Chapter 2 - U of L Class Index
... If the # protons changes, then it is not the same element. eg. The carbon atom has 6 protons in the nucleus. If you remove 1 proton from the carbon nucleus, you change the nature of the element. C - p → B if you add 1 proton to the carbon nucleus you get nitrogen. C + p → N These are nuclear reactio ...
... If the # protons changes, then it is not the same element. eg. The carbon atom has 6 protons in the nucleus. If you remove 1 proton from the carbon nucleus, you change the nature of the element. C - p → B if you add 1 proton to the carbon nucleus you get nitrogen. C + p → N These are nuclear reactio ...
+ mass isotope 2
... in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. • His ideas account for the law of conservation of mass (atoms are neither created nor destroyed) and the law of constant composition (elements combine in fixed ratios). ...
... in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. • His ideas account for the law of conservation of mass (atoms are neither created nor destroyed) and the law of constant composition (elements combine in fixed ratios). ...
File
... Circle or highlight the correct word(s) in the brackets [ ] to complete the following sentences. [Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon] has a full valence shell and is a noble gas. Noble gases are [inert, very reactive, only react with certain elements]. [Potassium, Calcium, Sulfur, Neon] has properties most sim ...
... Circle or highlight the correct word(s) in the brackets [ ] to complete the following sentences. [Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon] has a full valence shell and is a noble gas. Noble gases are [inert, very reactive, only react with certain elements]. [Potassium, Calcium, Sulfur, Neon] has properties most sim ...
Biol 1441
... Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner. Ion: a charged atom (or molecule) Cation: a positive ...
... Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner. Ion: a charged atom (or molecule) Cation: a positive ...
Chemistry
... I. Discovered the atom’s nucleus by shooting Alpha particles into gold foil. J. First to theorize that atoms are small indivisible particles. K. Used the cathode ray tube to ID negative particles which led to the plum pudding model of the atom. L. Theorized that all matter is continuous and not made ...
... I. Discovered the atom’s nucleus by shooting Alpha particles into gold foil. J. First to theorize that atoms are small indivisible particles. K. Used the cathode ray tube to ID negative particles which led to the plum pudding model of the atom. L. Theorized that all matter is continuous and not made ...
The Periodic Table
... 13. A period (a row) on the periodic table has elements that have what in common… A. They have similar chemical properties B. They have the same number of electrons C. They have the same number of electron shells D. They are similarly reactive in compounds. 14. The vertical columns in a periodic tab ...
... 13. A period (a row) on the periodic table has elements that have what in common… A. They have similar chemical properties B. They have the same number of electrons C. They have the same number of electron shells D. They are similarly reactive in compounds. 14. The vertical columns in a periodic tab ...
element - Mrs. Phillips` Physical Science Webpage
... • The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. – During Mendeleev’s time, this arrangement left several blanks, however, the table exhibited a regularly repeating pattern, which could be used to predict the properties of elements that had not been discovered yet. – He was proven right ...
... • The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. – During Mendeleev’s time, this arrangement left several blanks, however, the table exhibited a regularly repeating pattern, which could be used to predict the properties of elements that had not been discovered yet. – He was proven right ...
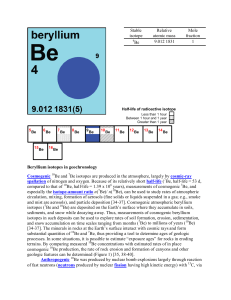
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... fission – the spontaneous (or induced by particle collision) splitting of a heavy nucleus into a pair (only rarely more) of nearly equal fission fragments (fission products) generally with some neutrons. Fission is accompanied by the release of a large quantity of energy. [return] gamma rays (gamma ...
... fission – the spontaneous (or induced by particle collision) splitting of a heavy nucleus into a pair (only rarely more) of nearly equal fission fragments (fission products) generally with some neutrons. Fission is accompanied by the release of a large quantity of energy. [return] gamma rays (gamma ...
study guide - atomic srtucture/_classification of matter
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
Document
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
Atoms and Atomic Structure
... one element differ from those of another. • Compounds form when atoms of elements combine in certain proportions • During chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, not changed or destroyed. ...
