Science Outline - cloudfront.net
... EX: All Hydrogen has 1 proton in its nucleus. Therefore, its atomic number is always 1. How many protons does an element with an atomic number of 94 have? What is this element? Most matter contains only a few kinds of elements o Ex: hamburgers, gasoline and paper are all made up of: __________ ...
... EX: All Hydrogen has 1 proton in its nucleus. Therefore, its atomic number is always 1. How many protons does an element with an atomic number of 94 have? What is this element? Most matter contains only a few kinds of elements o Ex: hamburgers, gasoline and paper are all made up of: __________ ...
Another look at chemical reactions HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WATER
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
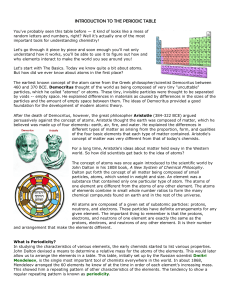
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
... Let's start with The Basics. Today we know quite a bit about atoms. But how did we ever know about atoms in the first place? The earliest known concept of the atom came from the Greek philosopher/scientist Democritus between 460 and 370 BCE. Democritus thought of the world as being composed of very ...
... Let's start with The Basics. Today we know quite a bit about atoms. But how did we ever know about atoms in the first place? The earliest known concept of the atom came from the Greek philosopher/scientist Democritus between 460 and 370 BCE. Democritus thought of the world as being composed of very ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... Periodic Table • A chart in which all known elements are listed in order of atomic number • http://theodoregray.com/periodictable/ ...
... Periodic Table • A chart in which all known elements are listed in order of atomic number • http://theodoregray.com/periodictable/ ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Introduction to Atoms & Nuclei
... Families on the Periodic Table • Elements on the periodic table can be grouped into FAMILIES bases on their chemical properties. • Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. • Elements in each family ...
... Families on the Periodic Table • Elements on the periodic table can be grouped into FAMILIES bases on their chemical properties. • Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. • Elements in each family ...
Unit 3 - Chemistry
... • Showed that the atoms of any element can be made to emit tiny negative particles - called _______________. • Thompson knew that the entire atom was not negatively charged so he concluded that the atom must also contain _______________ particles that balance the negative charge, giving the atom a _ ...
... • Showed that the atoms of any element can be made to emit tiny negative particles - called _______________. • Thompson knew that the entire atom was not negatively charged so he concluded that the atom must also contain _______________ particles that balance the negative charge, giving the atom a _ ...
Basic atomic structure
... the center of the atom containing protons and neutrons Electron cloud: sparse area with – charge surrounding the nucleus containing electrons ...
... the center of the atom containing protons and neutrons Electron cloud: sparse area with – charge surrounding the nucleus containing electrons ...
a worksheet on C1.1
... atom is called an element. There are about 100 different elements. Elements are shown in the periodic table. The groups contain elements with similar properties. Candidates should understand where metals and non-metals appear in the periodic table. b) Atoms of each element are represented by a chemi ...
... atom is called an element. There are about 100 different elements. Elements are shown in the periodic table. The groups contain elements with similar properties. Candidates should understand where metals and non-metals appear in the periodic table. b) Atoms of each element are represented by a chemi ...
Atomic Theory
... empty space….so he also discovered the orbital theory of electrons, in other words, electrons orbit the nucleus (small charge) in circular paths ...
... empty space….so he also discovered the orbital theory of electrons, in other words, electrons orbit the nucleus (small charge) in circular paths ...
rocks and minerals quiz
... An atom is mostly empty space between the electrons and the nucleus. This presents a conceptual problem: How do atoms form solids with all this empty space? ATOMIC STRUCTURE ANALOGY Imagine a jungle gym on a children’s playground. If you are a bug up close, you would see a large jungle gym with plen ...
... An atom is mostly empty space between the electrons and the nucleus. This presents a conceptual problem: How do atoms form solids with all this empty space? ATOMIC STRUCTURE ANALOGY Imagine a jungle gym on a children’s playground. If you are a bug up close, you would see a large jungle gym with plen ...
