Guided notes 2 Histology - Liberty Union High School District
... Schwann cells layer around the axon and squeeze the cytoplasm out of themselves leave layers of__________________ ___________________surrounding the axion. This layer is called the ______________________________________. This is discontinuous…so there are spaces with no sheath. These areas are calle ...
... Schwann cells layer around the axon and squeeze the cytoplasm out of themselves leave layers of__________________ ___________________surrounding the axion. This layer is called the ______________________________________. This is discontinuous…so there are spaces with no sheath. These areas are calle ...
The Nervous System WS-11A Review Quest
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
Chapter 48 Worksheet
... a. The neuron's plasma membrane is much more permeable to potassium than to sodium. b. The concentration of sodium is much higher inside the cell than outside. c. The sodium-potassium pump plays a role in maintaining the resting potential. d. Inside the cell, the concentration of potassium is much h ...
... a. The neuron's plasma membrane is much more permeable to potassium than to sodium. b. The concentration of sodium is much higher inside the cell than outside. c. The sodium-potassium pump plays a role in maintaining the resting potential. d. Inside the cell, the concentration of potassium is much h ...
Neuron Labeling WS
... The connection between adjacent neurons. The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. The structure at the end of an axon that produces neurotransmitters to tran ...
... The connection between adjacent neurons. The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. The structure at the end of an axon that produces neurotransmitters to tran ...
Slideshow
... travels from neuron to neuron • To complete the signal, a NEUROTRANSMITTER is released at the gap to signal the next neuron ...
... travels from neuron to neuron • To complete the signal, a NEUROTRANSMITTER is released at the gap to signal the next neuron ...
Ch. 35.2
... stimulated by another neuron or by its environment The protein channels help ions pass in and out of the cell When positive ions flow in, gains a positive charge an then switches to a negative charge ACTION POTENTIAL One impulse causes another impulse at the next point on the membrane ...
... stimulated by another neuron or by its environment The protein channels help ions pass in and out of the cell When positive ions flow in, gains a positive charge an then switches to a negative charge ACTION POTENTIAL One impulse causes another impulse at the next point on the membrane ...
NeuroReview3
... • Both the timing and the type of the pharmacologic agent to be given can have a significant impact on the success of therapy. • With neuroprotective agents the general rule is that the earlier they are given the better, especially if the mode of action is increasing inhibitory tone in the brain. • ...
... • Both the timing and the type of the pharmacologic agent to be given can have a significant impact on the success of therapy. • With neuroprotective agents the general rule is that the earlier they are given the better, especially if the mode of action is increasing inhibitory tone in the brain. • ...
Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... ER, mitochondria, golgi complex, etc). Is where most the synthesis of new cellular products occurs. ...
... ER, mitochondria, golgi complex, etc). Is where most the synthesis of new cellular products occurs. ...
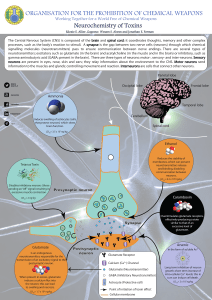
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... Edoxie E. Allier-Gagneur, Wesam S. Alwan and Jonathan E. Forman ...
... Edoxie E. Allier-Gagneur, Wesam S. Alwan and Jonathan E. Forman ...
Nervous System Ch 10 Notes - Reading Community Schools
... conducts nerve impulses from the cell body • Terminates at another neuron, muscle or gland • May be up to a meter ...
... conducts nerve impulses from the cell body • Terminates at another neuron, muscle or gland • May be up to a meter ...
Types of neurons
... if resting potential rises above threshold an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon Figure shows resting axon being approached by an AP ...
... if resting potential rises above threshold an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon Figure shows resting axon being approached by an AP ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Is the major biosynthetic center Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
... Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Is the major biosynthetic center Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
Nervous Sys Learning targets
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
CH 12 shortened for test three nervous tissue A and P 2016
... neuromodulating hormones = long term effectors = NO, dopa, serotonin, histamine ...
... neuromodulating hormones = long term effectors = NO, dopa, serotonin, histamine ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... A neuron can produce only one kind of neurotransmitter at its synapse. The post-synaptic neuron will have receptors for this neurotransmitter that will either cause an increase or decrease in membrane potential. Acetylcholine (ACh) Released by neurons that control muscles (motor neurons), neurons th ...
... A neuron can produce only one kind of neurotransmitter at its synapse. The post-synaptic neuron will have receptors for this neurotransmitter that will either cause an increase or decrease in membrane potential. Acetylcholine (ACh) Released by neurons that control muscles (motor neurons), neurons th ...
Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely
... molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity for fundamental and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, simultaneous photocontrol of synaptic receptors and fluorescence imaging of neuronal activity in vivo will allow studying synaptic plasticity from the single dendrit ...
... molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity for fundamental and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, simultaneous photocontrol of synaptic receptors and fluorescence imaging of neuronal activity in vivo will allow studying synaptic plasticity from the single dendrit ...
Postsynaptic Potential
... Neurons have 4 important zones • Axon process – transmits the impulses to the nerve endings. • Nerve endings - release the synaptic transmitters. ...
... Neurons have 4 important zones • Axon process – transmits the impulses to the nerve endings. • Nerve endings - release the synaptic transmitters. ...
Neurons and synapses..
... A brief recovery period occurs during which the nerve cell membrane cannot be stimulated to carry impulses. This refractory period lasts a few thousandths of a second. The rate at which an impulse travels depends on the size of the nerve and whether or not it is myelinated (unmyelinated = 2 m/s an ...
... A brief recovery period occurs during which the nerve cell membrane cannot be stimulated to carry impulses. This refractory period lasts a few thousandths of a second. The rate at which an impulse travels depends on the size of the nerve and whether or not it is myelinated (unmyelinated = 2 m/s an ...
M.learning.hccs.edu
... A) 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. B) 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. C) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. D) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions. E) 3 extracellular sodium ions for ...
... A) 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. B) 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. C) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. D) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions. E) 3 extracellular sodium ions for ...
48 - Groupfusion.net
... between “nodes of Ranvier” (area on the axon not covered by the myelin sheath), speeds up the conduction of the nerve impulse. ...
... between “nodes of Ranvier” (area on the axon not covered by the myelin sheath), speeds up the conduction of the nerve impulse. ...
click - Uplift Education
... 15) When a neuron is at resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the interstitial fluid (outside the cell)? When a neuron is a resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the cytosol (inside the cell)? What processes position the ions in these locations? 16 ...
... 15) When a neuron is at resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the interstitial fluid (outside the cell)? When a neuron is a resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the cytosol (inside the cell)? What processes position the ions in these locations? 16 ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
Graded Potential - wquerryeducation
... • no cure • b interferon (anti-viral drug) • steroids • physical therapy ...
... • no cure • b interferon (anti-viral drug) • steroids • physical therapy ...
Worksheet for Nervous Systems
... 34. The action potential arises because the plasma membrane has ___ ____ ion channels. 35. Which two types of voltage-gated ion channels contribute to the action potential? ...
... 34. The action potential arises because the plasma membrane has ___ ____ ion channels. 35. Which two types of voltage-gated ion channels contribute to the action potential? ...