Atomic Structure ppt File
... contain a positive charge to balance the negative electrons 2. Because electrons have so much less mass than atoms, atoms must contain other particles that account for most of their mass • With this knowledge the first model of the atoms was purposed ...
... contain a positive charge to balance the negative electrons 2. Because electrons have so much less mass than atoms, atoms must contain other particles that account for most of their mass • With this knowledge the first model of the atoms was purposed ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 12) Period: a horizontal row in the periodic table of elements that have varying properties. 13) Reactive: indicates how likely an element is to undergo a chemical change. 14) Metal: an element that tends to be shiny, easily shaped, and a good conductor of electricity and heat. 15) Nonmetal: an elem ...
... 12) Period: a horizontal row in the periodic table of elements that have varying properties. 13) Reactive: indicates how likely an element is to undergo a chemical change. 14) Metal: an element that tends to be shiny, easily shaped, and a good conductor of electricity and heat. 15) Nonmetal: an elem ...
Unit 1: Atomic Structure AP Chemistry
... Law of Definite Proportions Nearly discovered the Law of multiple proportions, but his data used percentages instead of weights. ...
... Law of Definite Proportions Nearly discovered the Law of multiple proportions, but his data used percentages instead of weights. ...
Extra Credit Test Review
... greater than 92 is found naturally in measurable quantities on Earth. The remaining elements are artificially produced in a laboratory setting. 2. What did Rutherford contribute to the Atomic Theory? Most of the atom is empty space (with electrons in the space) AND there is a positive center to the ...
... greater than 92 is found naturally in measurable quantities on Earth. The remaining elements are artificially produced in a laboratory setting. 2. What did Rutherford contribute to the Atomic Theory? Most of the atom is empty space (with electrons in the space) AND there is a positive center to the ...
Chapter 7 Review Sheet
... 5. It would require more energy to remove an electron from Az than from any other element. 6. Jq has one more valence electron than Dw but one less valence electron than Gt. 7. The sizes of the 3 isoelectronic species are: Cx+ < Hs < By–. 8. Ev and Kp both lose the same number of electrons when they ...
... 5. It would require more energy to remove an electron from Az than from any other element. 6. Jq has one more valence electron than Dw but one less valence electron than Gt. 7. The sizes of the 3 isoelectronic species are: Cx+ < Hs < By–. 8. Ev and Kp both lose the same number of electrons when they ...
Atoms - misshoughton.net
... Each element has its own distinct properties. cannot be broken down into simpler parts by a chemical change. Compounds: pure substances made of more than one type of atom. Compounds are made of elements. NaCl (sodium chloride) is an example of a compound. ...
... Each element has its own distinct properties. cannot be broken down into simpler parts by a chemical change. Compounds: pure substances made of more than one type of atom. Compounds are made of elements. NaCl (sodium chloride) is an example of a compound. ...
Midterm Practice Test Answers
... 4. Give the electron configuration for each of the following. (You can do the short-hand notation): ...
... 4. Give the electron configuration for each of the following. (You can do the short-hand notation): ...
Atomic/Periodic Table Review
... 2. Where is most of the mass of an atom found? 3. What is the overall charge of the nucleus and why? 4. Where are the electrons and what keeps them from flying off? 5. What does the atomic number tell you about an element? 6. What is the difference b/w atomic mass and the mass number? 7. How can you ...
... 2. Where is most of the mass of an atom found? 3. What is the overall charge of the nucleus and why? 4. Where are the electrons and what keeps them from flying off? 5. What does the atomic number tell you about an element? 6. What is the difference b/w atomic mass and the mass number? 7. How can you ...
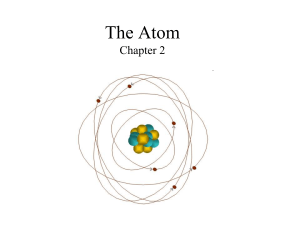
The Atom Chapter 2
... Hund’s Rule: electrons pair only after each orbital of equal energy is occupied by a single electron ...
