Sub Unit Plan 1 Chem Periodic Table
... 3.1bb The succession of elements across the same period demonstrates characteristic trends: differences in atomic radius, ionic radius, electronegativity, first ionization energy, metallic/nonmetallic properties. Explain chemical bonding in terms of the behavior of electrons. Major Understandings: 5 ...
... 3.1bb The succession of elements across the same period demonstrates characteristic trends: differences in atomic radius, ionic radius, electronegativity, first ionization energy, metallic/nonmetallic properties. Explain chemical bonding in terms of the behavior of electrons. Major Understandings: 5 ...
ppt
... • Compare ions to their neutral counterparts • Ion: charged atom that results from the gaining or losing of electrons • Cation: loses electrons and produces a positive charge • Anion: gains electrons and produces a negative charge ...
... • Compare ions to their neutral counterparts • Ion: charged atom that results from the gaining or losing of electrons • Cation: loses electrons and produces a positive charge • Anion: gains electrons and produces a negative charge ...
The Periodic Table HL Page 1 of 3 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... Defn: Newland’s Octaves are arrangements of elements in which the first and the eighth element, counting from a particular element, have similar properties. 3. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of incre ...
... Defn: Newland’s Octaves are arrangements of elements in which the first and the eighth element, counting from a particular element, have similar properties. 3. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of incre ...
Subject - Currituck County Schools
... Structure of Matter Illustrate how observations and conclusions from experimentation changed atomic theory over time. Explain Dalton’s atomic theory, which states the following: o Chemical elements are made up of atoms. o The atoms of an element are identical in their masses. (Be sure students under ...
... Structure of Matter Illustrate how observations and conclusions from experimentation changed atomic theory over time. Explain Dalton’s atomic theory, which states the following: o Chemical elements are made up of atoms. o The atoms of an element are identical in their masses. (Be sure students under ...
answers
... d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
... d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
Fire Up Your Atoms!!
... physical property of metals that lets them be flattened into thin sheets Draw it: ...
... physical property of metals that lets them be flattened into thin sheets Draw it: ...
Ch 11 Atoms etc GNC
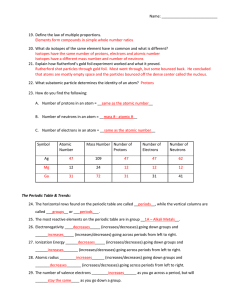
... 1. There are 115 known elements. 2. 90 naturally occurring elements, 25 synthetic elements—made in laboratories B. Periodic Table—Chart that organizes and displays information about the elements 1. Atomic number—the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element a. The number of proto ...
... 1. There are 115 known elements. 2. 90 naturally occurring elements, 25 synthetic elements—made in laboratories B. Periodic Table—Chart that organizes and displays information about the elements 1. Atomic number—the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element a. The number of proto ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations
... atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically represent elements and isotopes chemists ...
... atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically represent elements and isotopes chemists ...
Deconstructed HS-PS1-2
... Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a simple chemical reaction based on the outermost electron states of atoms, trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties.[Clarification Statement: Examples of chemical reactions could include the reaction of ...
... Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a simple chemical reaction based on the outermost electron states of atoms, trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties.[Clarification Statement: Examples of chemical reactions could include the reaction of ...
Honors Chemistry Chapter 6 Student Notes
... These compounds are not found alone in nature - why? explosive with water - they are stored under kerosene - very reactive. They react with nonmetals to form salts. Many of the compounds they form are white in color. They are silvery, shiny (luster), have a low melting point, conduct electricity, an ...
... These compounds are not found alone in nature - why? explosive with water - they are stored under kerosene - very reactive. They react with nonmetals to form salts. Many of the compounds they form are white in color. They are silvery, shiny (luster), have a low melting point, conduct electricity, an ...
File - Science With BLT
... 1. The periodic law allows some properties of an element to be predicted based on its a. position in the periodic table. c. symbol. b. number of isotopes. d. color. 2. The periodic law states that a. no two electrons with the same spin can be found in the same place in an atom. b. the physical and c ...
