* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1: Atomic Structure AP Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
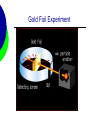
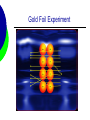
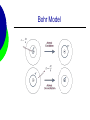
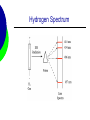
Unit 1: Atomic Structure AP Chemistry Evolution of Atomic Theory Democritus – 400 B.C. Greek Philosopher Imagined particles that were indivisible Constituents of matter Atom comes from “atomos” Opposed Aristotle Aristotle – 350 B.C. Widely accepted theory that all matter can be continually divided. Set science back for thousands of years. Alchemy A pseudoscience that superceded scientific discoveries. Alchemists attempted to turn metals into gold and developing the “elixir” of life (able to cause immortality and create life). Pierre Gassendi - 1650 Reintroduced Particulate theory No experimental evidence Supported by Sir Isaac Newton Robert Boyle - 1661 Studied Gases 1st to use the term element in its current context in his book The Skeptical Chemist George Stahl - 1717 Suggested “phlogiston” flowed from burning material A necessary ingredient of combustible material Joseph Priestly - 1774 discovered oxygen supports combustion Antoine Lavoisier - 1778 Developed Law of Conservation of Mass Explained combustion Joseph Proust - 1799 Developed “Proust’s Law” using copper oxide Later renamed, the Law of Definite Proportions Nearly discovered the Law of multiple proportions, but his data used percentages instead of weights. John Dalton - 1802 First to develop an atomic theory. It has 4 postulates. Each element is made up of atoms Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and properties. Atoms of different elements differ in some way. John Dalton - 1802 Compounds are made when atoms combine. If elements combine in more than one whole number ratio, the resulting compound has different properties Chemical reactions involve the reorganization of atoms. Amedeo Avogadro - 1811 Developed Avogadro’s Law. Equal volumes of gases have equal number of molecules at constant temperature and pressure. Expanded Dalton’s concept of atomic masses J.J. Berzelius - 1813 Established the 1st system of using letters to represent elements. William Prout - 1815 Proposed that Hydrogen was the fundamental material that all other elements were made from. All atomic masses were multiples of the mass of hydrogen. Michael Faraday - 1833 Found Faraday’s Constant. 1 mole of e- = 96500 coulombs. Alexandre Béguyer de Chancourtois 1862 1st periodic arrangement of elements. Divided surface of a cylindrical base into 16 segments because oxygen has a mass of 16. John Newland - 1863 Developed the law of octaves Properties of elements repeat every eighth element. Dimitri Mendeleev - 1869 Classification based on chemical properties. Considered the first periodic table. Left gaps for missing elements and predicted their properties William Crookes - 1879 Showed that cathode rays stream from the negative pole Eugene Goldstein - 1886 Discovered the proton using a cathode ray tube. William Roentgen - 1895 Discovered x-rays. Rays were penetrating and of short wavelength Henri Becquerel - 1896 Discovered radioactivity. Used uranium salts Marie Curie - 1897 Student of Becquerel Showed that radioactivity is atomic property Isolated radium and polonium J.J. Thomson - 1897 Determined the mass/charge ratio of the electron. 5.69 x 10-9 Used the cathode ray tube Proposed a model of the atom that was mockingly called the “plum pudding” model Robert Millikan - 1909 Determined the charge of the electron using the famous oil-drop experiment 1.60 x 10-19 From this and Thomson’s value, the mass was calculated to be 9.11 x 10-28g Ernest Rutherford - 1911 Performed the famous gold foil experiment Determined 3 things The atom is mostly empty space The nucleus is positively charged The nucleus is a small dense part of the atom Gold Foil Experiment Gold Foil Experiment Henry Moseley - 1913 Calculated atomic number by determining the nuclear charge of an atom. Niels Bohr - 1913 Observed spectral lines for hydrogen Proposed an orbit theory of the electron around the atom. Bohr Model Hydrogen Spectrum Gilbert Lewis - 1916 Suggested that noble gases have 8 valence electrons Atoms will gain or lose electrons to achieve 8 outer electrons. Louis De broglie - 1924 Suggested that matter could exhibit wave properties Observed diffraction patterns in electrons Wolfgang Pauli - 1924 Pauli Exclusion Principle – 2 electrons cannot have the same 4 quantum numbers Erwin Schrödinger - 1926 Developed a wave equation. Mathematical function that described the nature of the electron James Chadwick - 1932 Discovered the neutron Other Contributions C.D. Anderson – 1932 Discovered the positron Enrico Fermi – 1940 Prepared more than 40 radioactive elements