Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level
... concentration gradient. depolarization Once a membrane potential of 40mV is reached, the sodium channels close, and Potassium channels open. This causes a rush of Potassium ions to the outside of the cell, and the cell is repolarized. ...
... concentration gradient. depolarization Once a membrane potential of 40mV is reached, the sodium channels close, and Potassium channels open. This causes a rush of Potassium ions to the outside of the cell, and the cell is repolarized. ...
Nervous System
... impulses At resting potential the axon has negative voltage Action potential gated channels allow positive sodium ions to move freely into axon, voltage becomes positive. Myelinated axons: action potential concentrated at the nodes. ...
... impulses At resting potential the axon has negative voltage Action potential gated channels allow positive sodium ions to move freely into axon, voltage becomes positive. Myelinated axons: action potential concentrated at the nodes. ...
Neuron (Nerve Cell)
... the Axon • Whitish, fatty protein layer • Serves to protect & electrically insulate axon • Increases the speed of transmission of nerve impulses (up to 150 times faster) • Only associated with axons, not dendrites ...
... the Axon • Whitish, fatty protein layer • Serves to protect & electrically insulate axon • Increases the speed of transmission of nerve impulses (up to 150 times faster) • Only associated with axons, not dendrites ...
Slide ()
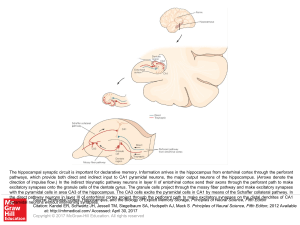
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
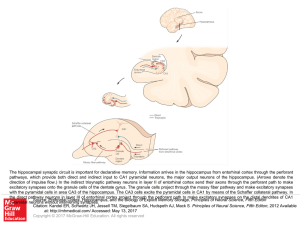
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Long-term depression
... Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers ...
... Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... • Seratonin is the brain chemical that is associated with moods, concentration and attention Thinking about the information in the last slides, explain what happens in the brain with people who are depressed ...
... • Seratonin is the brain chemical that is associated with moods, concentration and attention Thinking about the information in the last slides, explain what happens in the brain with people who are depressed ...
Prémio Artigo Destaque SPN_2011 Cellular and Molecular
... Neurons are capable of integrating information spatially and temporally. They can process electrical signals at specific locations called synapses, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. The information can then be built or not into an output signal, the action potential, carried by the axon. The dy ...
... Neurons are capable of integrating information spatially and temporally. They can process electrical signals at specific locations called synapses, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. The information can then be built or not into an output signal, the action potential, carried by the axon. The dy ...
Lectures220Week7Note..
... Schwann cells) prevents ions from leaking out across the plasma membrane. Node of Ranvier ...
... Schwann cells) prevents ions from leaking out across the plasma membrane. Node of Ranvier ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VI. Growth Factors
... majority of nerve cells are present at birth. Surprisingly, two thirds of all neurons born during fetal development will die during the first decade of life in a process termed apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The remarkable growth of the brain during these first few years is due primarily to th ...
... majority of nerve cells are present at birth. Surprisingly, two thirds of all neurons born during fetal development will die during the first decade of life in a process termed apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The remarkable growth of the brain during these first few years is due primarily to th ...
overview of neural f..
... When a neurotransmitter and receptor combine together two possibilities: 1. The resting potential may become less negative (an excitatory post-synaptic potential - E.P.S.P). Effect of E.P.S.P is to INCREASE probability that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
... When a neurotransmitter and receptor combine together two possibilities: 1. The resting potential may become less negative (an excitatory post-synaptic potential - E.P.S.P). Effect of E.P.S.P is to INCREASE probability that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
Slide 1
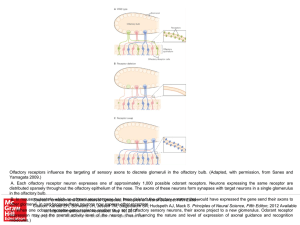
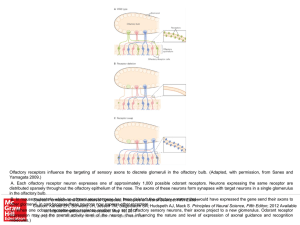
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... Many neurons are insulated by myelin: multiple layers of cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals ( ‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Myelin reduces leakage of electrical charge from the axon, resul ...
... Many neurons are insulated by myelin: multiple layers of cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals ( ‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Myelin reduces leakage of electrical charge from the axon, resul ...
Chapter 7
... – Carries electrical impulse away from cell body – May be covered by Schwann cells • Forms discontinuous myelin sheath along length of axon ...
... – Carries electrical impulse away from cell body – May be covered by Schwann cells • Forms discontinuous myelin sheath along length of axon ...
Nervous from Cyber
... are called post-synaptic cells. There are two types of synapses: electrical and chemical. An electrical synapse allows the signal to spread directly from the pre-synaptic to the post-synaptic cells. Chemical synapses allows for cells that so not have an electrical connection to spread their messages ...
... are called post-synaptic cells. There are two types of synapses: electrical and chemical. An electrical synapse allows the signal to spread directly from the pre-synaptic to the post-synaptic cells. Chemical synapses allows for cells that so not have an electrical connection to spread their messages ...
The Neuron: Building Block of the Nervous System
... The Action Potential All-or-None Principle – Refers to the fact that the ...
... The Action Potential All-or-None Principle – Refers to the fact that the ...
BLoA Neurotransmission
... The distance between a presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron is about 20-40 nanometers! ...
... The distance between a presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron is about 20-40 nanometers! ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... But not the strength of action potentials 28.6 Neurons communicate at synapses Synapses are junctions where signals are transmitted between Two neurons or between neurons and effector cells Electrical synapses ...
... But not the strength of action potentials 28.6 Neurons communicate at synapses Synapses are junctions where signals are transmitted between Two neurons or between neurons and effector cells Electrical synapses ...
neuroplasticity 2016
... Unmasking of silent synapses • Disinhibition of silent synapses • Many synapses in the central nervous system appear to be non-functional (silent) • An injury to pathways in the brain can unmask these synapses and they can ...
... Unmasking of silent synapses • Disinhibition of silent synapses • Many synapses in the central nervous system appear to be non-functional (silent) • An injury to pathways in the brain can unmask these synapses and they can ...
7. Describe what membrane potential is, and how
... cells (glia) are used for. • Supporting cells are essential for the structure and function of neurons • Help to “glue” neurons together • A type called “astrocytes” form tight junctions between cells lining the capillaries in the brain, leading to the blood-brain barrier ...
... cells (glia) are used for. • Supporting cells are essential for the structure and function of neurons • Help to “glue” neurons together • A type called “astrocytes” form tight junctions between cells lining the capillaries in the brain, leading to the blood-brain barrier ...
Document
... Input travels along several pathways Pathways are integrated in different CNS systems One stimulus promotes numerous responses ...
... Input travels along several pathways Pathways are integrated in different CNS systems One stimulus promotes numerous responses ...
Netter`s Atlas of Neuroscience - 9780323265119 | US Elsevier
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...