The New Alchemy
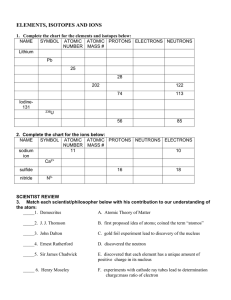
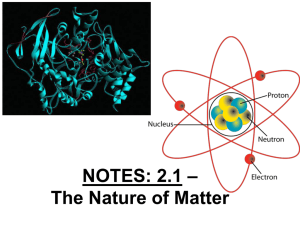
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
Minerals * Chemistry Review
... • Protons have a positive charge and are located in the nucleus • Neutrons have no charge and are located in the nucleus • Electrons are negatively charged and are located outside of the nucleus ...
... • Protons have a positive charge and are located in the nucleus • Neutrons have no charge and are located in the nucleus • Electrons are negatively charged and are located outside of the nucleus ...
Notes
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... become more stable by emitting radiation. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. This radiation can be emitted in the form of a positively charged alpha particle, a negatively charged ...
... become more stable by emitting radiation. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. This radiation can be emitted in the form of a positively charged alpha particle, a negatively charged ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
Chemistry Study Guide - Atomic structure and the Periodic Table 2010
... 3. Each of the more than 100 elements of matter has distinct properties and a distinct atomic structure. All forms of matter are composed of one or more of the elements. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. What is the structure of the atom and how are protons, neutrons, and electrons arran ...
... 3. Each of the more than 100 elements of matter has distinct properties and a distinct atomic structure. All forms of matter are composed of one or more of the elements. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. What is the structure of the atom and how are protons, neutrons, and electrons arran ...
Fall Final Exam Review Questions
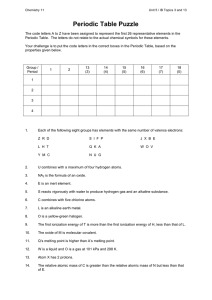
... 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and where are they generally located? 44. Make sure you know the major groups/chemical families ...
... 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and where are they generally located? 44. Make sure you know the major groups/chemical families ...
I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
Homework Geochem Test Review
... 12. What part of an atom is negative? _________ What part is positive? _________ What part is neutral? ___________ 13. What is the atomic mass? Why don’t we count the electrons when determining the ...
... 12. What part of an atom is negative? _________ What part is positive? _________ What part is neutral? ___________ 13. What is the atomic mass? Why don’t we count the electrons when determining the ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... Dimitri Mendeleev (18341907) organized information about all the known elements in a table that visually organized the similarities between them. Mendeleev placed each element on the table in a certain row and column based on its properties. ...
... Dimitri Mendeleev (18341907) organized information about all the known elements in a table that visually organized the similarities between them. Mendeleev placed each element on the table in a certain row and column based on its properties. ...
Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: Due date: SPS1
... Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: __________________________________Due date: _____________________ SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of ...
... Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: __________________________________Due date: _____________________ SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of ...
Abstract
... changing isotope ratios, because heavier isotopes are more difficult to move than lighter ones. Such isotope changes are called mass-dependent fractionation. The large isotope fractionation takes place between two isotopes with a large mass difference. In the case of oxygen, the fractionation in (18 ...
... changing isotope ratios, because heavier isotopes are more difficult to move than lighter ones. Such isotope changes are called mass-dependent fractionation. The large isotope fractionation takes place between two isotopes with a large mass difference. In the case of oxygen, the fractionation in (18 ...
Notes: Nuclear Fusion Basics
... • in the core of a star, temperatures reach 15,000,000oC • this causes the hydrogen atoms to move VERY fast ...
... • in the core of a star, temperatures reach 15,000,000oC • this causes the hydrogen atoms to move VERY fast ...
Atomic Crossword Name: Period: ____
... 4. The smallest element 7. Particle with no charge 8. Greek thinker who first coined the term "atomos" 11. A _____________ electron is in the outermost shell of an atom 12. Formed when atoms share electrons 14. Has a different number of neutrons than normal 15. The splitting of an atomic nucleus (us ...
... 4. The smallest element 7. Particle with no charge 8. Greek thinker who first coined the term "atomos" 11. A _____________ electron is in the outermost shell of an atom 12. Formed when atoms share electrons 14. Has a different number of neutrons than normal 15. The splitting of an atomic nucleus (us ...
Ions
... particle called an ion. When an atom loses an electron it has more protons therefore becoming positively charged. When an atom gains an electron it has more electrons therefore becoming negatively charged. ...
... particle called an ion. When an atom loses an electron it has more protons therefore becoming positively charged. When an atom gains an electron it has more electrons therefore becoming negatively charged. ...
Atom Structure and Isotopes
... Videoclip #2 Questions 1) What is the atomic number? number of protons in the nucleus 2) What are isotopes? Atoms with the same number of protons, but a DIFFERENT number of neutrons. 3) How many protons and neutrons are in the following carbon isotopes? Carbon-12 Carbon-13 Carbon-14 ...
... Videoclip #2 Questions 1) What is the atomic number? number of protons in the nucleus 2) What are isotopes? Atoms with the same number of protons, but a DIFFERENT number of neutrons. 3) How many protons and neutrons are in the following carbon isotopes? Carbon-12 Carbon-13 Carbon-14 ...
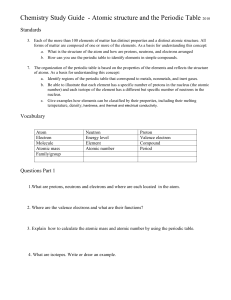
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW Electron Configurations Explain the
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
CHEMISTRY TERMS Period: Elements in the same horizontal row
... Period: Elements in the same horizontal row with the same ground state energy level. Periodic Law: Elements list in order of their atomic numbers that fall into reoccurring groups. Ionic Radius: the radius of an atom’s ion, measured by the distance between ions in a crystal lattice. Atomic Radius: o ...
... Period: Elements in the same horizontal row with the same ground state energy level. Periodic Law: Elements list in order of their atomic numbers that fall into reoccurring groups. Ionic Radius: the radius of an atom’s ion, measured by the distance between ions in a crystal lattice. Atomic Radius: o ...
Ions and isotopes
... • In any element, the # of protons is always constant. • the # of electrons and neutrons can change in an element without changing the identity of the element. ...
... • In any element, the # of protons is always constant. • the # of electrons and neutrons can change in an element without changing the identity of the element. ...