Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
Lecture 2
... An element is defined its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more ...
... An element is defined its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more ...
Reading Quiz
... Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons. An atom that loses an electron becomes a positive ion (CATION) An atom that gains an electron becomes a negative ion (ANION) ...
... Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons. An atom that loses an electron becomes a positive ion (CATION) An atom that gains an electron becomes a negative ion (ANION) ...
Building an Atom
... For this extra credit project you must build a 3D model of the atom Sulfur- 33. You can use whatever type of supplies you can think of, as long as it looks semi-professional. (Sloppy or incorrect models will receive little to no credit, don’t waste your time). Your model of the atom MUST include all ...
... For this extra credit project you must build a 3D model of the atom Sulfur- 33. You can use whatever type of supplies you can think of, as long as it looks semi-professional. (Sloppy or incorrect models will receive little to no credit, don’t waste your time). Your model of the atom MUST include all ...
Atomic Structure/Electrons
... 10. He discovered the electron and developed the “plum pudding” model of the atom. 11. His five postulates make up atomic theory. 12. His gold foil experiment led to his discovery of the nucleus. 13. He developed the planetary model of the atom, which described the light spectrum. 14. What is the sh ...
... 10. He discovered the electron and developed the “plum pudding” model of the atom. 11. His five postulates make up atomic theory. 12. His gold foil experiment led to his discovery of the nucleus. 13. He developed the planetary model of the atom, which described the light spectrum. 14. What is the sh ...
CHAPTER 18 NOTES
... • Area around the nucleus of an atom where its electrons are most likely found • Farther an electron is from the nucleus, the more energy • Electrons with lower amount of energy are in the first level • 1st – 2 electrons 2nd – 8 electrons 3rd – 18 electrons 4th – 32 electrons ...
... • Area around the nucleus of an atom where its electrons are most likely found • Farther an electron is from the nucleus, the more energy • Electrons with lower amount of energy are in the first level • 1st – 2 electrons 2nd – 8 electrons 3rd – 18 electrons 4th – 32 electrons ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this year is the Periodic Table and its power of predicting the existence and properties of elements yet to be discovered. Dimitri Mendeleev placed the 65 known elements of his time into a grid table and observed gaps in the table. Based on ...
... The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this year is the Periodic Table and its power of predicting the existence and properties of elements yet to be discovered. Dimitri Mendeleev placed the 65 known elements of his time into a grid table and observed gaps in the table. Based on ...
Chapter 14 Inside the Atom Notes
... 1. When a proton is released, one element changes into another, a process called transmutation. ...
... 1. When a proton is released, one element changes into another, a process called transmutation. ...
Atoms and Elements Notes
... made into wire) 5. Malleable (Can be flattened) 6. All solids except Hg and H ...
... made into wire) 5. Malleable (Can be flattened) 6. All solids except Hg and H ...
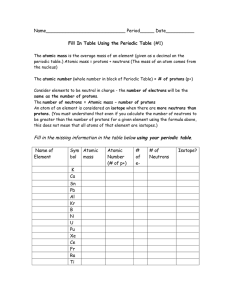
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
Periodic Table of Elements * Study Guide
... Study and understand the following: Atomic Structure: How to find an element’s: atomic number atomic mass what two particles make up the atomic mass? what makes up the atom’s volume? # of protons Electrical charge of proton, electron, neutron # of electrons # of neutrons group # ...
... Study and understand the following: Atomic Structure: How to find an element’s: atomic number atomic mass what two particles make up the atomic mass? what makes up the atom’s volume? # of protons Electrical charge of proton, electron, neutron # of electrons # of neutrons group # ...
SS18A - Atoms, Isotopes and Ions
... 1. What are isotopes? In addition to the atomic number, every atom can also be described by its mass number. The mass number is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Recall that atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Atoms of the same element can ...
... 1. What are isotopes? In addition to the atomic number, every atom can also be described by its mass number. The mass number is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Recall that atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Atoms of the same element can ...
Chapter 5
... • Left blank spots in table which predicted _________ of elements not yet discovered ...
... • Left blank spots in table which predicted _________ of elements not yet discovered ...
File
... b. How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Identify the solute: _____________________________________________________________________ d. Identify the solvent: ____________________________________________________________________ 1. List the 4 signs of ...
... b. How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Identify the solute: _____________________________________________________________________ d. Identify the solvent: ____________________________________________________________________ 1. List the 4 signs of ...
TEST II Study Guide-Atomic Theory Honors Chemistry
... 6. ______ What type of bombarding particle was used in Rutherford's "gold foil" experiment? A) alpha; B) beta; C) gamma; D) neutron; E) neutrino; F) X rays. 7. ______ This color-blind English schoolteacher studied the findings of many of his contemporaries, and put forth the first comprehensive atom ...
... 6. ______ What type of bombarding particle was used in Rutherford's "gold foil" experiment? A) alpha; B) beta; C) gamma; D) neutron; E) neutrino; F) X rays. 7. ______ This color-blind English schoolteacher studied the findings of many of his contemporaries, and put forth the first comprehensive atom ...
Name: Chapter 4 and 5 Study Guide Who was the Greek
... a. Its atomic mass b. Attractions between its atoms c. Its number of valence electrons d. The ratio of protons and neutrons 26. Which of the halogens is the most reactive? ...
... a. Its atomic mass b. Attractions between its atoms c. Its number of valence electrons d. The ratio of protons and neutrons 26. Which of the halogens is the most reactive? ...
Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
Chemical Change
... The chemical properties of elements are related to the energy changes that take place when atoms lose, gain or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. ...
... The chemical properties of elements are related to the energy changes that take place when atoms lose, gain or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. ...
Atoms Vs. Molecules
... Isotopes (atoms with different numbers of protons and neutrons) can become unstable and are called radioactive. They can be used to identify certain chemical reactions, or for nuclear development. ...
... Isotopes (atoms with different numbers of protons and neutrons) can become unstable and are called radioactive. They can be used to identify certain chemical reactions, or for nuclear development. ...
Ch. 6 Vocabulary
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...