Chapter 5b
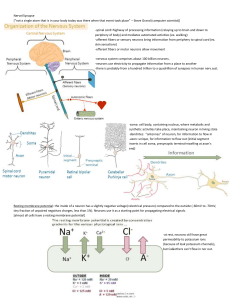
... Changes in resting potential Resting Potential Becomes Less than -70 mvolts = Depolarization Resting Potential Becomes More than -70 mvolts = Hyperpolarization If voltage exceeds threshold (~-55mV) the neuron fires. ...
... Changes in resting potential Resting Potential Becomes Less than -70 mvolts = Depolarization Resting Potential Becomes More than -70 mvolts = Hyperpolarization If voltage exceeds threshold (~-55mV) the neuron fires. ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
The Nervous System- Nervous Tissue
... Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: • Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards ...
... Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: • Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards ...
1: Nervous System II: Anatomy Review
... the ___________________(a gap between the neurons) to the receiving neuron. Advantages of the chemical synapse: 1. The signal can be either ____________ or ____________. 2. The signal can be ______________ as it passes from one neuron to the next. ...
... the ___________________(a gap between the neurons) to the receiving neuron. Advantages of the chemical synapse: 1. The signal can be either ____________ or ____________. 2. The signal can be ______________ as it passes from one neuron to the next. ...
PG1006 Lecture 2 Nervous Tissue 1
... • Junc4on between two neurones – Links presynap4c and postsynap4c neurone to transmit signal ...
... • Junc4on between two neurones – Links presynap4c and postsynap4c neurone to transmit signal ...
N1 - Kůra mozku HE
... • Golgi type I neurons – motor neurons of CNS with long axon (up to 1 meter) terminate on skeletal muscle • Golgi type II neurons – short axons • axon hillock, initial segment – site of action potential generation • axonal transport transport vesicles, mitochondria , proteins…by anterograde x growth ...
... • Golgi type I neurons – motor neurons of CNS with long axon (up to 1 meter) terminate on skeletal muscle • Golgi type II neurons – short axons • axon hillock, initial segment – site of action potential generation • axonal transport transport vesicles, mitochondria , proteins…by anterograde x growth ...
Chapter 14
... postsynaptic cells. They are connected by a gap junction, which allows ion flow between the cells. In a chemical synapse, the most common type in humans, a neurotransmitter passes between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells. ...
... postsynaptic cells. They are connected by a gap junction, which allows ion flow between the cells. In a chemical synapse, the most common type in humans, a neurotransmitter passes between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells. ...
Text 4-Nervous system: Organization and Physiology
... •Ion flows from all inputs summate or average at the initial segment •An action potential in the postsynaptic neuron occurs if the membrane potential at the initial segment reaches threshold ...
... •Ion flows from all inputs summate or average at the initial segment •An action potential in the postsynaptic neuron occurs if the membrane potential at the initial segment reaches threshold ...
MYELINATED AXON - Union County College Faculty Web Site
... The synapse is located at the end of each axonal end branch. Here the end branch forms a small synaptic knob (sk). This knob is adjacent to a tiny cleft or synapse (s). When a nerve impulse reaches this knob, a drug called a neurotransmitter is released from vesicles into the synapse The neurotransm ...
... The synapse is located at the end of each axonal end branch. Here the end branch forms a small synaptic knob (sk). This knob is adjacent to a tiny cleft or synapse (s). When a nerve impulse reaches this knob, a drug called a neurotransmitter is released from vesicles into the synapse The neurotransm ...
Neurotransmitters & Synapses - IB
... • K+ channels open, K+ rushes out • OR Cl- channels open, Cl- rushes in • Membrane potential becomes more negative • Ac AP is prevented from p propagating ...
... • K+ channels open, K+ rushes out • OR Cl- channels open, Cl- rushes in • Membrane potential becomes more negative • Ac AP is prevented from p propagating ...
1
... Satellite Cells actually look like they form a satellite dish, u can just picture it on top of a roof. Schwann Cells can work as white tiles of the roof itself. ...
... Satellite Cells actually look like they form a satellite dish, u can just picture it on top of a roof. Schwann Cells can work as white tiles of the roof itself. ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... o Sensory (collect internal and external information) o Motor (controls muscles) o Interneurons o Morphology (shape) o study of neuron shape is called neuroanatomy o in some cases, the shape of a neuron is indicative of function o 3 basic shapes ▪ Multipolar (2.1) ● Dendrites have spines ...
... o Sensory (collect internal and external information) o Motor (controls muscles) o Interneurons o Morphology (shape) o study of neuron shape is called neuroanatomy o in some cases, the shape of a neuron is indicative of function o 3 basic shapes ▪ Multipolar (2.1) ● Dendrites have spines ...
Nervous Tissue (Ch
... - contains typical organelles * Nissl bodies – dense networks of rough endoplasmic reticulum, compartmentalized by * neurofibrils - intermediate filaments (actin) of cytoskeleton 2. dendrites - receive - short, highly branched - not usually myelinated 3. axon - sends - long, few branches (except for ...
... - contains typical organelles * Nissl bodies – dense networks of rough endoplasmic reticulum, compartmentalized by * neurofibrils - intermediate filaments (actin) of cytoskeleton 2. dendrites - receive - short, highly branched - not usually myelinated 3. axon - sends - long, few branches (except for ...
Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two parts: 1
... All neurons have three parts: 1. cell body (perikaryon) Has a centrally located prominent nucleus Usually has a prominent nucleolus Has Nissl Bodies which are dense accumulations of RER and Polyribosomes for making proteins. Will also find some Nissl substance in the dendrites, NEVER in the axon. Al ...
... All neurons have three parts: 1. cell body (perikaryon) Has a centrally located prominent nucleus Usually has a prominent nucleolus Has Nissl Bodies which are dense accumulations of RER and Polyribosomes for making proteins. Will also find some Nissl substance in the dendrites, NEVER in the axon. Al ...
1 Introduction to Neurobiology Rudolf Cardinal NST 1B
... is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any inhibition from IPSPs) they may sum and trigger an AP. In this way the postsynaptic neuron can integrate information from ...
... is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any inhibition from IPSPs) they may sum and trigger an AP. In this way the postsynaptic neuron can integrate information from ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluTs). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the presynaptic membrane. After release into the extracellular space, glutamate binds to ionotropic glutamate receptors (NMDA rec ...
... Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluTs). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the presynaptic membrane. After release into the extracellular space, glutamate binds to ionotropic glutamate receptors (NMDA rec ...
Nerve cells - Dr Magrann
... receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. ...
... receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... membrane anymore), black widow venom makes vesicles fuse spontaneously w/ membrane. -excitatory synapses are only found on spines, inhibitory synapses are found on dendrites shafts or soma ...
... membrane anymore), black widow venom makes vesicles fuse spontaneously w/ membrane. -excitatory synapses are only found on spines, inhibitory synapses are found on dendrites shafts or soma ...
nervous5
... Exceptions: Peptide NTs originate in cell body, move in vesicles by fast orthograde axonal transport to axon terminal. ...
... Exceptions: Peptide NTs originate in cell body, move in vesicles by fast orthograde axonal transport to axon terminal. ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... • About 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) in the human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
... • About 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) in the human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...