Unit 7: The Nature of Matter Essential Questions:
... o Describe the structure of an atom o Discus the early history of the study of the atom; including the contributions of Aristotle, Democritus, Joseph Priestly, Antoine Lavoisier, John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, Niels Bohr, and Gilbert Lewis o Explain the organization of the Periodic Ta ...
... o Describe the structure of an atom o Discus the early history of the study of the atom; including the contributions of Aristotle, Democritus, Joseph Priestly, Antoine Lavoisier, John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, Niels Bohr, and Gilbert Lewis o Explain the organization of the Periodic Ta ...
Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE True/False Indicate whether the statement
... 13. Water and hydrogen peroxide have different properties because ____. a. they are made from different elements b. one contains a greater percentage of oxygen than the other c. one is a compound and one is a mixture d. only water follows the law of definite proportions ...
... 13. Water and hydrogen peroxide have different properties because ____. a. they are made from different elements b. one contains a greater percentage of oxygen than the other c. one is a compound and one is a mixture d. only water follows the law of definite proportions ...
Unit C3, C3.1
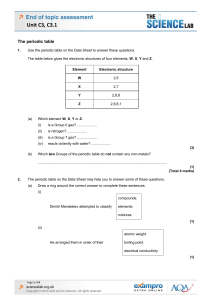
... Use the periodic table on the Data Sheet to answer these questions. The table below gives the electronic structures of four elements, W, X, Y and Z. ...
... Use the periodic table on the Data Sheet to answer these questions. The table below gives the electronic structures of four elements, W, X, Y and Z. ...
Big History Chemistry Study Guide File
... mass and releasing energy in the process. 8. In nuclear _____________, radioactive elements such as ________________ break apart into smaller elements (“decay products”), also releasing energy. 9. The significance of Henry ___________________’s experiment with x-rays and atoms is that it found a num ...
... mass and releasing energy in the process. 8. In nuclear _____________, radioactive elements such as ________________ break apart into smaller elements (“decay products”), also releasing energy. 9. The significance of Henry ___________________’s experiment with x-rays and atoms is that it found a num ...
Tendencies of ionic/atomic radii in the periodic table
... Tendencies of ionic and atomic radii in the periodic table Tendencies: 1. The atomic radii increase down a group (e.g. first group 157 – 272 pm) and within the s and p blocks, decrease from left to right across a period (e.g. second period 157 – 64 pm). 2. The atomic radii for elements following the ...
... Tendencies of ionic and atomic radii in the periodic table Tendencies: 1. The atomic radii increase down a group (e.g. first group 157 – 272 pm) and within the s and p blocks, decrease from left to right across a period (e.g. second period 157 – 64 pm). 2. The atomic radii for elements following the ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... Solubility (def.) __________________________________________________________________________ In Kool-Aid, identify the solute: ___________________ and the solvent: _______________ TRUE / FALSE. When a solid dissolves in water, each particle becomes surrounded by water molecules. ...
... Solubility (def.) __________________________________________________________________________ In Kool-Aid, identify the solute: ___________________ and the solvent: _______________ TRUE / FALSE. When a solid dissolves in water, each particle becomes surrounded by water molecules. ...
atomic structure - IGCSE STUDY BANK
... neutrons respectively but both have 2 protons. Helium-3 is formed in the Sun by the initial nuclear fusion process. Helium-4 is also formed in the Sun and as a product of radioactive alpha decay of an unstable nucleus. An alpha particle is a helium nucleus, it picks up two electrons and becomes the ...
... neutrons respectively but both have 2 protons. Helium-3 is formed in the Sun by the initial nuclear fusion process. Helium-4 is also formed in the Sun and as a product of radioactive alpha decay of an unstable nucleus. An alpha particle is a helium nucleus, it picks up two electrons and becomes the ...
File
... PATTERNS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE 1. Atomic numbers increase by ONE . 2. Atomic MASS tends to increase along with the atomic number, with some EXCEPTIONS. ...
... PATTERNS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE 1. Atomic numbers increase by ONE . 2. Atomic MASS tends to increase along with the atomic number, with some EXCEPTIONS. ...
O 2 (g)
... – All 3 metals are soft – All 3 metals are less dense than water – All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points – The most interesting feature is that all 3 metals react with the same elements in a nearly identical manner • As you see in the periodic table, these elements are all list ...
... – All 3 metals are soft – All 3 metals are less dense than water – All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points – The most interesting feature is that all 3 metals react with the same elements in a nearly identical manner • As you see in the periodic table, these elements are all list ...
