Chapter 4 notes outline
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
Preliminary Course Atomic Structure 1 + 2
... John Dalton (1803) updates the theory: • Matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms. • Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to for ...
... John Dalton (1803) updates the theory: • Matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms. • Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to for ...
Ch 1.1 ppt
... arranged the elements into the Periodic Table. • Certain chemical properties were repeated regularly. • These properties were related to the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. ...
... arranged the elements into the Periodic Table. • Certain chemical properties were repeated regularly. • These properties were related to the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. ...
Regents Chemistry Review
... together in the 12 o’clock position, continue placing electrons in the remaining positions (3, 6 & 9 o’clock), one at a time, until you have two in each; the max is an OCTET. ...
... together in the 12 o’clock position, continue placing electrons in the remaining positions (3, 6 & 9 o’clock), one at a time, until you have two in each; the max is an OCTET. ...
Periodic Table
... electrons are also called valence electrons. They are the ones involved in chemical bonds with other elements. Besides that, a row goes from left to right, it’s is called a period. Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells. - Every element in the first column (group one) ha ...
... electrons are also called valence electrons. They are the ones involved in chemical bonds with other elements. Besides that, a row goes from left to right, it’s is called a period. Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells. - Every element in the first column (group one) ha ...
Chapter 11 and 12-2 Review/Study Guide for Test
... 6. What is an isotope? When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons from each other. 7. What determines the identity of an element? The number of protons in the nucleus (the atomic number) 8. How do you calculate the atomic mass of an element? It is the weighted average of the m ...
... 6. What is an isotope? When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons from each other. 7. What determines the identity of an element? The number of protons in the nucleus (the atomic number) 8. How do you calculate the atomic mass of an element? It is the weighted average of the m ...
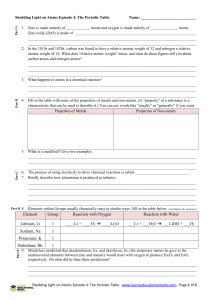
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... 9. Mendeleev predicted that ekaaluminium, Ea, and ekasilicon, Es, (the temporary names he gave to the undiscovered elements between zinc and arsenic) would react with oxygen to produce Ea2O3 and EsO2 respectively. On what did he base these predictions? ...
... 9. Mendeleev predicted that ekaaluminium, Ea, and ekasilicon, Es, (the temporary names he gave to the undiscovered elements between zinc and arsenic) would react with oxygen to produce Ea2O3 and EsO2 respectively. On what did he base these predictions? ...
2nd nine weeks benchmark review homework
... Which of the following would most improve the validity of an experiment? a- increasing the number of variables b- decreasing the range of the independent variable c- repeating the ...
... Which of the following would most improve the validity of an experiment? a- increasing the number of variables b- decreasing the range of the independent variable c- repeating the ...
First 9 weeks Study Guide 8th Grade
... Atoms are the smallest part of an element. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Elements ...
... Atoms are the smallest part of an element. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Elements ...
Elements, Compounds, Mixtures
... Homogeneous mixtures are also referred as solutions: Solvent - the dissolving agent; usually present in greater amount; defines the phase of the solution Solute - the substance which is dissolved • Liquid solution: gases, liquids, and ...
... Homogeneous mixtures are also referred as solutions: Solvent - the dissolving agent; usually present in greater amount; defines the phase of the solution Solute - the substance which is dissolved • Liquid solution: gases, liquids, and ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... • A substance formed by joining atoms together. • The smallest unit of a compound is a molecule. • Formulas: tell types of elements in the compound and their ratios. ...
... • A substance formed by joining atoms together. • The smallest unit of a compound is a molecule. • Formulas: tell types of elements in the compound and their ratios. ...
Valence Electrons
... The ionic radii positive ions (cations) generally decrease from left to right. The ionic radii of negative ions (anions) generally decrease from left to right, beginning with group 15 or 16. Both positive and negative ions increase in size moving down a group. ...
... The ionic radii positive ions (cations) generally decrease from left to right. The ionic radii of negative ions (anions) generally decrease from left to right, beginning with group 15 or 16. Both positive and negative ions increase in size moving down a group. ...
GCSE Chemistry coursework: Research Study on `Francium and the
... This is an example of the Bohr atomic structure model of a lithium atom. [10] The Bohr model can explain the reactivity of the alkali metals because it says that atoms are at their most stable when they have a stable octet and seeing as the alkali metals only need to lose one electron to gain a stab ...
... This is an example of the Bohr atomic structure model of a lithium atom. [10] The Bohr model can explain the reactivity of the alkali metals because it says that atoms are at their most stable when they have a stable octet and seeing as the alkali metals only need to lose one electron to gain a stab ...
File - Cynthia Campbell
... intended the table to illustrate recurring ("periodic") trends in the properties of the elements. The layout of the table has been refined and extended over time, as new elements have been discovered, and new theoretical models have been developed to explain chemical behavior. The periodic table is ...
... intended the table to illustrate recurring ("periodic") trends in the properties of the elements. The layout of the table has been refined and extended over time, as new elements have been discovered, and new theoretical models have been developed to explain chemical behavior. The periodic table is ...
1 - cloudfront.net
... How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. What does the number 84 represent in the name ...
... How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. What does the number 84 represent in the name ...
Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonding
... eight electrons in their outer energy level or, in the case of elements 1-5, two in their outer shell level. ...
... eight electrons in their outer energy level or, in the case of elements 1-5, two in their outer shell level. ...
File - Mr. Meyer`s Science Page
... (7) Group 1 of the periodic table consists of the ______________________, a highly reactive group of elements. (8) Atoms of alkaline-earth metals, such as calcium, have __________valence electrons. (9) Group 2 elements that have two valence electrons are ______________________________. (10) The ____ ...
... (7) Group 1 of the periodic table consists of the ______________________, a highly reactive group of elements. (8) Atoms of alkaline-earth metals, such as calcium, have __________valence electrons. (9) Group 2 elements that have two valence electrons are ______________________________. (10) The ____ ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.