Chapter 12 - FacultyWeb
... Electrical synapses involve a neurotransmitter/chemical synapses Electrical synapses involve direct connection between cells/electrical synapses Chemical synapses involve direct connection between cells/chemical synapses Electrical synapses always use ACh/both are equally abundant ...
... Electrical synapses involve a neurotransmitter/chemical synapses Electrical synapses involve direct connection between cells/electrical synapses Chemical synapses involve direct connection between cells/chemical synapses Electrical synapses always use ACh/both are equally abundant ...
Answers - Mosaiced.org
... 91. Period during which Na+ channels will not open in response to stimulus, however large. Therefore no action potentials can be generated. 92. No – skeletal muscle is an example of one that doesn’t 93. K+ channels remain open, so permeability to K+ is greater than at rest. Na+ channels are shut so ...
... 91. Period during which Na+ channels will not open in response to stimulus, however large. Therefore no action potentials can be generated. 92. No – skeletal muscle is an example of one that doesn’t 93. K+ channels remain open, so permeability to K+ is greater than at rest. Na+ channels are shut so ...
Part 1 (nerve impulses, ppt file)
... move across muscle cells, and does in the heart. You can detect the changes in potential caused by this depolarization wave by ...
... move across muscle cells, and does in the heart. You can detect the changes in potential caused by this depolarization wave by ...
Neurons – A whistle-stop Tour
... Axon terminals contain many synaptic vesicules loaded with 2000 molecules of a specialised compound called a neurotransmitter. An electrical impulse called a ‘spike’ sends electrical impulses down the axon. Waiting for the ‘spike’ from the neurotransmitter is a receiver, called the dendrite. Between ...
... Axon terminals contain many synaptic vesicules loaded with 2000 molecules of a specialised compound called a neurotransmitter. An electrical impulse called a ‘spike’ sends electrical impulses down the axon. Waiting for the ‘spike’ from the neurotransmitter is a receiver, called the dendrite. Between ...
Chapter 6 - Sensory - Austin Community College
... Motor unit - motor neuron and the muscle fibers it stimulates. A single motor unit may contain from 2 to 2000 muscle fibers A motor neuron transmits a nerve impulse (action potential) to a neuromuscular junction. Neuromuscular junction - region where the of the motor neuron axon terminal and muscle ...
... Motor unit - motor neuron and the muscle fibers it stimulates. A single motor unit may contain from 2 to 2000 muscle fibers A motor neuron transmits a nerve impulse (action potential) to a neuromuscular junction. Neuromuscular junction - region where the of the motor neuron axon terminal and muscle ...
Synaptic Transmission
... •How a neuron communicates with another neuron and the effects of drugs on this process. •Types of Neurotransmitters ...
... •How a neuron communicates with another neuron and the effects of drugs on this process. •Types of Neurotransmitters ...
Nature Versus Nurture
... § And as cells divide they are influenced by the environment around them. § This results in differentiation of cells, into specific tissues such as muscle and nerve and the formation of organ systems such as the nervous system ...
... § And as cells divide they are influenced by the environment around them. § This results in differentiation of cells, into specific tissues such as muscle and nerve and the formation of organ systems such as the nervous system ...
The Neuron
... 1) Dendrite picks up a signal and if strong enough neuron fires 2) Impulse (signal) starts down axon until it reaches the end (axon terminal or synaptic end) 3) Gap (called synaptic space or cleft) between axon terminal and next dendrite 4) Axon terminals contain tiny, oval sacs (synaptic vesicles) ...
... 1) Dendrite picks up a signal and if strong enough neuron fires 2) Impulse (signal) starts down axon until it reaches the end (axon terminal or synaptic end) 3) Gap (called synaptic space or cleft) between axon terminal and next dendrite 4) Axon terminals contain tiny, oval sacs (synaptic vesicles) ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... cortex in layer IVC, revealed by injecting [3H]-proline into the vitreous of one eye. Light stripes (columns) represent sites containing the anterograde transported 3H-amino acid from the injected eye. Dark regions are occupied by axons driven by the other eye. (B) Monocular deprivation by lid sutur ...
... cortex in layer IVC, revealed by injecting [3H]-proline into the vitreous of one eye. Light stripes (columns) represent sites containing the anterograde transported 3H-amino acid from the injected eye. Dark regions are occupied by axons driven by the other eye. (B) Monocular deprivation by lid sutur ...
