CHEM 1301 FALL 2003 TEST 1 VERSION 1 NO CHEATING
... The mass of an atom in amu is approximated as the number of protons plus the number of neutrons present in the nucleus. Atoms can be split into a nucleus and the electrons, but usually the electrons are stuck in the nucleus. Different isotopes of an element contain different numbers of electrons. Th ...
... The mass of an atom in amu is approximated as the number of protons plus the number of neutrons present in the nucleus. Atoms can be split into a nucleus and the electrons, but usually the electrons are stuck in the nucleus. Different isotopes of an element contain different numbers of electrons. Th ...
Atomic Theory- 1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles
... Atomic Theory1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. An element is composed of one type of atom. Properties of atoms are identical to each other. 3. A compound contains two or more different elements. The relative number of atoms of each element in a compound is the sam ...
... Atomic Theory1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. An element is composed of one type of atom. Properties of atoms are identical to each other. 3. A compound contains two or more different elements. The relative number of atoms of each element in a compound is the sam ...
22-Introduction to Radioactivity
... electron. Since the electron has only about 1/2000th the mass of a proton or neutron, when beta decay occurs, the mass number ______________________ the same. But because the β-particle has a negative charge, the atomic number _______________________ by one. For example, C-14 undergoes beta decay to ...
... electron. Since the electron has only about 1/2000th the mass of a proton or neutron, when beta decay occurs, the mass number ______________________ the same. But because the β-particle has a negative charge, the atomic number _______________________ by one. For example, C-14 undergoes beta decay to ...
Isotopes
... 1. Use Video #5 – to take notes over isotopes on the back of your paper from today. Then write the paragraph at the bottom of the page. 2. Study for quiz tomorrow! (over scientists and ...
... 1. Use Video #5 – to take notes over isotopes on the back of your paper from today. Then write the paragraph at the bottom of the page. 2. Study for quiz tomorrow! (over scientists and ...
Chapter 5
... •Center of atom was called nucleus. •Nucleus made up most of the weight of the atom. •Electrons were negative particles that randomly orbited the nucleus. ...
... •Center of atom was called nucleus. •Nucleus made up most of the weight of the atom. •Electrons were negative particles that randomly orbited the nucleus. ...
Ch4StudyGuide
... Why do most atoms have no charge even though they are made up of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons? ...
... Why do most atoms have no charge even though they are made up of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons? ...
The Chemical Context of Life
... The different stages of energy that electrons have are called energy levels, or electron shells ...
... The different stages of energy that electrons have are called energy levels, or electron shells ...
Slide 1
... We cannot show videos due to copyright. Sources for appropriate videos may include: Discovery Education and AGC Educational Media ...
... We cannot show videos due to copyright. Sources for appropriate videos may include: Discovery Education and AGC Educational Media ...
Dmitri MendeleevанааA Russian chemist, noticed a repeating
... pattern of chemical properties in the elements that were known at the time. Mendeleev arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic mass to form something close to the modern day periodic table. The pattern of repeating order is called periodicity. ...
... pattern of chemical properties in the elements that were known at the time. Mendeleev arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic mass to form something close to the modern day periodic table. The pattern of repeating order is called periodicity. ...
Atoms and Isotopes Worksheet
... 3. The atomic masses of two isotopes of Cobalt are 59 and 60. If Cobalt has 27 electrons, what is the number of protons and neutrons in each isotope? ...
... 3. The atomic masses of two isotopes of Cobalt are 59 and 60. If Cobalt has 27 electrons, what is the number of protons and neutrons in each isotope? ...
Atom Building blocks of matter Proton Sub
... Electron found in outermost shell of an atom; determines atoms chemical properties ...
... Electron found in outermost shell of an atom; determines atoms chemical properties ...
Atomic Structure
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
Structure of the Atom
... Note the following symbols: (they are not to scale) = proton (positive charge) = electron (negative charge) = neutron (no charge) The following three diagrams are hydrogen atoms: ...
... Note the following symbols: (they are not to scale) = proton (positive charge) = electron (negative charge) = neutron (no charge) The following three diagrams are hydrogen atoms: ...
3-2 Radioactivity and the nucleus
... At first the atom was thought to be a solid ball but then when electrons were discovered it was thought to be like plum pudding with the negative electrons embedded in a positive atom (Fig.1 p.280). ...
... At first the atom was thought to be a solid ball but then when electrons were discovered it was thought to be like plum pudding with the negative electrons embedded in a positive atom (Fig.1 p.280). ...
10.2
... • He concluded that most of the atom is made of ‘empty space’, and that the core of the atom carried a positive charge (he called the core nucleus and the positive charges the protons). • He also suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun (Fig.3 p.281). ...
... • He concluded that most of the atom is made of ‘empty space’, and that the core of the atom carried a positive charge (he called the core nucleus and the positive charges the protons). • He also suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the Sun (Fig.3 p.281). ...
Extension 18.2: Isotopes
... The number of protons does determine which element it is, but the mass number essentially determines its mass (the nucleus’s mass is approximately equal to the mass number times the proton’s mass): M nucleus ≈ A x mproton. So different forms of an element may have different mass. ...
... The number of protons does determine which element it is, but the mass number essentially determines its mass (the nucleus’s mass is approximately equal to the mass number times the proton’s mass): M nucleus ≈ A x mproton. So different forms of an element may have different mass. ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioactive decay or bombardment with another particle. Many isotopes are unstable, and undergo spontaneous radioactive d ...
... changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioactive decay or bombardment with another particle. Many isotopes are unstable, and undergo spontaneous radioactive d ...
Unit 2 Notes - School City of Hobart
... • For a nuclide to be considered radioactive, it must have an unstable nucleus due to an imbalance between # of protons and neutrons ~1:1 ratio = stable *The further an isotope is from a 1:1 ratio, the more likely it is to be radioactive (Figure 21.2, p.881) • Types of Nuclear Decay (aka Radioactivi ...
... • For a nuclide to be considered radioactive, it must have an unstable nucleus due to an imbalance between # of protons and neutrons ~1:1 ratio = stable *The further an isotope is from a 1:1 ratio, the more likely it is to be radioactive (Figure 21.2, p.881) • Types of Nuclear Decay (aka Radioactivi ...
The study of biology can help you better understand human
... Atoms of isotopes of an element have different number of protons The nucleus of an atom has positive charge. Atoms are mostly empty space. ...
... Atoms of isotopes of an element have different number of protons The nucleus of an atom has positive charge. Atoms are mostly empty space. ...
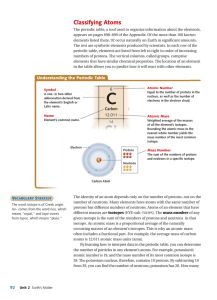
Classifying Atoms
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...