Structural elements and mechanisms involved in the transformation
... • mostly striated fibers attached to the bone by tendons • innervated by ALPHA motor neurons : cell body in ventral horn of the spinal cord contribute to maintain muscle tone resist further stretches Intrafusal muscle fibers: • serve as sensory organs detect the amount of change in the muscle • ...
... • mostly striated fibers attached to the bone by tendons • innervated by ALPHA motor neurons : cell body in ventral horn of the spinal cord contribute to maintain muscle tone resist further stretches Intrafusal muscle fibers: • serve as sensory organs detect the amount of change in the muscle • ...
Synaptic transmission
... synapses, these synapses become more capable of transmitting the same type of signal the next time, a process called facilitation. • After the sensory signals have passed through the synapses a large number of times, the synapses become so facilitated that signals generated within the brain itself c ...
... synapses, these synapses become more capable of transmitting the same type of signal the next time, a process called facilitation. • After the sensory signals have passed through the synapses a large number of times, the synapses become so facilitated that signals generated within the brain itself c ...
Lecture 3 Review
... Most neurons are contacted by thousands of axons. If the PSPs from two or more of these axons occur together, then the PSPs will sum together. This is called summation. There are two types of summation: spatial summation and temporal summation. You should know the differences between these types of ...
... Most neurons are contacted by thousands of axons. If the PSPs from two or more of these axons occur together, then the PSPs will sum together. This is called summation. There are two types of summation: spatial summation and temporal summation. You should know the differences between these types of ...
Neurons
... information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks called SYNAPTIC VESICLES Vesicles fuse together with the membrane and spill contents into the synaptic gap They may bind to certain areas at various receptor sites ...
... information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks called SYNAPTIC VESICLES Vesicles fuse together with the membrane and spill contents into the synaptic gap They may bind to certain areas at various receptor sites ...
Ch 11 Part 1 - Groch Biology
... Supporting cells found in the CNS are called neuroglia. ___ _______________ Neurons are mitotic. ___ ____________________ Schwann cells and satellite cells are found only in the CNS. ___ ________________ Ependymal cells show irritability and conductivity. ___ ____________________ Almost 50% of the v ...
... Supporting cells found in the CNS are called neuroglia. ___ _______________ Neurons are mitotic. ___ ____________________ Schwann cells and satellite cells are found only in the CNS. ___ ________________ Ependymal cells show irritability and conductivity. ___ ____________________ Almost 50% of the v ...
Name
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
Nervous System Neurons And Synapses
... 2. Describe how the following substances exert their effects on the body: botulism; curare; tetrodotoxin; and nerve gas. Botulism is caused by botulinum toxin, produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The toxin inhibits acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junctions. Characterized by m ...
... 2. Describe how the following substances exert their effects on the body: botulism; curare; tetrodotoxin; and nerve gas. Botulism is caused by botulinum toxin, produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The toxin inhibits acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junctions. Characterized by m ...
PPT and questions for class today.
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
Chapter 02: Neurons and Glia
... Dendritic tree for all the dendrites of a neuron “Antennae” of neurons - covered with thousands of synapses Dendritic membrane (postsynaptic membrane) contains many specialized receptors for neurotransmitters Dendritic spines Some neurons have these structures for receiving some types of inputs Disc ...
... Dendritic tree for all the dendrites of a neuron “Antennae” of neurons - covered with thousands of synapses Dendritic membrane (postsynaptic membrane) contains many specialized receptors for neurotransmitters Dendritic spines Some neurons have these structures for receiving some types of inputs Disc ...
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling
... synapse in rapid succession- in this case the EPSP’s add together. Spatial Summation- two EPSP’s produced simultaneously at different synapses on the same postsynaptic neuronEPSP’s added together. ...
... synapse in rapid succession- in this case the EPSP’s add together. Spatial Summation- two EPSP’s produced simultaneously at different synapses on the same postsynaptic neuronEPSP’s added together. ...
The Nervous System (Chapter 7)
... Clusters of neuron cell bodies and collection of nerve fibers are named differently when they are in the CNS than when they are part of the PNS. 12. What are nuclei? _____________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is the difference between white matter and gray ...
