Matter on Earth and in the universe is made of atoms that have
... Metals are located below the staircase B to At. Nonmetals are located above the staircase. Metalloids are located on the staircase. Metals are elements that tend to give up electrons to stabilize. Metals have characteristics such as: lustrous, conductors, and high malleability. Metals form positive ...
... Metals are located below the staircase B to At. Nonmetals are located above the staircase. Metalloids are located on the staircase. Metals are elements that tend to give up electrons to stabilize. Metals have characteristics such as: lustrous, conductors, and high malleability. Metals form positive ...
Electron
... ENERGY LEVEL • The fixed amount of energy that a system described by quantum mechanics, such as a molecule, atom, electron, or nucleus, can have. ...
... ENERGY LEVEL • The fixed amount of energy that a system described by quantum mechanics, such as a molecule, atom, electron, or nucleus, can have. ...
Physical Science Lesson Plans
... Argon (Ar). Draw a Bohr model which shows the proper placement of these particles. Draw a Lewis structure showing the valence electrons for Argon. Periodic Table Basics Activity (Bohr models, Lewis structures, and color coding) HW: Quiz tomorrow over determining proper number of protons, neutrons, a ...
... Argon (Ar). Draw a Bohr model which shows the proper placement of these particles. Draw a Lewis structure showing the valence electrons for Argon. Periodic Table Basics Activity (Bohr models, Lewis structures, and color coding) HW: Quiz tomorrow over determining proper number of protons, neutrons, a ...
Chapter 2—Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... • In 1911, Rutherford proved the existence of the proton with his nowfamous gold-foil experiment • He shot α-particles at the foil…most passed through, but some were reflected back at the fluorescent ...
... • In 1911, Rutherford proved the existence of the proton with his nowfamous gold-foil experiment • He shot α-particles at the foil…most passed through, but some were reflected back at the fluorescent ...
Subject Area Standard Area Organizing Category Course Standard
... 3.2.C.A5: MODELS Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory. Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear at ...
... 3.2.C.A5: MODELS Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory. Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear at ...
ch 4 notes
... • EX: About 8 out of 10 chlorine atoms are chlorine-35. Two out of 10 are chlorine-37. ...
... • EX: About 8 out of 10 chlorine atoms are chlorine-35. Two out of 10 are chlorine-37. ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... The periodic table groups similar elements together The order is based on the number of protons an atom of that element has in its nucleus Periodic law: properties of elements tend to change in a regular pattern when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, or number of protons in ...
... The periodic table groups similar elements together The order is based on the number of protons an atom of that element has in its nucleus Periodic law: properties of elements tend to change in a regular pattern when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, or number of protons in ...
Periodic_Table
... Some Important Nonmetals • Carbon – important element for making up living organisms • Noble Gases – group 18 – very nonreactive. Have full outer shells. ...
... Some Important Nonmetals • Carbon – important element for making up living organisms • Noble Gases – group 18 – very nonreactive. Have full outer shells. ...
CHEM 101 Dual Enrollment HW4 Question 1 of 12 Dalton`s
... They react with alkali metals to form salts. They are highly reactive. They have the same boiling point. They have one electron missing in their outer shell. They only have one electron in their outer shell. ...
... They react with alkali metals to form salts. They are highly reactive. They have the same boiling point. They have one electron missing in their outer shell. They only have one electron in their outer shell. ...
Introduction to Atomic Theory
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in single whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearra ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in single whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearra ...
Name ____ Date
... I can Statements (You should be able to do these things at the end of the unit.) STANDARD 1: Students will understand that all matter in the universe has a common origin and is made of atoms, which have structure and can be systematically arranged on the periodic table. ...
... I can Statements (You should be able to do these things at the end of the unit.) STANDARD 1: Students will understand that all matter in the universe has a common origin and is made of atoms, which have structure and can be systematically arranged on the periodic table. ...
JJ Thompson Webquest
... He found that when carbon combined with oxygen to form a gas, there were two possible outcomes, depending on the conditions - and in one outcome each gram of carbon combined with precisely twice as much oxygen as in the other. He correctly interpreted this as the formation of CO2 and CO respectively ...