Modification of brain circuits as a result of experience
... • Ca stimulates multiple Ca++ dependent protein kinases • Mice mutant in these kinases have defects in LTP, learning, and memory. – Kinases • Get more AMPA receptors into the spine. More receptors = more depolarization in response to glutamate. • Grow more spines = increases number of synapses with ...
... • Ca stimulates multiple Ca++ dependent protein kinases • Mice mutant in these kinases have defects in LTP, learning, and memory. – Kinases • Get more AMPA receptors into the spine. More receptors = more depolarization in response to glutamate. • Grow more spines = increases number of synapses with ...
PNS
... “As the entomologist chasing butterflies of bright colors, my attention was seeking in the garden of gray matter, those cells of delicate and elegant forms, the mysterious butterflies of the soul, whose ...
... “As the entomologist chasing butterflies of bright colors, my attention was seeking in the garden of gray matter, those cells of delicate and elegant forms, the mysterious butterflies of the soul, whose ...
Chapter 11: Your Neurons and their Electrical Activity
... 11. How does the oligodendrocyte work differently than the neurolemmocyte? They do not wrap their cell body around the myelin sheath Each oligodendrocyte wraps portions of its membrane around several ...
... 11. How does the oligodendrocyte work differently than the neurolemmocyte? They do not wrap their cell body around the myelin sheath Each oligodendrocyte wraps portions of its membrane around several ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CH 48 AND 49
... send info to interneurons which send info to motor neurons which send info to muscles or glands ...
... send info to interneurons which send info to motor neurons which send info to muscles or glands ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron Postsynaptic membrane permeability changes due to opening of ion channels, causing an excitatory or ...
... Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron Postsynaptic membrane permeability changes due to opening of ion channels, causing an excitatory or ...
9.1-9.4 Notes
... – Axon hillock-elevated portion leading into the axon from the cell body – May have side branches – PNS axons-made of Schwann cells that make myelin – Neurilemma-covering that surrounds myelin sheath – Nodes of Ranvier-gaps in between myelin sheath of axon • Myelinated in CNS are called white matter ...
... – Axon hillock-elevated portion leading into the axon from the cell body – May have side branches – PNS axons-made of Schwann cells that make myelin – Neurilemma-covering that surrounds myelin sheath – Nodes of Ranvier-gaps in between myelin sheath of axon • Myelinated in CNS are called white matter ...
Nervous System Lecture Notes Page
... Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
Slide ()
... Principles of Neural Science, Editoncord. During development the two processes of the embryonic bipolar cell fuse and emerge from the cell body as a single process that has two functionally segments. function as Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Princi ...
... Principles of Neural Science, Editoncord. During development the two processes of the embryonic bipolar cell fuse and emerge from the cell body as a single process that has two functionally segments. function as Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Princi ...
What is the structure of the neuron? (continued)
... 3. Multipolar neurons: Have more than two projections extending from the cell body—typically, one axon and many dendrites. The most common type of neuron in the CNS. ...
... 3. Multipolar neurons: Have more than two projections extending from the cell body—typically, one axon and many dendrites. The most common type of neuron in the CNS. ...
Chapter 5a
... Neurofibrils: Channels for Communication in Cell. These filaments repel each other, so their development enlarges the diameter of the axon and ...
... Neurofibrils: Channels for Communication in Cell. These filaments repel each other, so their development enlarges the diameter of the axon and ...
Neuron
... The synapse( Gr. Synapsis , union) is responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses from neuron to another cell and insure that transmission is unidirectional. The function of the synapse is to convert an electrical signal (impulse) from the pre synaptic cell into a chemical signal that act ...
... The synapse( Gr. Synapsis , union) is responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses from neuron to another cell and insure that transmission is unidirectional. The function of the synapse is to convert an electrical signal (impulse) from the pre synaptic cell into a chemical signal that act ...
LTP
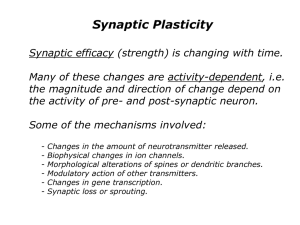
... Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
... Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
Nervous System
... • Bundles of nerve fibers carry impulses in the PNS are kknown as peripheral i h l nerves or jjustt ...
... • Bundles of nerve fibers carry impulses in the PNS are kknown as peripheral i h l nerves or jjustt ...