* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Theory - OCPS TeacherPress
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
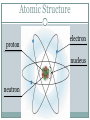
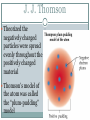
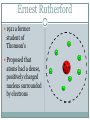
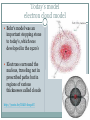
Atomic Theory ATOMIC STRUCTURE REVIEW AND HISTORY OF THE ATOMIC MODEL Matter All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms Atomic Structure electron proton nucleus + + + neutron + Atom An atom is made up of Protons + Neutrons 0 Electrons - Electric charge Location in the atom Protons Neutron Electron positive No charge / neutral negative In nucleus In nucleus Outside nucleus How big is an atom? The typical atom is about One ten-billionth of a meter in diameter The average nucleus of an atom is about One million billionth of a meter in diameter http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yQP4UJhNn0I#t=188 The mass of an atom The nucleus is made up of the protons and neutrons The protons and neutrons have about the same mass The electrons surrounding the nucleus have a mass about one two-thousandths the mass of the protons or neutrons Most of an atoms mass is in the nucleus Size of an atom The subatomic particles of the atom are tiny compared to the atom as a whole The majority of an atoms volume consists of empty space There are more than a million million billion atoms in a sing drop of water http://youtu.be/qxXf7AJZ73A The History of the Atomic Theory Democritus Greek philosopher in 440 bc Was the first to proposed the existence of atoms “Atomos” meaning “not to be cut” John Dalton British chemist 1803 Atomic Theory – He came up with the theory that all substances were made of atoms Atoms were small, hard, dense spheres that could not be created, destroyed, or altered Dmitri Mendeleev Known as the father of the present day periodic table Organized the elements (each type of atom) by similar properties in 1869 J. J. Thomson British scientist 1898 Proposed that atoms themselves were made of smaller particles . He discovered that atoms contained negatively charged particles, but did not know their location J. J. Thomson Theorized the negatively charged particles were spread evenly throughout the positively charged material Thomson’s model of the atom was called the “plum-pudding” model Ernest Rutherford 1911 a former student of Thomson's Proposed that atoms had a dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons Niels Bohr 1913 Danish scientist Said that electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular paths, called orbits And that electrons could only exist in certain orbits and at certain energy levels http://youtu.be/wCCz20JOXXk Today’s model electron cloud model Bohr’s model was an important stepping stone to today’s, which was developed in the 1920’s Electrons surround the nucleus, traveling not in prescribed paths but in regions of various thicknesses called clouds http://youtu.be/kYkD-dcupAU Law of Conservation of Matter Matter (mass) cannot be created or destroyed but it can be rearranged. The mass of the reactants must be equal to the mass of the products. The mass of the substance you end with must be equal to the mass of the substances you begin with.