... Clusters of neuron cell bodies and collection of nerve fibers are named differently when they are in the CNS than when they are part of the PNS. 12. What are nuclei? _____________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is the difference between white matter and gray ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Voltage-gated ion channels: channels that open and close in response to membrane potential changes. These ion channels are responsible the action potential Potassium channels: closed when resting, opens slowly in response to depolarization Sodium channels: (two types of gates) Activation: clos ...
... Voltage-gated ion channels: channels that open and close in response to membrane potential changes. These ion channels are responsible the action potential Potassium channels: closed when resting, opens slowly in response to depolarization Sodium channels: (two types of gates) Activation: clos ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... • cells that have the ability to change their membrane potentials + neurons and muscle cells - resting potential (unexcited) + change from resting potential can result in active electrical impulse + gated ion channels - special channels that allow cell to change membrane potential ...
... • cells that have the ability to change their membrane potentials + neurons and muscle cells - resting potential (unexcited) + change from resting potential can result in active electrical impulse + gated ion channels - special channels that allow cell to change membrane potential ...
Document
... The transfer of information between neurons is called a ___________________. Most synapses occur between the __________________ ______________________ of one neuron and the ________________________ of another. The fluid-filled space approximately 1 millionth of an inch wide between 2 neurons is call ...
... The transfer of information between neurons is called a ___________________. Most synapses occur between the __________________ ______________________ of one neuron and the ________________________ of another. The fluid-filled space approximately 1 millionth of an inch wide between 2 neurons is call ...
This Week in The Journal - Journal of Neuroscience
... loss of synapses and neurodegeneration remain uncertain. To understand how AD pathologydevelopsinamodelsystem,Zhaoetal. overexpressed A isoforms in flight-related motor and interneurons in Drosophila and examined the effects at different ages. A accumulated in neuronal somata and axons, and this c ...
... loss of synapses and neurodegeneration remain uncertain. To understand how AD pathologydevelopsinamodelsystem,Zhaoetal. overexpressed A isoforms in flight-related motor and interneurons in Drosophila and examined the effects at different ages. A accumulated in neuronal somata and axons, and this c ...
Neuroplasticity - Bakersfield College
... ~50% more neurons than are needed are produced – death is normal Neurons die due to failure to compete for chemicals provided by targets ...
... ~50% more neurons than are needed are produced – death is normal Neurons die due to failure to compete for chemicals provided by targets ...
Chapter 17 Part A
... - whitish, inner myelin sheath insulates & increases conduction - multiple sclerosis disease causes scars on sheath and motor abnormality - gaps between Schwann cells along the neuron fibers termed nodes of Ranvier - role of satellite cells found associated with Schwann cells is unclear (moore’s sch ...
... - whitish, inner myelin sheath insulates & increases conduction - multiple sclerosis disease causes scars on sheath and motor abnormality - gaps between Schwann cells along the neuron fibers termed nodes of Ranvier - role of satellite cells found associated with Schwann cells is unclear (moore’s sch ...
Document
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Synaptic cleft Presynaptic neuron Synaptic vesicles Neurotransmitters ...
... Synaptic cleft Presynaptic neuron Synaptic vesicles Neurotransmitters ...
Slide ()
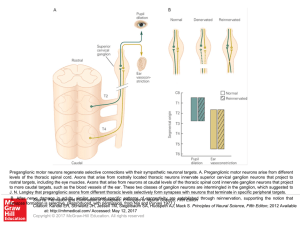
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
Neurons, Synapses, the Nervous System
... down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells. There are two categories of neurotransmitters; excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory causes depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane, whereas inhibitory causes hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. ...
... down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells. There are two categories of neurotransmitters; excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory causes depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane, whereas inhibitory causes hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. ...
Neural Tissue
... – Processes sensory information received from afferent neurons by analyzing, storing and making decisions for appropriate responses ...
... – Processes sensory information received from afferent neurons by analyzing, storing and making decisions for appropriate responses ...