* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atoms and the Periodic Table
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
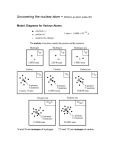
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 3 Vocabulary Words (27 words) Nucleus Proton Neutron Electron Energy level Orbital Valence electron Periodic law Period Group Ionization Ion Cation Anion Atomic number Mass number Isotopes Atomic mass unit (amu) Average atomic mass Metals Nonmetals Semiconductors Alkali metals Alkaline-earth metals Transition metals Halogens Noble gases A. Atomic Structure 1. What are atoms? a. b. c. Atoms are tiny units that determine properties of all matter. Democritus was the first to suggest that the universe was made of atoms, but couldn’t provide evidence to prove it! 1808 John Dalton proposed the atomic theory with evidence to support it 1. John Dalton’s Atomic Theory a. b. c. Every element is made of tiny, unique particles called atoms that cannot be subdivided. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. Atoms of different elements can join to form molecules. 2. What’s in an Atom? a. Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons 1. 2. 3. 4. nucleus: the center of an atom made up of protons and neutrons Protons: a positively charged subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom Neutron: a neutral subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom Electron: a tiny negatively charged subatomic particle moving around outside the nucleus of an atom 5. The number of protons and electrons an atom has is unique for each element. b. Atoms have no overall charge 1. Atoms don’t have a charge because they have an equal number of protons and electrons whose charges exactly cancel. 2. Example: Helium- 2 protons/2 electrons 3. Models of the Atom a. Bohr’s model compares electrons to planets 1. 2. 3. 1913 Niels Bohr suggested that electrons in an atom move in set paths around the nucleus like the planets around the sun. Energy level: any of the possible energies an electron may have in an atom Electrons must gain or lose energy to move up or down the energy levels b. According to modern theory, electrons behave more like waves 1. 2. Since Bohr’s model couldn’t explain everything, the modern model believes electrons behave like waves on a vibrating string. Don’t exactly know where the electrons are at, but can calculate an area they are found 3. Just like a fan blade moving 3. Electrons are found in orbitals within energy levels 4. a. Orbitals: a region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons b. There are four different kinds of orbitals Every atom has one or more valence electrons a. Valence electron: an electron in the outermost energy level of an atom B. A Guided Tour of the Periodic Table 1. Organization of the Periodic Table a. b. c. The periodic table groups similar elements together The order is based on the number of protons an atom of that element has in its nucleus Periodic law: properties of elements tend to change in a regular pattern when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, or number of protons in their atoms. 4. Using the periodic table to determine electronic arrangement a. Period: a horizontal row of elements in the periodic table b. Just as the number of protons increase left to right, so does the number of electrons 5. Elements in the same group have similar properties a. Group (family): a vertical column of elements in the periodic table b. Valence electrons determine properties c. Atoms in the same group have the same number of valence electrons 2. Some Atoms Form Ions a. b. c. d. Atoms that do not have filled outermost energy levels may undergo ionization. Ionization: the process of adding electrons to or removing electrons from an atom or group of atoms Atoms do this to fill their outermost energy levels Ion: an atom or group of atoms that has lost or gained one or more electrons and therefore has a net electric charge e. Cation: an ion with a positive charge 1. Caused by losing electrons f. Anion: an ion with a negative charge 1. Caused by gaining electrons 3. How do the Structures of Atoms Differ? A. Atomic number equals the number of protons 1. Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom 2. Each element has a different number of proton. B. Mass number equals the total number of subatomic particles in the nucleus 1. Mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom C. Isotopes of an element have different number of neutrons 1. Isotopes: any atoms having the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons D. Some isotopes are more common than others E. Calculating the number of neutrons in an atom 1. Subtract atomic number from the mass number F. The mass of an atom a. b. c. Atomic mass unit (amu): a quantity equal to one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon12 atom Proton and neutron have a mass of 1amu Average atomic mass: the weighted average of masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element 1. Often found on the periodic table C. 1. Families of Elements How are Elements Classified? a. b. c. Elements are either metals or nonmetals Metals: the elements that are good conductors of heat and electricity Nonmetals: the elements that are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity d. Semiconductors: the elements that are intermediate conductors of heat and electricity 2. Metals a. Alkali Metals 1. Alkali metals: the highly reactive metallic elements located in Group 1 of the periodic table b. Alkaline-earth metals 1. Alkaline-earth metals: the reactive metallic elements located in Group 2 of the periodic table c. Transition metals 1. Transition metals: the metallic elements located in groups 3-12 of the periodic table d. Synthetic elements 1. Man-made elements 3. Nonmetals a. b. Found on the right side of the periodic table, except for hydrogen Carbon is found in three different forms and can also form many compounds c. Nonmetals and their compounds are plentiful on Earth d. Chlorine is a halogen that protects you from harmful bacteria 1. halogen: the highly reactive elements located in Group 17 of the periodic table d. The noble gas neon is inert 1. Noble gases: the unreactive gaseous elements located in Group 18 of the periodic table e. Semiconductors are intermediate conductors of heat and electricity f. Silicon is the most familiar semiconductor