... Hund’s Rule: electrons pair only after each orbital of equal energy is occupied by a single electron ...
Periodic Trends
... • Top number is the Atomic Number. It is the number of protons which equals the number of electrons • The bottom number is the Atomic Mass. The average number of Protons and Neutrons in an ...
... • Top number is the Atomic Number. It is the number of protons which equals the number of electrons • The bottom number is the Atomic Mass. The average number of Protons and Neutrons in an ...
File - Norris Science
... the tiny alpha particles would pass through the gold atoms and fly straight into the screen. ...
... the tiny alpha particles would pass through the gold atoms and fly straight into the screen. ...
Extra Credit Test Review
... 12.One atom has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 17 electrons. Another atom has 17 protons, 19 neutrons and 17 electrons. Are these the same element? Yes No Explain: __________________________________________________________________ 13.Today we use Mendeleev’s arrangement, elements are arranged by incre ...
... 12.One atom has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 17 electrons. Another atom has 17 protons, 19 neutrons and 17 electrons. Are these the same element? Yes No Explain: __________________________________________________________________ 13.Today we use Mendeleev’s arrangement, elements are arranged by incre ...
Chapter 11 and 12-2 Review/Study Guide for Test
... 13. Explain the difference between a group and a period on the periodic table of elements. Groups = columns (there are 18 total) and Periods = Rows (there are 7). Also, a group shares similar properties. 14. Why are neither the alkali metals nor the alkaline-earth metals found uncombined in nature? ...
... 13. Explain the difference between a group and a period on the periodic table of elements. Groups = columns (there are 18 total) and Periods = Rows (there are 7). Also, a group shares similar properties. 14. Why are neither the alkali metals nor the alkaline-earth metals found uncombined in nature? ...
Periodic Table Vocab page 7
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number identifies the atom. Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elem ...
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number identifies the atom. Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elem ...
1st Term Review
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... Atoms, Molecules, Ions – fundamentals of elements o Protons, electrons and neutrons make up an atom o Atoms make up molecules, all matter is made of atoms o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are buzzing outside the nucleus around the nucleus in orbitals o # of protons defines an ...
... Atoms, Molecules, Ions – fundamentals of elements o Protons, electrons and neutrons make up an atom o Atoms make up molecules, all matter is made of atoms o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are buzzing outside the nucleus around the nucleus in orbitals o # of protons defines an ...
answers_to_questions_on_pages_100
... Answers to Questions on Pages 100-101 5. A) Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus while the electrons orbit the nucleus in their respective energy levels. B) The protons and neutrons make up the majority of the mass of an atom. C) CORRECTION – The electrons make up most of the space as their ...
... Answers to Questions on Pages 100-101 5. A) Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus while the electrons orbit the nucleus in their respective energy levels. B) The protons and neutrons make up the majority of the mass of an atom. C) CORRECTION – The electrons make up most of the space as their ...
Section 1 Review
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
Periodic Table cloze activity.
... atom, atomic number, column, element, gold, inert, Mendeleev, metals, nonmetals, periodic, properties, symbol All matter is composed of various elements. An _________________ is a form of matter that is composed of a single type of _________________. In 1869, Dmitri _________________ created the ___ ...
... atom, atomic number, column, element, gold, inert, Mendeleev, metals, nonmetals, periodic, properties, symbol All matter is composed of various elements. An _________________ is a form of matter that is composed of a single type of _________________. In 1869, Dmitri _________________ created the ___ ...
(null): 096.AtomReview
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
File
... Some atomic masses may be written as a decimal (e.g. Carbon is actually 12.01, not ‘12’) This is because some elements have atoms with varying numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. ...
... Some atomic masses may be written as a decimal (e.g. Carbon is actually 12.01, not ‘12’) This is because some elements have atoms with varying numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. ...
Vocabulary and Section Summary
... Name ______________________________ Class___________________Date__________________ ...
... Name ______________________________ Class___________________Date__________________ ...