... one element differ from those of another. • Compounds form when atoms of elements combine in certain proportions • During chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, not changed or destroyed. ...
Topic 2.1- The Nuclear Atom
... the cloud and recorded where the beams came out. Can you figure out the shape of the target? ...
... the cloud and recorded where the beams came out. Can you figure out the shape of the target? ...
Metals
... “elements”: air, fire, water, and earth. People believed this for many centuries! • In the late 1600s, early chemists began to discover that this was not the case, that there are more than 4 elements and they are not what the Greeks thought they were. • Now we know that all matter in the universe is ...
... “elements”: air, fire, water, and earth. People believed this for many centuries! • In the late 1600s, early chemists began to discover that this was not the case, that there are more than 4 elements and they are not what the Greeks thought they were. • Now we know that all matter in the universe is ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
... parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) elements that are lighter than the parent atom. • During the fission of U235, ...
... parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) elements that are lighter than the parent atom. • During the fission of U235, ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Notes
... particles called ________________________. 2) ______________________ of the same _______________________ are ____________________. Atoms of __________________ _________________ are ...
... particles called ________________________. 2) ______________________ of the same _______________________ are ____________________. Atoms of __________________ _________________ are ...
Subatomic Heavyweights
... Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS have the same number of protons • Atomic weight: the weighted average atomic mass of the naturally occurring isotopes (the # on the periodic table) ...
... Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS have the same number of protons • Atomic weight: the weighted average atomic mass of the naturally occurring isotopes (the # on the periodic table) ...
Atomic structure and periodic table
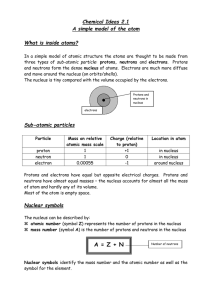
... Atomic number (proton number) The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Atomic number is characteristic of each element No two elements can have the same atomic number Mass number (nucleon number) The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom Atomic number and mass number are often writt ...
... Atomic number (proton number) The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Atomic number is characteristic of each element No two elements can have the same atomic number Mass number (nucleon number) The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom Atomic number and mass number are often writt ...
Present - Images
... Nuclear Reactions Nuclear reactions change the composition of an atom’s nucleus –the element will change!! Examples of naturally occurring nuclear reactions include alpha and beta decay, and fission and fusion. Some nuclei can become unstable by artificial transmutation, where a nucleus is bom ...
... Nuclear Reactions Nuclear reactions change the composition of an atom’s nucleus –the element will change!! Examples of naturally occurring nuclear reactions include alpha and beta decay, and fission and fusion. Some nuclei can become unstable by artificial transmutation, where a nucleus is bom ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... Has no electrical charge (neutral). Found in the nucleus of an atom. More massive than electrons. Protons + Neutrons = Atomic Mass ...
... Has no electrical charge (neutral). Found in the nucleus of an atom. More massive than electrons. Protons + Neutrons = Atomic Mass ...
Atomic Structure
... as a whole. • If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be about the size of a ...
... as a whole. • If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be about the size of a ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Also on closer inspection of the different n levels, additional fine structure is observed within each n level and these are assigned different letters of the alphabet. According to the mathematics each s, p, d level can accommodate 2 electrons. There is one s level for each shelf, three equivalent ...
... Also on closer inspection of the different n levels, additional fine structure is observed within each n level and these are assigned different letters of the alphabet. According to the mathematics each s, p, d level can accommodate 2 electrons. There is one s level for each shelf, three equivalent ...
answers
... c.) Rutherford – discovered positively charged nucleus d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
... c.) Rutherford – discovered positively charged nucleus d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
Chapter 1 D Study Guide
... 1. Charges: protons = positive, electrons = negative, neutrons = non 2. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. Th ...
... 1. Charges: protons = positive, electrons = negative, neutrons = non 2. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. Th ...