Chemistry - Rainhill High School
... The structure of the atom in terms of its sub atomic particles. How they make elements compounds and mixture and how they are separated. Groups and periods and how electronic configuration contributes to simple bonding models. How the atom is a model and how it has changed over time with key players ...
... The structure of the atom in terms of its sub atomic particles. How they make elements compounds and mixture and how they are separated. Groups and periods and how electronic configuration contributes to simple bonding models. How the atom is a model and how it has changed over time with key players ...
Reading Comprehension - Easy Peasy All-in
... atoms that are all the same kind. It is a pure form of matter. Elements join together with other elements to make the different materials that we see and use every day. Some common elements that you might have heard about are oxygen, carbon, helium, gold and silver. If you have a lump of silver, all ...
... atoms that are all the same kind. It is a pure form of matter. Elements join together with other elements to make the different materials that we see and use every day. Some common elements that you might have heard about are oxygen, carbon, helium, gold and silver. If you have a lump of silver, all ...
The Periodic table
... Classification Systems for the Elements: A noble gas element: group VIII A. All elements are gases. Do not react.All have 8 electrons around them , other than He. A representative element: Located in s area or first 5 columns of the p area. Transition element: Element located in d ...
... Classification Systems for the Elements: A noble gas element: group VIII A. All elements are gases. Do not react.All have 8 electrons around them , other than He. A representative element: Located in s area or first 5 columns of the p area. Transition element: Element located in d ...
C1.1 The fundamental ideas in chemistry
... Atoms and elements are the building blocks of chemistry. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons. When elements react they produce compounds. ...
... Atoms and elements are the building blocks of chemistry. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons. When elements react they produce compounds. ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... Groups Each group is also called a “family” of elements. Just like members of the same family, they share similar characteristics. Each element family has a unique name as well! Let’s look at them now… ...
... Groups Each group is also called a “family” of elements. Just like members of the same family, they share similar characteristics. Each element family has a unique name as well! Let’s look at them now… ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... Groups Each group is also called a “family” of elements. Just like members of the same family, they share similar characteristics. Each element family has a unique name as well! Let’s look at them now… ...
... Groups Each group is also called a “family” of elements. Just like members of the same family, they share similar characteristics. Each element family has a unique name as well! Let’s look at them now… ...
File - Mr. Gittermann
... • The number of protons in a nucleus; all atoms of any given element have the same atomic number; because an uncharged atom has the same number of protons and electrons, typically the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number ...
... • The number of protons in a nucleus; all atoms of any given element have the same atomic number; because an uncharged atom has the same number of protons and electrons, typically the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number ...
Elements02
... next 30 years many new elements were discovered by scientists such as Englishman John Dalton. Dalton is also famous for his 1808 theory, which explained why elements differ from each other and non-elements. His theory came to be known as the atomic theory and it states that; ...
... next 30 years many new elements were discovered by scientists such as Englishman John Dalton. Dalton is also famous for his 1808 theory, which explained why elements differ from each other and non-elements. His theory came to be known as the atomic theory and it states that; ...
Unit 1: Atomic Structure AP Chemistry
... Compounds are made when atoms combine. If elements combine in more than one whole number ratio, the resulting compound has different properties Chemical reactions involve the reorganization of atoms. ...
... Compounds are made when atoms combine. If elements combine in more than one whole number ratio, the resulting compound has different properties Chemical reactions involve the reorganization of atoms. ...
Chem 200 Dr. Saidane
... a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions. b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
... a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions. b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
form revision a
... Knowledge of the structure of the periodic table, groups and periods. All matter is made of atoms. When a substance contains only one kind of atom it is known as an element. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons each with a specific charge, mass and position within the atom. The number of pr ...
... Knowledge of the structure of the periodic table, groups and periods. All matter is made of atoms. When a substance contains only one kind of atom it is known as an element. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons each with a specific charge, mass and position within the atom. The number of pr ...
Structure of Atoms Study Guide
... 9. Lithium has an atomic mass of 7 atomic mass units and an atomic number of 3. How many neutrons does Lithium have? ...
... 9. Lithium has an atomic mass of 7 atomic mass units and an atomic number of 3. How many neutrons does Lithium have? ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.