Week 3 Answers - Stephen P. van Vlack
... not something that occurs naturally. Additionally, there is a demonstrable change in behavior as a result of an association having been made. For example, a startle reaction to a tulip is seen as being a conditioned response to a conditioned stimulus because in the natural world this type of stimulu ...
... not something that occurs naturally. Additionally, there is a demonstrable change in behavior as a result of an association having been made. For example, a startle reaction to a tulip is seen as being a conditioned response to a conditioned stimulus because in the natural world this type of stimulu ...
The Neural Optimal Control Hierarchy
... act as the highest levels in the motor hierarchy, generating signals that proceed through M1, and eventually to motor neurons, causing muscle activation. 2 - Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia has been characterized in several ways: 1) As a winner-take-all (WTA) circuit [5], 2) as responsible for scali ...
... act as the highest levels in the motor hierarchy, generating signals that proceed through M1, and eventually to motor neurons, causing muscle activation. 2 - Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia has been characterized in several ways: 1) As a winner-take-all (WTA) circuit [5], 2) as responsible for scali ...
中樞神經系統
... Broca’s area speech production Lateral prefrontal cortex language comprehension and ...
... Broca’s area speech production Lateral prefrontal cortex language comprehension and ...
test1short answer - answer key
... function though the electrical activity of the neurons (2). Metabolic brain imaging techniques indirectly measure brain function and can be described as correlational, relying on the subtractive technique to measure brain function. Metabolic techniques measure blood flow, glucose and/or oxygen level ...
... function though the electrical activity of the neurons (2). Metabolic brain imaging techniques indirectly measure brain function and can be described as correlational, relying on the subtractive technique to measure brain function. Metabolic techniques measure blood flow, glucose and/or oxygen level ...
Theoretical Neuroscience: From Single Neuron to Network Dynamics
... faster than the response of the membrane; ...
... faster than the response of the membrane; ...
Spontaneous activity and functional connectivity in the developing
... Del Rio-Bermudez C, Plumeau AM, Sattler NJ, Sokoloff G, Blumberg MS. Spontaneous activity and functional connectivity in the developing cerebellorubral system. J Neurophysiol 116: 1316 –1327, 2016. First published July 6, 2016; doi:10.1152/jn.00461.2016.—The development of the cerebellar system depe ...
... Del Rio-Bermudez C, Plumeau AM, Sattler NJ, Sokoloff G, Blumberg MS. Spontaneous activity and functional connectivity in the developing cerebellorubral system. J Neurophysiol 116: 1316 –1327, 2016. First published July 6, 2016; doi:10.1152/jn.00461.2016.—The development of the cerebellar system depe ...
Odor- and context dependent modulation of mitral cell
... Signals traveling to the olfactory bulb do not go through the thalamus Prone to disconnection in traumatic head injuries (sieve bone acts as guillotine) In rats, the olfactory bulb is very large, relatively much larger than in humans. OB contains mitral cells that communicate via action pote ...
... Signals traveling to the olfactory bulb do not go through the thalamus Prone to disconnection in traumatic head injuries (sieve bone acts as guillotine) In rats, the olfactory bulb is very large, relatively much larger than in humans. OB contains mitral cells that communicate via action pote ...
Wade Chapter 8 Learning
... “Give me a dozen healthy infants, wellformed, and my own special world to bring them up in, and I’ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to be any type of specialist I might select - doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief, and yes, beggar-man and thief, regardless of his talents, pench ...
... “Give me a dozen healthy infants, wellformed, and my own special world to bring them up in, and I’ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to be any type of specialist I might select - doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief, and yes, beggar-man and thief, regardless of his talents, pench ...
Previous lecture
... Synaptic inhibition; cable properties of neurons; electrical integration in cerebellum ...
... Synaptic inhibition; cable properties of neurons; electrical integration in cerebellum ...
In What Sense, if Any, do Hippocampal “Time Cells” Represent or
... instead looking at the beautiful landscape, or even with your eyes shut, you will still “see” the path before you, and this “sight” will continue to guide your steps. It will even update, in the standard case fairly correctly, while you “walk” according to it! Four points can be made here. First, th ...
... instead looking at the beautiful landscape, or even with your eyes shut, you will still “see” the path before you, and this “sight” will continue to guide your steps. It will even update, in the standard case fairly correctly, while you “walk” according to it! Four points can be made here. First, th ...
Chapter Outlines - Cengage Learning
... psychological aspects of color sensation. Additive color mixing, the mixing of different wavelengths of light, always produces a lighter color. In subtractive color mixing, continued combinations of color (as in paints) will produce black. 2. The Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision. According to the ...
... psychological aspects of color sensation. Additive color mixing, the mixing of different wavelengths of light, always produces a lighter color. In subtractive color mixing, continued combinations of color (as in paints) will produce black. 2. The Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision. According to the ...
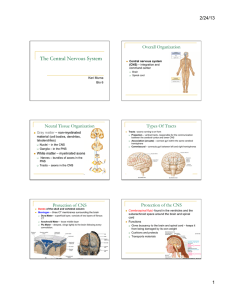
Central Nervous System
... The architecture of the cortex is determined by genetic and developmental processes but it can be modified due to “use-dependent competition” for cortical space Formation of new neural pathways and connections between existing neurons Some cortical regions can be remodeled throughout life while othe ...