... 1. The periodic law allows some properties of an element to be predicted based on its a. position in the periodic table. c. symbol. b. number of isotopes. d. color. 2. The periodic law states that a. no two electrons with the same spin can be found in the same place in an atom. b. the physical and c ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 12.3 g Cd 1.3 26.9814 u 1.5
... A period in the periodic table is a horizontal row of elements. A group is one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. ...
... A period in the periodic table is a horizontal row of elements. A group is one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. ...
Exam Review/SLO 1 Topics Mixtures Have two or more different
... Atoms consist of a small dense positive nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud Electron cloud is described with energy levels and atomic orbitals Periodic Table Groups & Periods Arranged by increasing atomic number Metals, metalloids, non-metals Location on PT Basic properties Energy levels & orbit ...
... Atoms consist of a small dense positive nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud Electron cloud is described with energy levels and atomic orbitals Periodic Table Groups & Periods Arranged by increasing atomic number Metals, metalloids, non-metals Location on PT Basic properties Energy levels & orbit ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 36. What are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order from lowest frequency/lowest energy to highest frequency/highest energy? ...
... 36. What are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order from lowest frequency/lowest energy to highest frequency/highest energy? ...
SNC1D- Grade 9- Unit: Chemistry March 03,2009 Periodic Table
... These consist of all 's' and 'p' block elements excluding the noble gases (group 18 elements). The chemical properties of the representative elements are determined by the number of valence electrons in their atoms. The number of valence electrons belonging to the above two blocks are: 's' block ele ...
... These consist of all 's' and 'p' block elements excluding the noble gases (group 18 elements). The chemical properties of the representative elements are determined by the number of valence electrons in their atoms. The number of valence electrons belonging to the above two blocks are: 's' block ele ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... 5. Chemical Formula: Where each _ELEMENT_ is represented by its chemical _SYMBOL_ and the _NUMBER__ of atoms is shown in __SUBSCRIPTS__. ...
... 5. Chemical Formula: Where each _ELEMENT_ is represented by its chemical _SYMBOL_ and the _NUMBER__ of atoms is shown in __SUBSCRIPTS__. ...
ionization energies
... • As more and more elements were discovered, chemists began to notice patterns in the chemical properties of certain elements. • Consider the three metals Li, Na, and K • All 3 metals are soft • All 3 metals are less dense than water • All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points • Th ...
... • As more and more elements were discovered, chemists began to notice patterns in the chemical properties of certain elements. • Consider the three metals Li, Na, and K • All 3 metals are soft • All 3 metals are less dense than water • All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points • Th ...
8.P.1.1 Warm-Up Questions for Website
... 182. An element X contains 14 protons, 15 neutrons, and 14 electrons. Which is MOST LIKELY the same element as element X? Element A: 13 protons, 15 neutrons, 14 electrons B. Element B: 14 protons, 14 neutrons, 14 electrons C. Element C: 15 protons, 14 neutrons, 15 electrons A. ...
... 182. An element X contains 14 protons, 15 neutrons, and 14 electrons. Which is MOST LIKELY the same element as element X? Element A: 13 protons, 15 neutrons, 14 electrons B. Element B: 14 protons, 14 neutrons, 14 electrons C. Element C: 15 protons, 14 neutrons, 15 electrons A. ...
19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form
... 24. The horizontal rows found on the periodic table are called __periods__, while the vertical columns are called ___groups__ or ___periods___. 25. The most reactive elements on the periodic table are in group __1A – Alkali Metals__. 26. Electronegativity ____decreases_____ (increases/decreases) goi ...
... 24. The horizontal rows found on the periodic table are called __periods__, while the vertical columns are called ___groups__ or ___periods___. 25. The most reactive elements on the periodic table are in group __1A – Alkali Metals__. 26. Electronegativity ____decreases_____ (increases/decreases) goi ...
Electron Behavior File
... the main-group elements increase across each period Group trends– among the main-group elements ionization energies generally decrease ...
... the main-group elements increase across each period Group trends– among the main-group elements ionization energies generally decrease ...
Chemistry DCA Review Sheet
... 6. How do valence electrons determine and element’s chemical properties? ...
... 6. How do valence electrons determine and element’s chemical properties? ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.