VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... number of positive charges equal the number of negative charges All elements on periodic table are stable atoms. ...
... number of positive charges equal the number of negative charges All elements on periodic table are stable atoms. ...
2.2 Periodic Trends
... What are the trends that occur in the periodic table by organizing elements by their atomic number? Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic t ...
... What are the trends that occur in the periodic table by organizing elements by their atomic number? Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic t ...
First Semester Honors Chemistry Exam Review (2011
... Dalton's atomic theory agrees with modern atomic theory except for what? The deflection of cathode rays in Thomson's experiments was evidence of the ____ nature of electrons. Whose series of experiments identified the nucleus of the atom? What happened to the alpha particles in Rutherford's experime ...
... Dalton's atomic theory agrees with modern atomic theory except for what? The deflection of cathode rays in Thomson's experiments was evidence of the ____ nature of electrons. Whose series of experiments identified the nucleus of the atom? What happened to the alpha particles in Rutherford's experime ...
Chemistry Test Review – 8th Science Vocabulary: Element atom
... Chemistry Test Review – 8th Science Vocabulary: ...
... Chemistry Test Review – 8th Science Vocabulary: ...
RAD 354 Chapt 3 Structure of Matter
... nucleus outward (also numbered 1,2,3,4,5 from the nucleus outward). • Max POTENTIAL number of electrons in any shell 2n2 • The number of electrons in the outer most shell tells which GROUP and PERIOD it exists in the periodic table ...
... nucleus outward (also numbered 1,2,3,4,5 from the nucleus outward). • Max POTENTIAL number of electrons in any shell 2n2 • The number of electrons in the outer most shell tells which GROUP and PERIOD it exists in the periodic table ...
Pre-class Activity 12/18
... For positive ions, charge numbers increase as more electrons are lost from the atom. The electrostatic force is greater for smaller numbers of electrons which decreases the ionic radius. For negative ions, as the charge number increases, so does the number of electrons. Electrostatic forces decrease ...
... For positive ions, charge numbers increase as more electrons are lost from the atom. The electrostatic force is greater for smaller numbers of electrons which decreases the ionic radius. For negative ions, as the charge number increases, so does the number of electrons. Electrostatic forces decrease ...
Physical Science Chapter 6 Study Guide Every element consists of
... Nuclear ______________—a type of controlled reaction used to harness useful energy ...
... Nuclear ______________—a type of controlled reaction used to harness useful energy ...
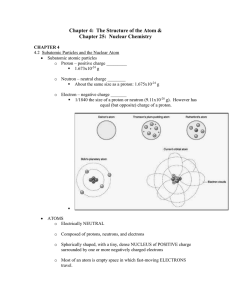
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... o Above the band of stability – too many _____________; Below the band of stability – too many _______________ or too few ______________ o BETA DECAY: For elements above the band of stability (too many neutrons) A NEUTRON will decay into a PROTON (stays in the nucleus) and an ELECTRON (leaves the ...
... o Above the band of stability – too many _____________; Below the band of stability – too many _______________ or too few ______________ o BETA DECAY: For elements above the band of stability (too many neutrons) A NEUTRON will decay into a PROTON (stays in the nucleus) and an ELECTRON (leaves the ...
Elements and the Periodic Table Section One
... Chemical Symbol: a one- or two- letter representation of an element (pg. 82) Family: elements in the same vertical column of the periodic table; also called group (pg. 82) Group: elements in the same vertical column of the periodic table; also called family (pg. 82) Period: a horizontal row of eleme ...
... Chemical Symbol: a one- or two- letter representation of an element (pg. 82) Family: elements in the same vertical column of the periodic table; also called group (pg. 82) Group: elements in the same vertical column of the periodic table; also called family (pg. 82) Period: a horizontal row of eleme ...
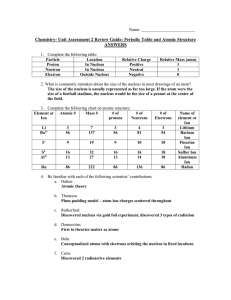
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what v ...
... Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what v ...
Date Period - Swift Classroom
... This repeating pattern is called _____________________ and he called his table the periodic table of elements. Arrangement of the Periodic Table: Each element is identified by the number of _____________________ it has in its nucleus (unique to each element) The number of protons in an atom of ...
... This repeating pattern is called _____________________ and he called his table the periodic table of elements. Arrangement of the Periodic Table: Each element is identified by the number of _____________________ it has in its nucleus (unique to each element) The number of protons in an atom of ...
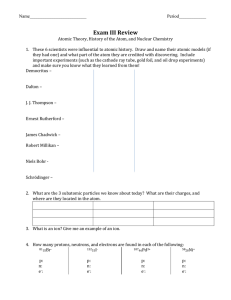
Exam III Review
... 7. Write the nuclear equation that represents the alpha decay of americium-243. ...
... 7. Write the nuclear equation that represents the alpha decay of americium-243. ...
Lesson 13 - Highline Public Schools
... A chemist investigating a sample of lithium found that some lithium atoms have a lower mass than other lithium atoms. The chemist drew models of the two different types of lithium atoms, as shown on the following slide. ...
... A chemist investigating a sample of lithium found that some lithium atoms have a lower mass than other lithium atoms. The chemist drew models of the two different types of lithium atoms, as shown on the following slide. ...
Atomic Structure - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... So, what’s up with all these isotopes anyway? In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more ...
... So, what’s up with all these isotopes anyway? In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more ...
File
... atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no ...
... atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no ...
PP - myndrs.com
... – Gives the order of elements on the periodic table – If an atom gains or loses a proton it not only changes its atomic number, it also becomes a new element. ...
... – Gives the order of elements on the periodic table – If an atom gains or loses a proton it not only changes its atomic number, it also becomes a new element. ...
Structure of an Atom structure_of_atom
... – Gives the order of elements on the periodic table – If an atom gains or loses a proton it not only changes its atomic number, it also becomes a new element. ...
... – Gives the order of elements on the periodic table – If an atom gains or loses a proton it not only changes its atomic number, it also becomes a new element. ...
Atom - Sites
... atoms join together chemically. •Combinations of two or more different elements are called compounds. •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together f ...
... atoms join together chemically. •Combinations of two or more different elements are called compounds. •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together f ...
Matter and the Periodic Table
... system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern chemistry's ...
... system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern chemistry's ...