... The architecture of the cortex is determined by genetic and developmental processes but it can be modified due to “use-dependent competition” for cortical space Formation of new neural pathways and connections between existing neurons Some cortical regions can be remodeled throughout life while othe ...
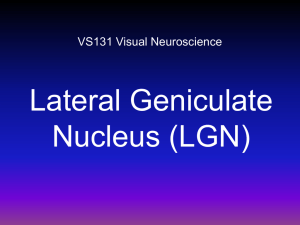
LGN
... LGN relay neurons project (I.e., send axons) to cortex. LGN interneurons make only local connections. There are more interneurons than relay neurons! LGN neurons get feedback connections from cortex. (The one-way connection from retina to rest of brain is unique in the visual system). LGN gets oth ...
... LGN relay neurons project (I.e., send axons) to cortex. LGN interneurons make only local connections. There are more interneurons than relay neurons! LGN neurons get feedback connections from cortex. (The one-way connection from retina to rest of brain is unique in the visual system). LGN gets oth ...
Behavioral verification of associative learning in whisker
... asymptotic amount of freezing was directly related to the intensity of the UCS (footshock). Other studies indicate that performance in conditioning training is an inverted-U function of footshock intensity (Leaton and Borszcz 1985, Witnauer and Miller 2013), and intermediate footshock intensities ap ...
... asymptotic amount of freezing was directly related to the intensity of the UCS (footshock). Other studies indicate that performance in conditioning training is an inverted-U function of footshock intensity (Leaton and Borszcz 1985, Witnauer and Miller 2013), and intermediate footshock intensities ap ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... FIGURE 48.13 A schematic diagram of principal pathways involved in classical conditioning of the eyeblink reflex. The role of structures at points a–e has been studied using reversible inactivation with a local anesthetic. Inactivation at point “c” (shaded areas) prevents learning, whereas inactiva ...
... FIGURE 48.13 A schematic diagram of principal pathways involved in classical conditioning of the eyeblink reflex. The role of structures at points a–e has been studied using reversible inactivation with a local anesthetic. Inactivation at point “c” (shaded areas) prevents learning, whereas inactiva ...
SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION GUIDE
... memories remain intact). The hippocampus and the medial temporal cortical areas which project to it are critical for long-term memory. The rat hippocampus is probably the single most studied brain structure, because of its simple organization. Hippocampal neurons undergo long-term potentiation (LTP) ...
... memories remain intact). The hippocampus and the medial temporal cortical areas which project to it are critical for long-term memory. The rat hippocampus is probably the single most studied brain structure, because of its simple organization. Hippocampal neurons undergo long-term potentiation (LTP) ...
Morphological Basis of Learning and Memory: Vertebrates
...
...
A separate developmental approach that was very fruitful in understanding brain substrates of
learning and memory involved enriching the lives of young animals with additional stimulation.
Donald Hebb (psychobiologist, 1904
Lecture 5 Sensory and Motor Systems
... • Contains over 50% of CNS neurons! It must be important! • Cerebellum coordinates complex sequences of actions by many muscles. • Takes an idea of a motion apart, and returns details of force, direction and timing. • Lesions result in ataxias. Alcohol-induced cerebellar inhibition causes same uncoo ...
... • Contains over 50% of CNS neurons! It must be important! • Cerebellum coordinates complex sequences of actions by many muscles. • Takes an idea of a motion apart, and returns details of force, direction and timing. • Lesions result in ataxias. Alcohol-induced cerebellar inhibition causes same uncoo ...
PowerPoint Ch. 6
... neuron responds They have both excitatory and inhibitory regions Lateral Inhibition-the reduction of activity in one neuron by activity in neighboring neurons Heightens contrasts-those receptors just inside the border are most excited and those outside the border are the least responsive ...
... neuron responds They have both excitatory and inhibitory regions Lateral Inhibition-the reduction of activity in one neuron by activity in neighboring neurons Heightens contrasts-those receptors just inside the border are most excited and those outside the border are the least responsive ...
The motor system Outline Muscles Reflexes Disorders of movement
... Ventromedial pathway Posture Coordinating _________________________ movements with eye movements Respiration, _________________________, sneezing Cerebellum Does not appear to _________________________ movements Plays a role in _________________________ movements _________________________ the muscle ...
... Ventromedial pathway Posture Coordinating _________________________ movements with eye movements Respiration, _________________________, sneezing Cerebellum Does not appear to _________________________ movements Plays a role in _________________________ movements _________________________ the muscle ...
Nerve Cells Images
... Phase contrast light microscopy image of neurons in the human cerebellum. The cerebellum is the posterior part of the brain that coordinates sensory inputs and muscular responses. The large cell bodies belong to Purkinje cells. This was a thick section, silver-stained and counterstained. Credit: Spi ...
... Phase contrast light microscopy image of neurons in the human cerebellum. The cerebellum is the posterior part of the brain that coordinates sensory inputs and muscular responses. The large cell bodies belong to Purkinje cells. This was a thick section, silver-stained and counterstained. Credit: Spi ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Selective Attention
... Necessary Conditions for CC Contiguity timing of the conditions ...
... Necessary Conditions for CC Contiguity timing of the conditions ...