Chapter 7
... Correlate atomic properties, such as ionization energy, with electron configuration, and explain how these relate to the chemical reactivity and physical properties of the alkali and alkaline earth metals (groups 1A and 2A). Write balanced equations for the reactions of the group 1A and 2A metals ...
... Correlate atomic properties, such as ionization energy, with electron configuration, and explain how these relate to the chemical reactivity and physical properties of the alkali and alkaline earth metals (groups 1A and 2A). Write balanced equations for the reactions of the group 1A and 2A metals ...
Chemical Bonding
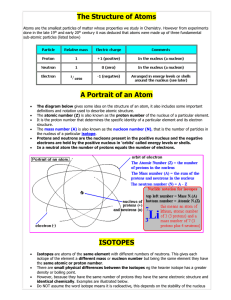
... • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
... • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Correlate atomic properties, such as ionization energy, with electron configuration, and explain how these relate to the chemical reactivity and physical properties of the alkali and alkaline earth metals (groups 1A and 2A). Write balanced equations for the reactions of the group 1A and 2A metals ...
... Correlate atomic properties, such as ionization energy, with electron configuration, and explain how these relate to the chemical reactivity and physical properties of the alkali and alkaline earth metals (groups 1A and 2A). Write balanced equations for the reactions of the group 1A and 2A metals ...
General Chemistry - Review for final exam: (Make sure you bring
... 35. How is a photon created as an atom is heated? 36. According to Schrodinger, where are you most likely to find the electron in an s orbital? 37. Where are periods and groups on the periodic table? 38. Where are the following found on the periodic table> a. Metals b. Non-metals c. Transitional met ...
... 35. How is a photon created as an atom is heated? 36. According to Schrodinger, where are you most likely to find the electron in an s orbital? 37. Where are periods and groups on the periodic table? 38. Where are the following found on the periodic table> a. Metals b. Non-metals c. Transitional met ...
Getting to Know: Periodic Table
... element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Remember that the atomic number tells you the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Remember that the atomic number tells you the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Notes matter energy
... Chemists organize matter on the periodic table of the elements (See Week 1 Handout). The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number (Z), which represents the number of protons in the nucleus. The periodic law states that properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbe ...
... Chemists organize matter on the periodic table of the elements (See Week 1 Handout). The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number (Z), which represents the number of protons in the nucleus. The periodic law states that properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbe ...
Notes
... Everything in the world is made up from about 100 elements. Every element is made up of very small particles called atoms. An element is a substance in which all the atoms are of one kind only. An element is a substance which cannot be broken into any simpler substances. Elements can be classified i ...
... Everything in the world is made up from about 100 elements. Every element is made up of very small particles called atoms. An element is a substance in which all the atoms are of one kind only. An element is a substance which cannot be broken into any simpler substances. Elements can be classified i ...
Full Text PDF - Science and Education Publishing
... The answer to the aforementioned question is given by quantum electrodynamics (QED), a theory that combines quantum mechanics and special relativity, usually taught in Physics advanced courses. The basic idea is easy to grasp: electrons (especially the most internal ones) interacting with a heavy nu ...
... The answer to the aforementioned question is given by quantum electrodynamics (QED), a theory that combines quantum mechanics and special relativity, usually taught in Physics advanced courses. The basic idea is easy to grasp: electrons (especially the most internal ones) interacting with a heavy nu ...
Atomic History - Wylie High School Advanced Chemistry
... He was killed in the fighting in Gallipoli by a sniper’s bullet, at the age of 28. Because of this loss, the British government later restricted its scientists to noncombatant duties during WWII. ...
... He was killed in the fighting in Gallipoli by a sniper’s bullet, at the age of 28. Because of this loss, the British government later restricted its scientists to noncombatant duties during WWII. ...
ch3 B - Manasquan Public Schools
... Later on, the discovery of protons and neutrons were discovered in the nucleus. And it was later concluded that all atoms are neutral in charge. The number of protons and electrons in any atom are always equal. ...
... Later on, the discovery of protons and neutrons were discovered in the nucleus. And it was later concluded that all atoms are neutral in charge. The number of protons and electrons in any atom are always equal. ...
Inside the Atom connections to the lower secondary (KS3
... Atoms, elements and compounds. Pupils are taught about: • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics rela ...
... Atoms, elements and compounds. Pupils are taught about: • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics rela ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.