Chemical Bonds
... compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
... compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... the back of the cards, cut the cards out. 3. Try to match the vocabulary word with the correct definition. You will know if you’re correct if the ...
... the back of the cards, cut the cards out. 3. Try to match the vocabulary word with the correct definition. You will know if you’re correct if the ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom - A Historical Perspective
... Isotopes: Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons – Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. – E.g. Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. – Often, at least one isotope is unstable.It breaks down, releasing radioactivity.These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes ...
... Isotopes: Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons – Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. – E.g. Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. – Often, at least one isotope is unstable.It breaks down, releasing radioactivity.These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes ...
Matter_Quiz_Topics_2017
... Understand what is meant by the following terms: atom, proton, neutron and electron, isotope, atomic number, mass number, matter, families, period, charge, atomic mass, ion Discuss the structure of an atom. How many electrons can each of the first three energy levels hold? Where is most of the mass ...
... Understand what is meant by the following terms: atom, proton, neutron and electron, isotope, atomic number, mass number, matter, families, period, charge, atomic mass, ion Discuss the structure of an atom. How many electrons can each of the first three energy levels hold? Where is most of the mass ...
are made up of
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
2 - My George School
... 4. Atoms of one element can combine with _______________ to form __________. A given compound always has the same _______________________________ ...
... 4. Atoms of one element can combine with _______________ to form __________. A given compound always has the same _______________________________ ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... neutrons and protons (4.3) Use the atomic number and mass number to find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an atom (4.3) (Quiz 8) Describe how the isotopes of an atom differ (4.3) Calculate the average atomic mass of an element from isotope data using weighted averages (4.3) (B ...
... neutrons and protons (4.3) Use the atomic number and mass number to find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an atom (4.3) (Quiz 8) Describe how the isotopes of an atom differ (4.3) Calculate the average atomic mass of an element from isotope data using weighted averages (4.3) (B ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
Chapter 2
... understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 7. Expl ...
... understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 7. Expl ...
Matter and the Periodic Table Study Guide Answer Key
... 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound List the number of each type of atom making up the compound NH4 1 Nit ...
... 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound List the number of each type of atom making up the compound NH4 1 Nit ...
Worksheet 2: 1-19-17 - Iowa State University
... 2. Which of the following is not part of Daltons Atomic Theory of Matter? a. atoms cannot be changed to other elements by chemical reactions b. atoms of the same element are identical to one another c. elements are composed of atoms d. multiple atoms of the same element can combine to form other ele ...
... 2. Which of the following is not part of Daltons Atomic Theory of Matter? a. atoms cannot be changed to other elements by chemical reactions b. atoms of the same element are identical to one another c. elements are composed of atoms d. multiple atoms of the same element can combine to form other ele ...
PP 04 Atoms_ molecules_ ions
... The Law of Multiple Proportions: The elements making up a compound will form whole number ratios. Atom: The smallest particle that an element can be broken down into and still maintain the properties of the element. ...
... The Law of Multiple Proportions: The elements making up a compound will form whole number ratios. Atom: The smallest particle that an element can be broken down into and still maintain the properties of the element. ...
Atoms and Their Electrons
... number of protons and the neutrons of an atom together. An element must have a certain number of protons but it can have a range of numbers of neutrons i.e. hydrogen can have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons to go with its 1 proton. These are called isotopes of hydrogen In real life there may be a number of diff ...
... number of protons and the neutrons of an atom together. An element must have a certain number of protons but it can have a range of numbers of neutrons i.e. hydrogen can have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons to go with its 1 proton. These are called isotopes of hydrogen In real life there may be a number of diff ...
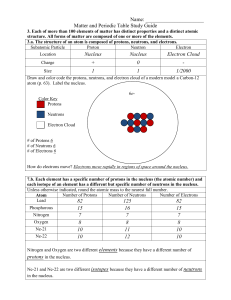
ISOTOPES 3 SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Proton Located inside the
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
ch2_objectives
... 9. Define the terms energy and potential energy. Explain why electrons in the first electron shell have less potential energy than electrons in higher electron shells. 10. Distinguish among nonpolar covalent, polar covalent and ionic bonds. 11. Explain why strong covalent bonds and weak bonds are b ...
... 9. Define the terms energy and potential energy. Explain why electrons in the first electron shell have less potential energy than electrons in higher electron shells. 10. Distinguish among nonpolar covalent, polar covalent and ionic bonds. 11. Explain why strong covalent bonds and weak bonds are b ...
Atomic Structure Power Point
... Because of ISOTOPES ! An isotope is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
... Because of ISOTOPES ! An isotope is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
Isotope PPT - MrsPage.com
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
PS7aChemistryReviewRevised
... NOW…Keep track of the electrons in the outer energy level! Where on the Periodic Table are the elements with 1 outer ...
... NOW…Keep track of the electrons in the outer energy level! Where on the Periodic Table are the elements with 1 outer ...
What is the history of chemistry and elements
... 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinat ...
... 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinat ...
atom - Images
... What is radioactivity? Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation from an element to achieve a more stable state. Uranium was the first radioactive element isolated (by Bequerel), followed by radium and polonium (by Marie Curie and her husband Pierre). There are no stable isotopes f ...
... What is radioactivity? Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation from an element to achieve a more stable state. Uranium was the first radioactive element isolated (by Bequerel), followed by radium and polonium (by Marie Curie and her husband Pierre). There are no stable isotopes f ...
2nd Semester Review
... 6. What causes a substance to change from one state to another?_______________________________ 7. Write physical or chemical change for each of the following: Water evaporating burning toast Fireworks exploding ice melting ...
... 6. What causes a substance to change from one state to another?_______________________________ 7. Write physical or chemical change for each of the following: Water evaporating burning toast Fireworks exploding ice melting ...
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE chapter three
... different numbers of neutrons. – This makes the mass of different atoms of the same element different. – The average mass is a weighted number so that more common isotopes have a greater affect on the average than rare isotopes. ...
... different numbers of neutrons. – This makes the mass of different atoms of the same element different. – The average mass is a weighted number so that more common isotopes have a greater affect on the average than rare isotopes. ...