widespread agreement that the Great Lakes presently are exhibiting symptoms of extreme stress from a combination of sources that include toxic contaminants, invasive species, nutrient loading, shoreline and upland land use changes, and hydrologic modifications. Many of these sources of stre ...
... There is widespread agreement that the Great Lakes presently are exhibiting symptoms of extreme stress from a combination of sources that include toxic contaminants, invasive species, nutrient loading, shoreline and upland land use changes, and hydrologic modifications. Many of these sources of stre ...
Syllabus for F612
... production of eggs and sperm to the successful transformation into the juvenile form, and all steps in between. Throughout this course we will consider environmental constraints on reproduction and larval ecology, and their effects on the evolution of early life-history strategies in the marine envi ...
... production of eggs and sperm to the successful transformation into the juvenile form, and all steps in between. Throughout this course we will consider environmental constraints on reproduction and larval ecology, and their effects on the evolution of early life-history strategies in the marine envi ...
The role of metapopulations in conservation
... wild dogs and to minimize conflict with livestock farmers. Fences act as important barriers to the movements of the dogs, so that there is little emigration and even less immigration. The reserves are isolated from each other, with no possibility at present to establish corridors, and almost all mov ...
... wild dogs and to minimize conflict with livestock farmers. Fences act as important barriers to the movements of the dogs, so that there is little emigration and even less immigration. The reserves are isolated from each other, with no possibility at present to establish corridors, and almost all mov ...
Effects of exploitation on an overabundant species: the lesser snow
... to lower the seasonal density of a population, thereby freeing up resources for those surviving and potentially improving their survival in the following season (i.e. for every life taken, a life is saved; Boyce, Sinclair & White 1999), but the density-dependent mechanism could occur at various poin ...
... to lower the seasonal density of a population, thereby freeing up resources for those surviving and potentially improving their survival in the following season (i.e. for every life taken, a life is saved; Boyce, Sinclair & White 1999), but the density-dependent mechanism could occur at various poin ...
The emerging role of pharmacology in understanding consumer
... in which secondary metabolites alter the foraging behavior or fitness of aquatic consumers, or both. However, our understanding of the mechanisms that mediate the fate and consequences of these metabolites in aquatic consumers remains in its infancy. Interactions between metabolites and consumers at ...
... in which secondary metabolites alter the foraging behavior or fitness of aquatic consumers, or both. However, our understanding of the mechanisms that mediate the fate and consequences of these metabolites in aquatic consumers remains in its infancy. Interactions between metabolites and consumers at ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.