The Chemical Basis of Life Chapter 4
... How is Matter Organized? •Divided into pure substances or mixtures based on composition. –Pure substance •Uniform composition with same properties throughout •Can be classified as either an element or a compound ...
... How is Matter Organized? •Divided into pure substances or mixtures based on composition. –Pure substance •Uniform composition with same properties throughout •Can be classified as either an element or a compound ...
Chemistry Notes
... sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, lead, mercury, radon. Day 3 99% of the atoms mass in the nucleus The energy of the atom in the electron shells Most of an atom empty space ...
... sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, lead, mercury, radon. Day 3 99% of the atoms mass in the nucleus The energy of the atom in the electron shells Most of an atom empty space ...
The_Atoms_Family
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
Chap 7: Around the Room Review
... 1. The central part of an atom is called the _____ 2. A proton has a _____ charge. 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom t ...
... 1. The central part of an atom is called the _____ 2. A proton has a _____ charge. 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom t ...
Test 1
... Atoms contain the same number of protons and electrons. The mass of an atom in amu is approximated as the number of photons plus the number of neutrons present in the nucleus. Atoms can be split into a nucleus and the electrons, and the electrons move around the nucleus. Different isotopes of an ele ...
... Atoms contain the same number of protons and electrons. The mass of an atom in amu is approximated as the number of photons plus the number of neutrons present in the nucleus. Atoms can be split into a nucleus and the electrons, and the electrons move around the nucleus. Different isotopes of an ele ...
Thursday, October 31, 2013 D-day
... • Radioactive Elements- no naturally occurring stable isotope (what is an isotope?). – These elements loose neutrons and protons and emit them as particles. – All manmade elements are radioactive. ...
... • Radioactive Elements- no naturally occurring stable isotope (what is an isotope?). – These elements loose neutrons and protons and emit them as particles. – All manmade elements are radioactive. ...
Chapter 5
... 〉What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? 〉If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge. ...
... 〉What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? 〉If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge. ...
Isotope - MrKanesSciencePage
... 4. First stated that atoms of different elements have different masses. 5. His model of the atom is often called the “planetary” model 6. Discovered that most of the mass and positive charge of an atom is located in the center. 7. Shot positive alpha particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. 8. E ...
... 4. First stated that atoms of different elements have different masses. 5. His model of the atom is often called the “planetary” model 6. Discovered that most of the mass and positive charge of an atom is located in the center. 7. Shot positive alpha particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. 8. E ...
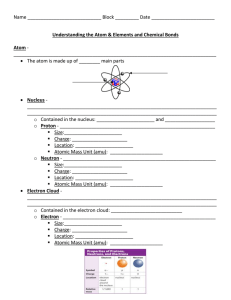
Understanding the Atom GN
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
Learning Objectives
... of atomic structure. 4. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 5. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 6. Explain how two is ...
... of atomic structure. 4. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 5. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 6. Explain how two is ...
6-Getting to Know the Periodic Table
... Complete the following objectives using the periodic table below. ...
... Complete the following objectives using the periodic table below. ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Vocabulary
... __________________________________________________________________ 2. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __ ...
... __________________________________________________________________ 2. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __ ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations
... atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically represent elements and isotopes chemists ...
... atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically represent elements and isotopes chemists ...
Unit 1 Atom
... when an x-ray photon transfers its energy to an orbital electron and ejects it from its shell. ...
... when an x-ray photon transfers its energy to an orbital electron and ejects it from its shell. ...
HW-1-Ch1-Atomic-structure-W16
... 8. How long would it take for a sample of 222Rn that weighs 0.750 g to decay to 0.100 g? Assume a half-life for 222Rn of 3.823 days? ...
... 8. How long would it take for a sample of 222Rn that weighs 0.750 g to decay to 0.100 g? Assume a half-life for 222Rn of 3.823 days? ...
200
... •Q How are the number of electrons in an atom determined? •A The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
... •Q How are the number of electrons in an atom determined? •A The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons ...
Chemistry Review: Antoine Lavoisier (1743
... there are 3 isotopes of hydrogen, with mass numbers of 1, 2 and 3. These atoms have different masses because they have different numbers of neutrons. However, since they have the same number of protons, they are the same element. Most elements have more than 1 naturally occurring isotope. However, t ...
... there are 3 isotopes of hydrogen, with mass numbers of 1, 2 and 3. These atoms have different masses because they have different numbers of neutrons. However, since they have the same number of protons, they are the same element. Most elements have more than 1 naturally occurring isotope. However, t ...
Atomic Structure
... •All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, only some are more common than others. •Atomic mass is the ______________________ of all isotopes of the element. •Even though isotopes have different amounts of neutrons they are still chemically alike since they have the same number of protons an ...
... •All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, only some are more common than others. •Atomic mass is the ______________________ of all isotopes of the element. •Even though isotopes have different amounts of neutrons they are still chemically alike since they have the same number of protons an ...
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure - Mercer Island School District
... • English schoolteacher John Dalton, 1803 – Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of ato ...
... • English schoolteacher John Dalton, 1803 – Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of ato ...
Chapter 18
... same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Average atomic mass—the weighted average mass of an element’s mixture of isotopes (used because most elements have more than one isotope) ...
... same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Average atomic mass—the weighted average mass of an element’s mixture of isotopes (used because most elements have more than one isotope) ...
Practice Test #2 - smhs
... The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to be 16.00% abundant, what is the percent abundance of the heaviest isotope? The average atomic mass ...
... The masses of these three isotopes are 148.1010 amu, 149.2005 amu, and 152.4107 amu, respectively. If the lightest isotope is three times as abundant as the heaviest, and the middle isotope is known to be 16.00% abundant, what is the percent abundance of the heaviest isotope? The average atomic mass ...
Quiz review
... Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called this. Vertical columns of the periodic table are called ‘groups’ or this. Which element in period 3 has 6 valence electrons? Which element in period 5 has only 1 electron in its 5s sublevel? Which element in period 3 has a full octet? What family of e ...
... Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called this. Vertical columns of the periodic table are called ‘groups’ or this. Which element in period 3 has 6 valence electrons? Which element in period 5 has only 1 electron in its 5s sublevel? Which element in period 3 has a full octet? What family of e ...
here
... 2. Describe how ionization energy and electronegativity change as you move from left to right along the periodic table and from top to bottom. Explain how all three of these plays a role in determining whether an atom “wants” to give away or take electrons. 3. Define what an atom’s atomic radius is. ...
... 2. Describe how ionization energy and electronegativity change as you move from left to right along the periodic table and from top to bottom. Explain how all three of these plays a role in determining whether an atom “wants” to give away or take electrons. 3. Define what an atom’s atomic radius is. ...