... He found that when carbon combined with oxygen to form a gas, there were two possible outcomes, depending on the conditions - and in one outcome each gram of carbon combined with precisely twice as much oxygen as in the other. He correctly interpreted this as the formation of CO2 and CO respectively ...
CP Chemistry First Semester Final Exam 1
... atoms bond in order to obtain 8 valence electrons are found in the outer s and p sublevels substances found on the left side of a chemical equation He listed the elements in order of increasing atomic number all electrons in the atom are in the lowest available energy levels substances found on the ...
... atoms bond in order to obtain 8 valence electrons are found in the outer s and p sublevels substances found on the left side of a chemical equation He listed the elements in order of increasing atomic number all electrons in the atom are in the lowest available energy levels substances found on the ...
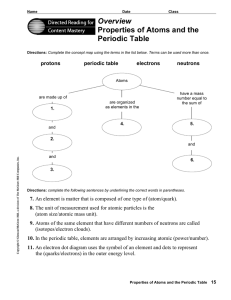
Reading Assignment Worksheet on Atoms - District 196 e
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
matter and its reactivity. Objects in the universe are composed of
... 3.1a Substances have characteristic properties. Some of these properties include color, odor, phase, density, solubility, heat and electrical conductivity, and boiling and freezing points. 3.1b Solubility can be affected by the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure. The rate of ...
... 3.1a Substances have characteristic properties. Some of these properties include color, odor, phase, density, solubility, heat and electrical conductivity, and boiling and freezing points. 3.1b Solubility can be affected by the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure. The rate of ...
Chemistry and elements 1. The rows of the periodic table are called
... Chemistry and elements 1. The rows of the periodic table are called: a. classes b. periods c. groups d. families 2. As you move from left to right across the periodic table: a. atomic number decreases b. atomic number increases c. The elements become darker in color d. The elements become lighter in ...
... Chemistry and elements 1. The rows of the periodic table are called: a. classes b. periods c. groups d. families 2. As you move from left to right across the periodic table: a. atomic number decreases b. atomic number increases c. The elements become darker in color d. The elements become lighter in ...
unit 4 hw packet File
... 2. Noticed that similar chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. 3. Published first modern periodic table. Periodic Table of Elements. Henry Moseley- Rearranged PT by atomic number Periods: Horizontal rows on the periodic table. Represent how many energy levels each atom should have. There ...
... 2. Noticed that similar chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. 3. Published first modern periodic table. Periodic Table of Elements. Henry Moseley- Rearranged PT by atomic number Periods: Horizontal rows on the periodic table. Represent how many energy levels each atom should have. There ...
Science 9 Unit B 2.0 - Vegreville Composite High
... within the elements when they were listed in increasing mass ...
... within the elements when they were listed in increasing mass ...
IPS Unit 8 – Periodic Table Review Worksheet
... Directions: Use the terms below to correctly complete the statements. Write the terms in the blanks to the left. Then find and circle each term in the puzzle. ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to correctly complete the statements. Write the terms in the blanks to the left. Then find and circle each term in the puzzle. ...
Early Greek Philosophers determined that atoms are the building
... shiny appearance, and can be shaped by pounding (malleability), bending, or being drawn into a thin wire (ductility) ...
... shiny appearance, and can be shaped by pounding (malleability), bending, or being drawn into a thin wire (ductility) ...
Ch. 2. Atomic Structure and Periodic Table
... for elements that had not been discovered. Ex: Germanium (Ge): He predicted it would have an atomic mass of 72. The fact that its mass is 72.6 supported his version of the periodic table. *As more discoveries were made, problems with Mendeleev’s table increased. Henry Moseley: British Physicist (188 ...
... for elements that had not been discovered. Ex: Germanium (Ge): He predicted it would have an atomic mass of 72. The fact that its mass is 72.6 supported his version of the periodic table. *As more discoveries were made, problems with Mendeleev’s table increased. Henry Moseley: British Physicist (188 ...
Figure 2: Alternative Periodic Table
... Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) Are there any elements that have not yet been discovered? If so, what would their properties be? This table has room for four more elements. The element ...
... Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) Are there any elements that have not yet been discovered? If so, what would their properties be? This table has room for four more elements. The element ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.